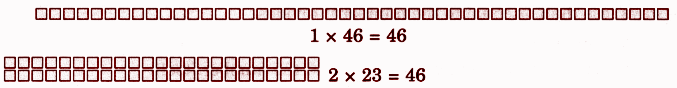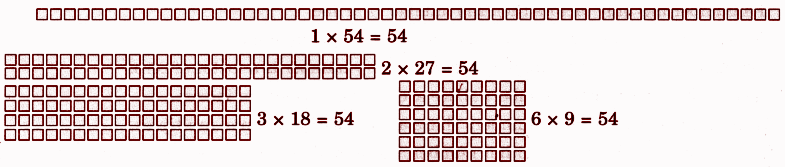Step-by-step Answers & Marking Tips for Animal Jumps (Class 5 Maths)
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 5 Maths Chapter 13 Animal Jumps - 2025-26
1. What does NCERT Solutions Class 5 Maths Chapter 13 Animal Jumps include?
NCERT Solutions for Class 5 Maths Chapter 13 Animal Jumps give complete, stepwise answers for all textbook exercises and questions as per the latest CBSE 2025–26 syllabus.
- Detailed, step-by-step solutions to all intext and back exercises
- Key definitions, diagrams, and formulae included
- Marking-scheme guidance for each type of question
- Downloadable PDF for easy offline revision
- Helps students score full marks and build solid exam confidence
2. How can I download the NCERT Solutions for Class 5 Maths Chapter 13 Animal Jumps in PDF format?
You can download the Class 5 Maths Chapter 13 Animal Jumps NCERT Solutions PDF for free from trusted educational sites.
- Look for the 'Download PDF' button on the solutions page
- Ensure it is for Chapter 13 Animal Jumps and updated for the 2025–26 syllabus
- PDFs are handy for offline learning and quick revision sessions
3. Are diagrams or definitions mandatory in NCERT Class 5 Maths Chapter 13 Animal Jumps answers?
Including neat diagrams and accurate definitions in your Animal Jumps answers is highly recommended for full marks.
- Many questions require labelled diagrams or sketches
- Proper definitions show conceptual clarity
- According to the CBSE marking scheme, these carry step marks
- Always label diagrams clearly and write definitions in simple language
4. How do stepwise NCERT solutions help in scoring full marks for Animal Jumps?
Stepwise NCERT solutions for Animal Jumps ensure you write answers as expected by examiners and gain maximum marks.
- Each step earns partial marks, even for long calculations
- Neatly structured steps show your understanding to the examiner
- Helps avoid skipping important reasoning or method marks
- Aligns with the CBSE step marking pattern
5. What types of questions can come from Class 5 Maths Chapter 13 Animal Jumps in exams?
Exams often ask various types of questions from Animal Jumps:
- Short answer sums: Direct calculations or single-step problems
- Long answer sums: Situational questions with multiple steps
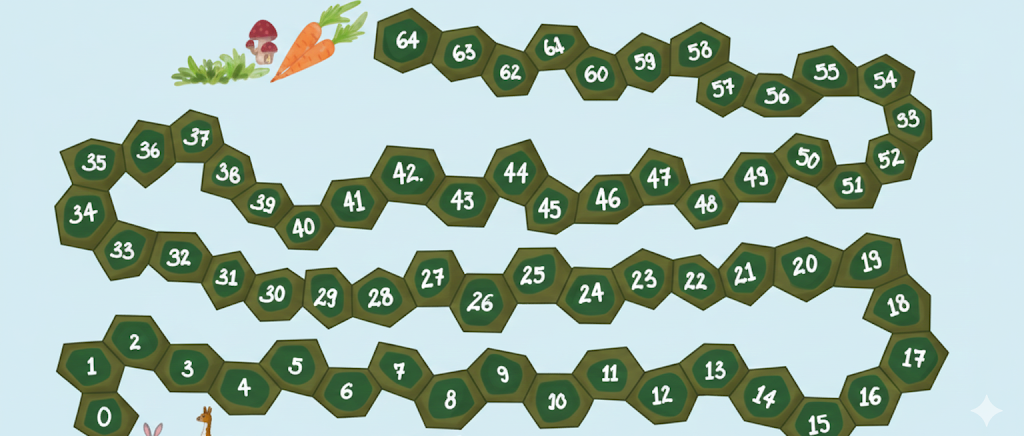
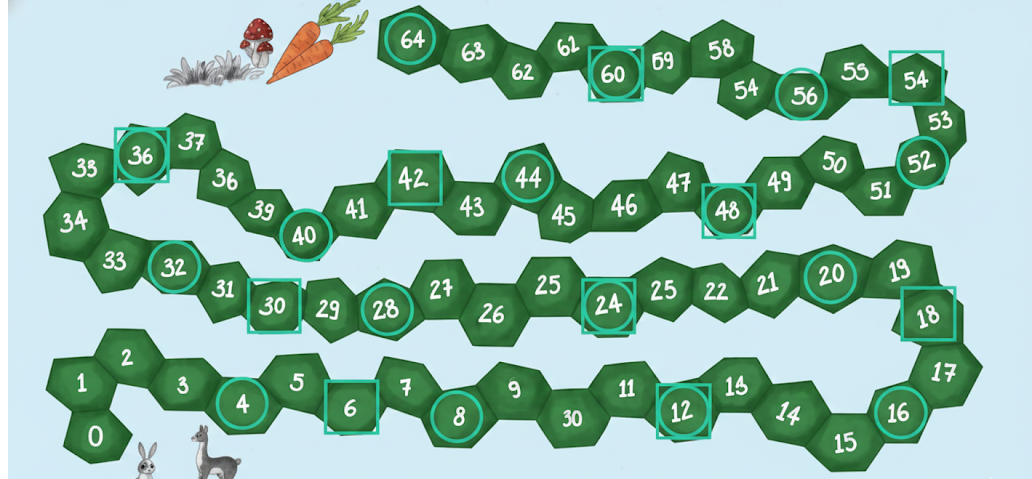
- Diagram labelling: Drawing and naming animal jumps or paths
- Definitions/explanations: Key terms from the chapter
- Application questions: Real-life situations using jump patterns
6. How should I present long answers from Animal Jumps to match the CBSE marking scheme?
For long answers from Animal Jumps, follow a clear structure:
- Start with what is asked (given/required/solution steps)
- Show all calculations step-by-step
- Use proper headers for each part (e.g., Step 1: finding distance, Step 2: calculating jumps)
- Add diagrams or tables, if relevant
- End with the final answer in a box for clarity
7. What are the key definitions and formulae to remember in Animal Jumps?
Important definitions and formulae for Animal Jumps include:
- Jump: The distance covered by an animal in one leap
- Number of jumps = Total distance ÷ Length of one jump
- Patterns in jumps: Spotting sequences or repetitions
- Shortcut methods for addition and multiplication related to jumps
Review these before your exam for quick recall and time saving.
8. What are common mistakes to avoid in Class 5 Maths Animal Jumps questions?
To avoid losing marks in Animal Jumps questions, remember:
- Don’t skip calculation steps – write every important step
- Always label diagrams clearly and neatly
- Check units (e.g., metre vs. centimetre)
- Don’t mix up number of jumps with jump length
- Recheck final answers for accuracy before submission
9. Where can I find revision notes and important questions for Animal Jumps?
You can find revision notes and important questions for Animal Jumps on the same educational platform that provides NCERT Solutions.
- Look for the dedicated 'Revision Notes' and 'Important Questions' section
- Notes include quick summaries, formulae, and diagrams
- Important Questions target likely exam topics from Chapter 13
- These resources help with last-minute preparation and understanding trends
10. Are NCERT solutions enough for Class 5 Maths Chapter 13 exam preparation?
NCERT solutions for Animal Jumps are usually sufficient for CBSE Class 5 exam preparation, but extra practice helps:
- All CBSE exam questions are based on the NCERT Animal Jumps chapter
- Try exemplar and previous year questions for extra confidence
- Practice diagrams and long answers for complete preparation
- Use the NCERT Solutions as your main guide for accurate answers