
A convex lens of focal length \[20cm\] and a concave lens of focal length \[10cm\] are placed \[10cm\] apart with their principal axis coinciding. A beam of light travelling parallel to the principal axis and having a beam diameter \[5.0mm\], is incident on the combination. Show that the emergent beam is parallel to the incident one. Find the beam diameter of the emergent beam.
Answer
568.5k+ views
Hint: A convex lens and a concave lens are placed at a certain distance apart such that the beam of light that will first be emergent on the convex lens is parallel to the principal axis. The principal axis will be the same for both lenses. The principal focus of the lens lies on the principal axis. Therefore, the principal focus of both the lenses will lie on the principal axis.
The diameter of the emergent beam and the distance of the image of the concave lens can be found by using Lens Maker’s formula.
Formula Used: The Lens Maker’s formula is given as: \[\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u}\] where, \[v\] is the distance of the image
\[u\] is the distance of the object and \[f\] is the focal length of the lens.
Complete step by step solution:
A convex lens is thin from the edges and thick from the middle. Whereas, a concave lens is thick from the edges and thin from the middle. It is given that the focal length for a convex lens is \[20cm\] and that for a concave lens is \[10cm\]. Thus, \[{f_{convex}} = 20cm\] and \[{f_{concave}} = 10cm\]. These lenses are \[10cm\] apart such that their principal axis coincides. Let the incident beam be focused at the convex lens. Let A be the focus of the convex lens where the image is formed.
For the concave lens, the virtual image will be formed at \[10cm\] distance. Then, by Lens Maker's formula
\[\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u}\] \[ \to (1)\]
where, \[v\]is the distance of the image , \[u\] is the distance of the object and \[f\] is the focal length of the lens. Thus for a concave lens, \[v = 10cm\]and \[f = - 10cm\]. Thus, from equation (1)
\[\
\dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{{10}} - \dfrac{1}{{ - 10}} \\
\therefore u = \infty \\
\ \]
Therefore, the principal axis will be parallel to the incident beam after refraction from the concave lens.
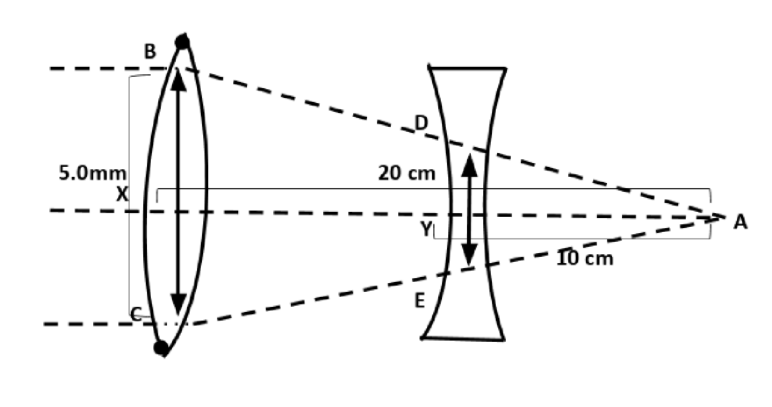
The beam diameter of the incident beam is \[5.0mm\]. From the diagram, consider \[\Delta BCA\]and \[\Delta DEA\].
\[\dfrac{{XA}}{{YA}} = \dfrac{{BC}}{{DE}}\] \[ \to (2)\]
\[XA = {f_{convex}} = 20cm = 200mm\]
\[YA = {f_{concave}} = 10cm = 100mm\]
\[BC = The{\text{ }}beam{\text{ }}diameter{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}the{\text{ }}incident{\text{
}}beam{\text{ }}is = 0.5mm\]
\[DE = beam{\text{ }}diameter{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}the{\text{ }}emergent{\text{ }}beam\]
Rearranging equation (2) in terms of DE
\[DE = \dfrac{{YA}}{{XA}} \times BC = \dfrac{{100}}{{200}} \times 5.0 = 2.5mm\]
Therefore, the beam diameter of the emergent beam is \[2.5mm\]
Note: Convex lenses can form real or virtual images whereas concave lenses can form only virtual images.
Here, the distance of the object from the concave lens is infinity. That is \[u = \infty \]. This only happens when the distance of the image from the lens is equal to the focal length of the lens. That is, \[v = f\].The image thus formed by the concave lens is diminished, virtual and erect.
The diameter of the emergent beam and the distance of the image of the concave lens can be found by using Lens Maker’s formula.
Formula Used: The Lens Maker’s formula is given as: \[\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u}\] where, \[v\] is the distance of the image
\[u\] is the distance of the object and \[f\] is the focal length of the lens.
Complete step by step solution:
A convex lens is thin from the edges and thick from the middle. Whereas, a concave lens is thick from the edges and thin from the middle. It is given that the focal length for a convex lens is \[20cm\] and that for a concave lens is \[10cm\]. Thus, \[{f_{convex}} = 20cm\] and \[{f_{concave}} = 10cm\]. These lenses are \[10cm\] apart such that their principal axis coincides. Let the incident beam be focused at the convex lens. Let A be the focus of the convex lens where the image is formed.
For the concave lens, the virtual image will be formed at \[10cm\] distance. Then, by Lens Maker's formula
\[\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u}\] \[ \to (1)\]
where, \[v\]is the distance of the image , \[u\] is the distance of the object and \[f\] is the focal length of the lens. Thus for a concave lens, \[v = 10cm\]and \[f = - 10cm\]. Thus, from equation (1)
\[\
\dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{{10}} - \dfrac{1}{{ - 10}} \\
\therefore u = \infty \\
\ \]
Therefore, the principal axis will be parallel to the incident beam after refraction from the concave lens.

The beam diameter of the incident beam is \[5.0mm\]. From the diagram, consider \[\Delta BCA\]and \[\Delta DEA\].
\[\dfrac{{XA}}{{YA}} = \dfrac{{BC}}{{DE}}\] \[ \to (2)\]
\[XA = {f_{convex}} = 20cm = 200mm\]
\[YA = {f_{concave}} = 10cm = 100mm\]
\[BC = The{\text{ }}beam{\text{ }}diameter{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}the{\text{ }}incident{\text{
}}beam{\text{ }}is = 0.5mm\]
\[DE = beam{\text{ }}diameter{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}the{\text{ }}emergent{\text{ }}beam\]
Rearranging equation (2) in terms of DE
\[DE = \dfrac{{YA}}{{XA}} \times BC = \dfrac{{100}}{{200}} \times 5.0 = 2.5mm\]
Therefore, the beam diameter of the emergent beam is \[2.5mm\]
Note: Convex lenses can form real or virtual images whereas concave lenses can form only virtual images.
Here, the distance of the object from the concave lens is infinity. That is \[u = \infty \]. This only happens when the distance of the image from the lens is equal to the focal length of the lens. That is, \[v = f\].The image thus formed by the concave lens is diminished, virtual and erect.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




