How To Solve Beyond Earth Class 6 Questions And Answers For Better Exam Preparation
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Beyond Earth (2025-26)
1. What key concepts are explained in NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Beyond Earth?
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Beyond Earth cover core concepts including the structure of the solar system, characteristics of planets and moons, the movement of celestial bodies, artificial satellites, space exploration, and how Earth's unique position supports life. Detailed solutions help students understand each topic as per the CBSE 2025–26 syllabus.
2. How do the step-wise NCERT Solutions help in answering Class 6 Science Chapter 12 questions?
The solutions provide step-by-step explanations matching the CBSE methodology, guiding students through each part of the question. This ensures clarity of reasoning, prevents skipped logic, and enables students to learn the correct approach for CBSE exam questions.
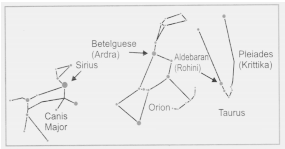
3. Why is Sirius brighter than the Pole Star, according to NCERT Solutions for Chapter 12?
Sirius is the brightest star in the night sky due to its high luminosity and proximity to Earth. In contrast, Pole Star (Polaris) is helpful for navigation but is less luminous than Sirius. This distinction is explained in the CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 12 solutions.
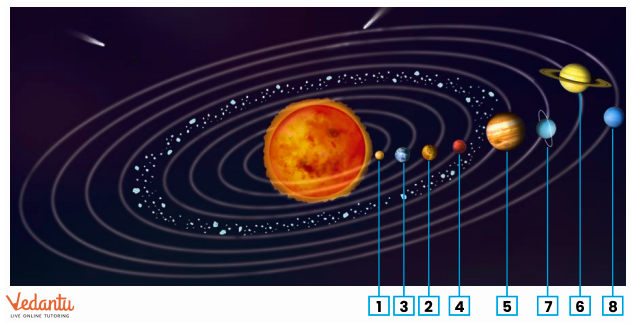
4. What is the correct order of planets in the solar system as per NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12?
The order of planets from the Sun is:
- Mercury
- Venus
- Earth
- Mars
- Jupiter
- Saturn
- Uranus
- Neptune
5. What is the difference between a planet and a star, according to CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 12 NCERT Solutions?
Planets are celestial bodies that revolve around stars and do not produce their own light, while stars are luminous bodies that emit their own light and heat due to nuclear fusion. This distinction is crucial in understanding the solar system topics in Chapter 12.
6. How do artificial satellites differ from natural satellites as explained in the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12?
According to the solutions, natural satellites like the Moon orbit planets naturally, while artificial satellites are human-made objects placed in orbit for purposes such as communication, weather monitoring, and scientific research.
7. Why can we not see stars during the day, based on the explanations in the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12?
During the day, sunlight scatters in Earth's atmosphere, making the sky bright and obscuring the faint light from stars. Therefore, stars are not visible in daylight as per the scientific explanation given in Chapter 12 solutions.
8. How does light pollution affect astronomy as discussed in the CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 12 NCERT Solutions?
Light pollution increases sky brightness from artificial lights, making it hard to observe faint celestial objects. This adversely impacts astronomical studies and is linked to environmental and health issues in the chapter's activities.
9. What are the ideal weather conditions for setting up an observatory as per the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12?
Ideal conditions include clear skies, low humidity, high altitude, minimal light pollution, and stable atmospheric conditions. These are why Hanle, Ladakh is suitable for astronomical observatories according to the solutions.
10. Which objects are not considered part of our solar system according to Class 6 Science Chapter 12 NCERT Solutions?
Sirius is not part of our solar system; it is a star found in the constellation Canis Major, outside the solar system. This answer follows the CBSE pattern for factual conceptual clarity.
11. How do NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 help students with exam preparation?
The solutions offer comprehensive answers to all in-text and end-of-chapter questions, enabling students to revise systematically, clear doubts, and gain confidence in the concepts required for CBSE 2025–26 board exams.
12. What is the significance of Earth's position in the solar system as described in Chapter 12?
Earth's location, optimal distance from the Sun, and atmosphere support the presence of water and life. Chapter 12 solutions explain how these factors contribute to unique living conditions on Earth.
13. How do the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 explain the movement of the Big Dipper in the night sky?
The Big Dipper appears to move across the night sky due to Earth's rotation. However, the Pole Star remains nearly fixed. This observation skill is reinforced through practical activities in the solutions, following the CBSE approach.
14. How do the NCERT Solutions address common misconceptions about the solar system from Chapter 12?
Common misconceptions, such as Pluto being a major planet or Sirius being part of our solar system, are clarified. The solutions provide facts aligning with the current scientific classification and CBSE guidelines.
15. How can students apply the knowledge from NCERT Solutions Class 6 Science Chapter 12 to real-life situations?
By understanding celestial movements, seasons, and the impact of artificial lighting, students can interpret day-to-day phenomena, participate in sky observations, and contribute to light pollution awareness as encouraged by CBSE Science Chapter 12.