




What is an Eclipse?
When one object in space masks another, an eclipse occurs. For instance, the Moon passes in front of the Sun to cause a solar eclipse. For a while, the Moon masks the Sun, preventing people on Earth from seeing it. Because planets, moons, and other celestial bodies are constantly moving through space, eclipses do occur. For instance, Earth follows a route known as an orbit as it revolves around the Sun. The Moon follows its own orbit around Earth as it revolves around the Sun. Three celestial bodies temporarily aligning in a row cause an eclipse.
What is Solar and Lunar Eclipse?
When the Moon moves in front of the Sun, it creates a solar eclipse where parts of the Earth experience a shadow. Only the locations where the shadow falls are able to see the eclipse. Nowhere else on Earth can. These places give the impression that the Sun has set.
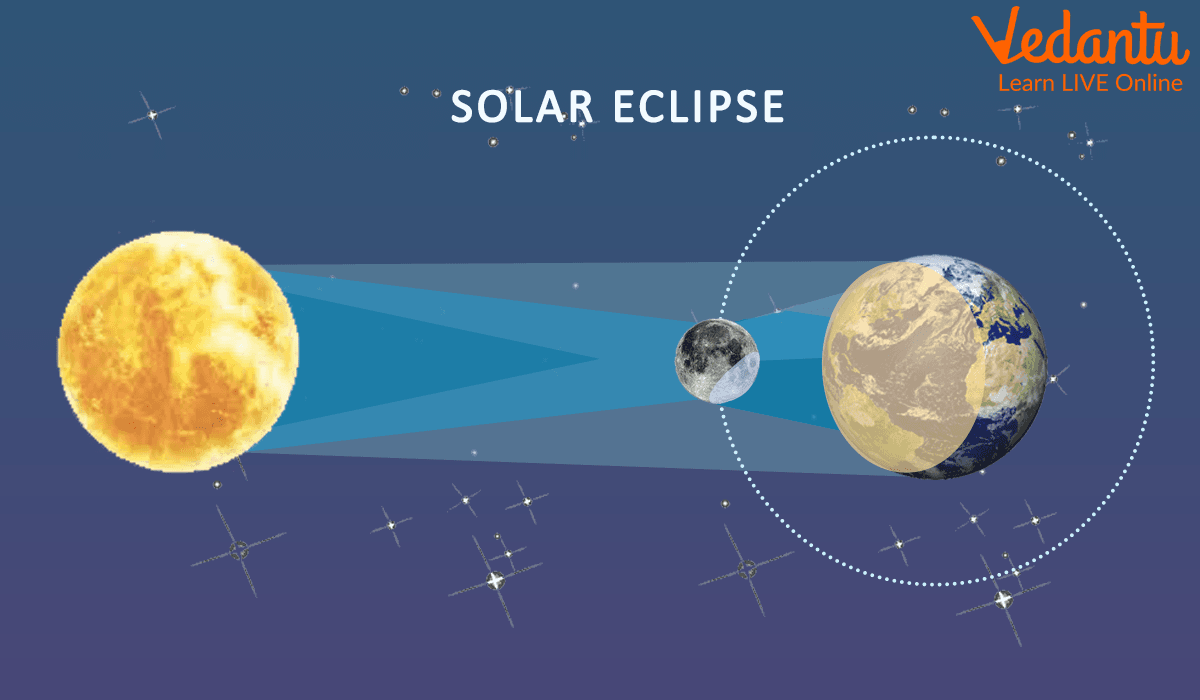
Solar Eclipse
Types of Solar Eclipses
Total Solar Eclipse: There is a small region on Earth where a total solar eclipse can be seen. The centre of the Moon's shadow as it strikes Earth is where observers of the total eclipse will be. The sky turns pitch-black, as though it were night. A direct line between the Sun, Moon, and Earth is necessary for a total eclipse to take place.
Partial Solar Eclipse: When the Sun, Moon, and Earth are not precisely lined up, this occurs. A tiny area of the Sun's surface appears to have a dark shadow.
Annular Eclipse: The Moon's annular eclipse occurs when it is farthest from Earth. The Moon appears smaller because of its greater distance. It does not completely obscure the Sun's view. The Moon appears as a dark disc on top of a larger disc that is Sun-colored when it is in front of the Sun. As a result, the Moon appears to have a ring around it.
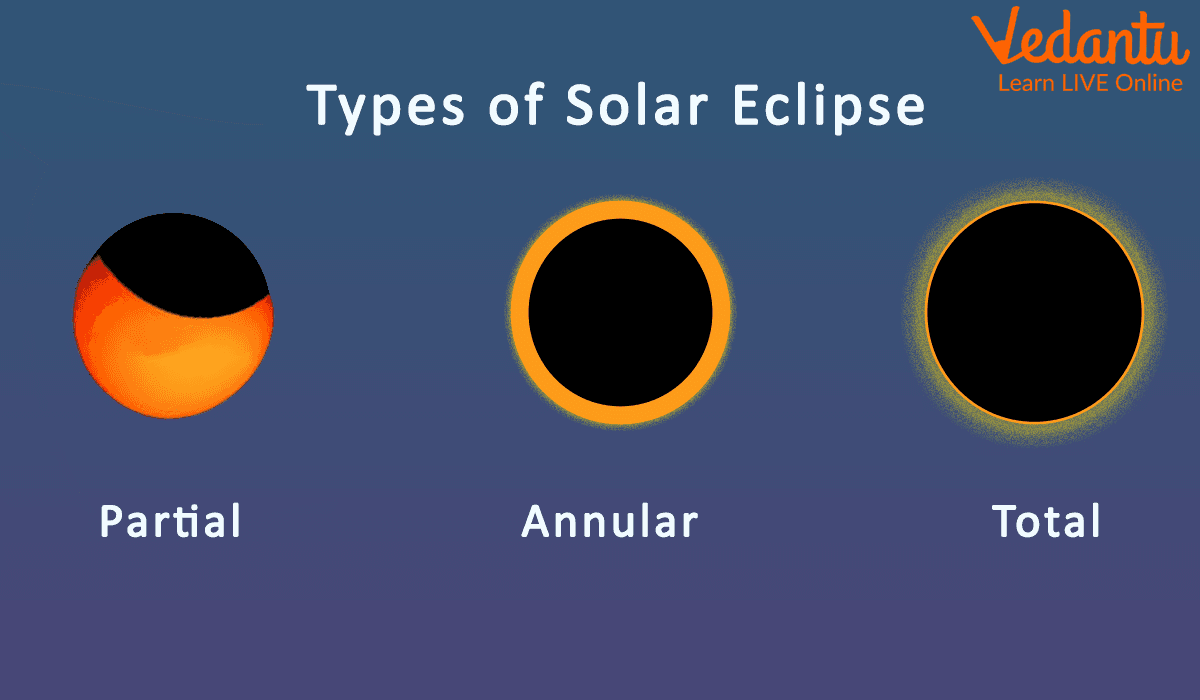
Types of Solar Eclipse
Lunar Eclipse
There is no light produced by the Moon itself. The Moon is visible from Earth because the Sun shines on it and is reflected by it. Earth prevents the Moon from receiving sunlight during a lunar eclipse. Earth is in the middle of a line formed by the Sun, Moon, and other planets. The Moon is then hidden by Earth. However, the Moon doesn't seem entirely dark. It emits a faint orange or red glow instead. This is so that the Moon can receive some light. This light strikes the Moon after reflecting off the gases that surround the Earth.
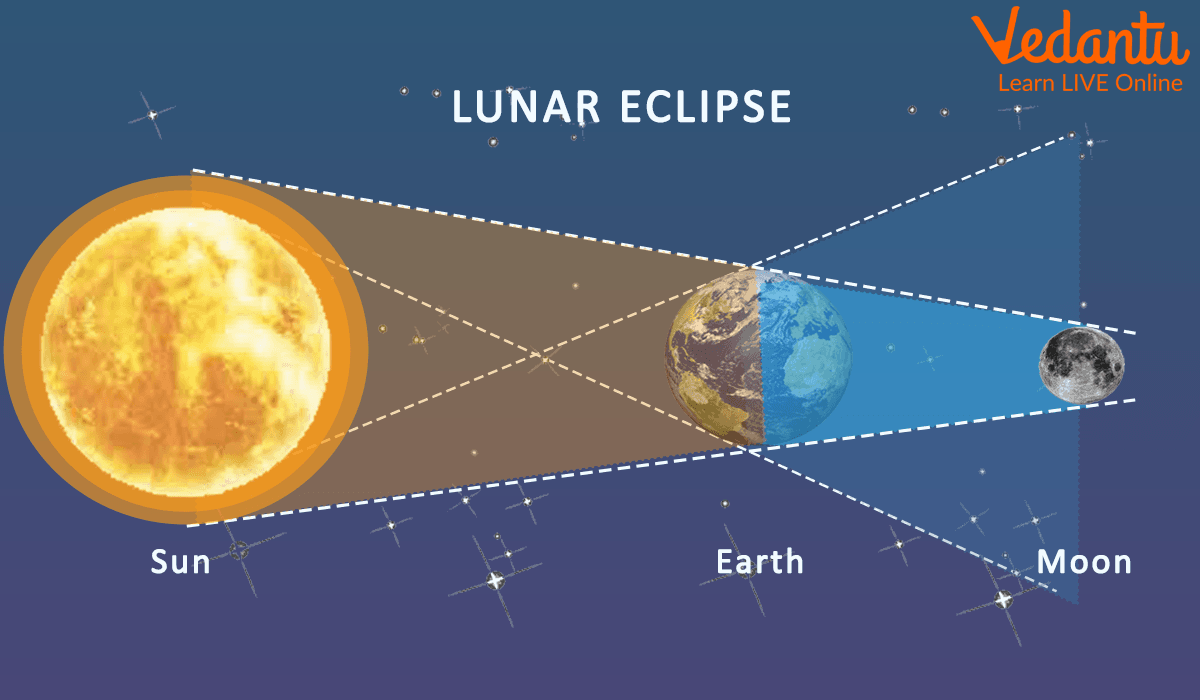
Lunar Eclipse
Types of Lunar Eclipses
Total Lunar Eclipse: When the Moon and Sun are located on the exact opposite sides of Earth, a total lunar eclipse takes place. Despite being in Earth's shadow, the Moon receives some sunlight. The sunlight travels through the atmosphere of Earth, which largely blocks out the blue light. To those on Earth, this causes the Moon to appear red.
Partial Lunar Eclipse: When a portion of the Moon passes through Earth's shadow, a partial lunar eclipse occurs. On the side of the Moon facing Earth during a partial eclipse, Earth's shadow appears to be very dark. The alignment of the Sun, Earth, and Moon determines what is visible to people on Earth during a partial lunar eclipse.
Interesting Facts
The Greek word "ekleipsis," which means "abandonment" or "downfall," is where the English word "eclipse" originates.
One total eclipse occurs once every 1.5 years.
The term "syzygy" refers to an alignment of the Earth, Sun, and Moon.
At the equator, the eclipse shadow travels at a speed of 1770 km/h.
During a total eclipse, wild animals become disoriented and would get ready for bed.
Solar Eclipse Facts for Kids
Only a partial solar eclipse is visible from the North or South Poles.
The maximum duration of a total solar eclipse is 7 minutes and 30 seconds.
The totality path's maximum width is 269 km.
There are two to five solar eclipses per year.
The Moon is travelling across the Sun at a speed of roughly 2,250 km/h (1,398 mph).
Summary
When an observer cannot see one space object while looking at another, there is an eclipse. Solar eclipses and lunar eclipses are the two main types of eclipses visible from Earth. This astronomic event comes with a lot of myth with it. Every year we witness the emergence of both eclipses. All three celestial bodies align in a way to create an eclipse.
Solved Questions
What is an eclipse?
Ans: A temporary obstruction of an astronomical object or spacecraft by passing into the shadow of another body or having another body move in front of it causes an eclipse, which is an astronomical event.
What has been the maximum duration of the solar eclipse?
Ans: The maximum duration of a total solar eclipse is 7 minutes and 30 seconds.
What are the types of solar eclipses?
Ans: There are three types of solar eclipse:
Total solar eclipse
Partial solar eclipse
Annular eclipse
Learning by Doing
Write True/False.
During a total eclipse, wild animals become disoriented and get ready for bed.
There are two to eight solar eclipses per year.
FAQs on Interesting Facts About Eclipses
1. What is an eclipse in simple terms?
An eclipse is a natural astronomical event that occurs when one celestial body, like a moon or a planet, moves into the shadow of another celestial body. On Earth, we experience two main types: solar eclipses, where the Moon blocks the Sun's light, and lunar eclipses, where the Earth's shadow covers the Moon.
2. What is the main difference between a solar and a lunar eclipse?
The main difference lies in the alignment of the Sun, Earth, and Moon. A detailed difference between a solar eclipse and a lunar eclipse is as follows:
Solar Eclipse: The Moon comes between the Sun and Earth, casting a shadow on Earth. The alignment is Sun-Moon-Earth.
Lunar Eclipse: The Earth comes between the Sun and Moon, casting a shadow on the Moon. The alignment is Sun-Earth-Moon.
Essentially, a solar eclipse is the Moon's shadow falling on us, while a lunar eclipse is us watching our own planet's shadow fall on the Moon.
3. Why is it dangerous to look directly at a solar eclipse?
It is extremely dangerous to look at a solar eclipse because even a small sliver of the Sun's surface emits intense ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR) radiation. This radiation can cause severe and permanent damage to the retina of the eye, a condition known as solar retinopathy. This can happen without feeling any pain, as the retina has no pain receptors. Always use certified eclipse glasses or a special solar filter to observe a solar eclipse safely.
4. What are the umbra and penumbra in the context of an eclipse?
The umbra and penumbra are the two parts of the shadow cast by a celestial body during an eclipse.
The Umbra is the darkest, central part of the shadow. An observer standing in the umbra experiences a total eclipse.
The Penumbra is the lighter, outer part of the shadow where the light source is only partially blocked. An observer in the penumbra experiences a partial eclipse.
Understanding the umbra and penumbra is key to knowing why total eclipses are only visible from a very narrow path on Earth.
5. If the Moon orbits Earth every month, why don't we have solar and lunar eclipses every month?
This is a common and excellent question. We don't have eclipses every month because the Moon's orbit around the Earth is tilted by about 5 degrees relative to the Earth's orbit around the Sun (known as the ecliptic plane). Because of this tilt, the Moon usually passes either above or below the Earth's shadow (for a lunar eclipse) or its shadow misses the Earth (for a solar eclipse). Eclipses only happen during a specific 'eclipse season' when the Sun, Earth, and Moon align perfectly on the same plane.
6. Why does the Moon appear red during a total lunar eclipse?
During a total lunar eclipse, the Moon appears red for the same reason our sunsets and sunrises are red. While the Earth blocks direct sunlight, some light still passes through Earth's atmosphere. Our atmosphere filters out most of the blue-coloured light but allows the red and orange light to pass through. This reddish light is then bent or refracted towards the Moon, illuminating its surface with a faint, coppery glow. This phenomenon is often called a 'Blood Moon'.
7. Why are eclipses scientifically important?
Eclipses are scientifically valuable for several reasons:
Studying the Sun's Corona: A total solar eclipse provides a rare opportunity to see the Sun's outer atmosphere, or corona, which is usually obscured by the Sun's bright face.
Testing Theories of Relativity: In 1919, an eclipse was famously used to confirm Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity by observing how the Sun's gravity bends starlight.
Understanding Celestial Mechanics: Accurate eclipse predictions, like those made by ancient astronomers such as Aryabhata, demonstrate a deep understanding of the precise movements of celestial bodies in our solar system.
8. Can eclipses happen on other planets?
Yes, eclipses can and do happen on other planets that have moons. For example, Jupiter experiences frequent eclipses from its many moons, which can be seen as small black dots moving across the planet's surface. Mars also has solar eclipses caused by its moons, Phobos and Deimos. However, a perfect total solar eclipse like we experience on Earth is considered a rare cosmic coincidence due to the precise size and distance of our Moon relative to the Sun.























