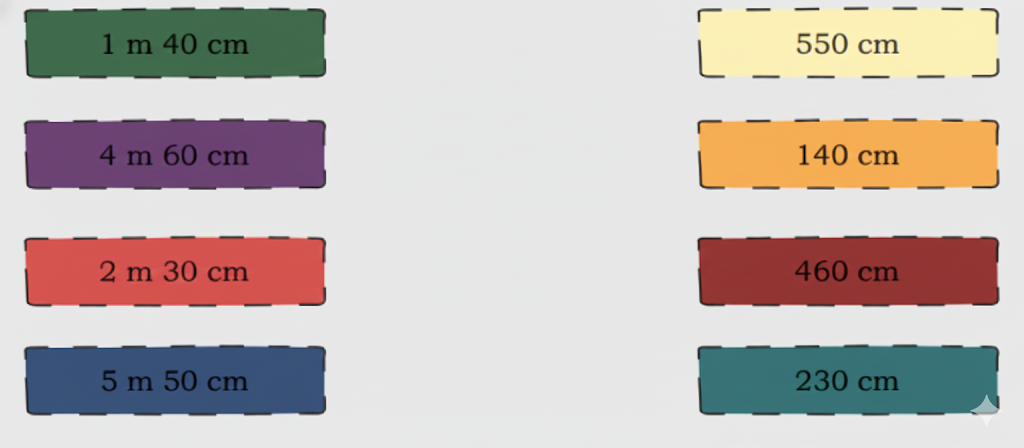
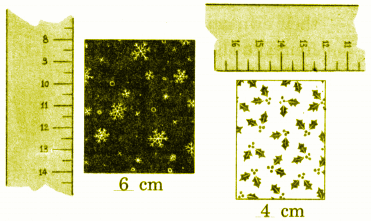
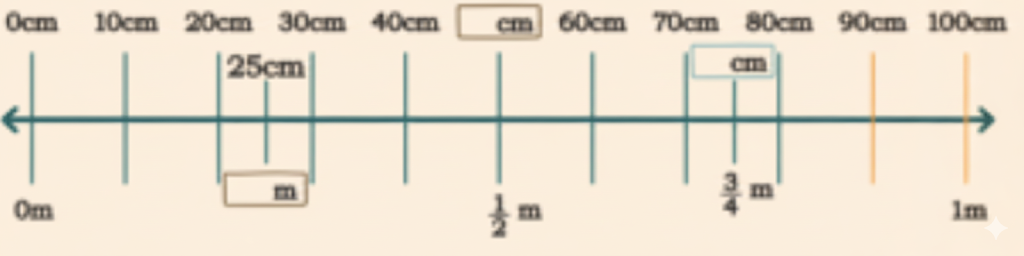
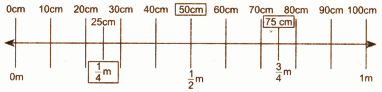
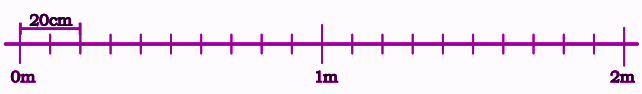
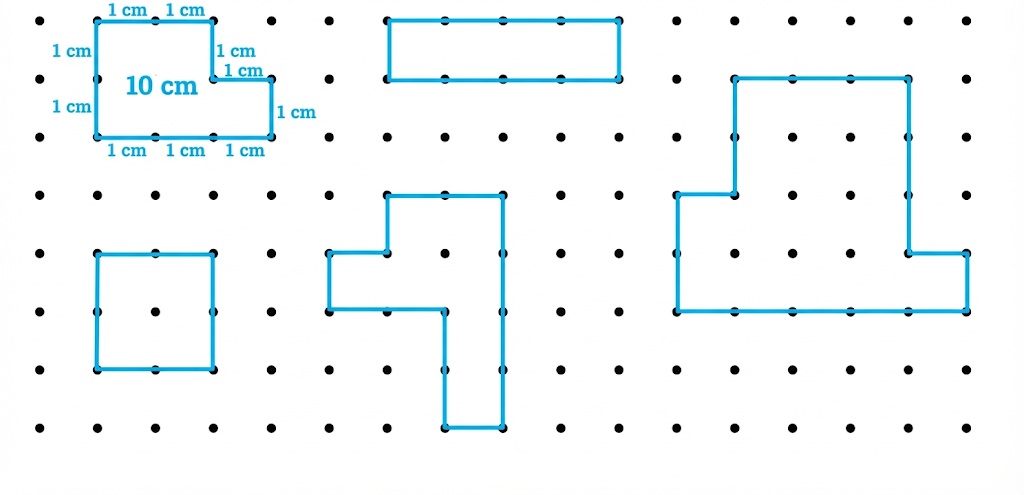
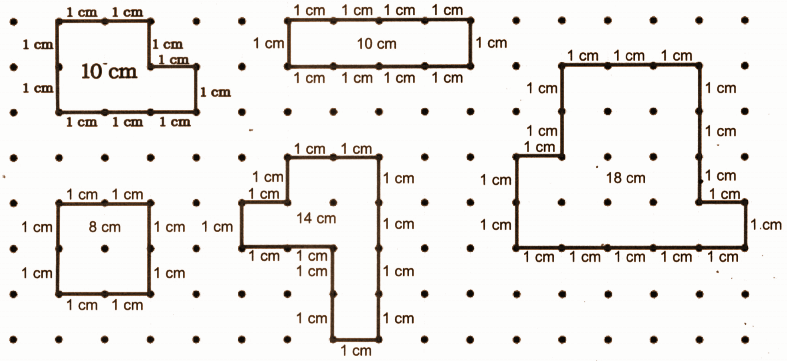
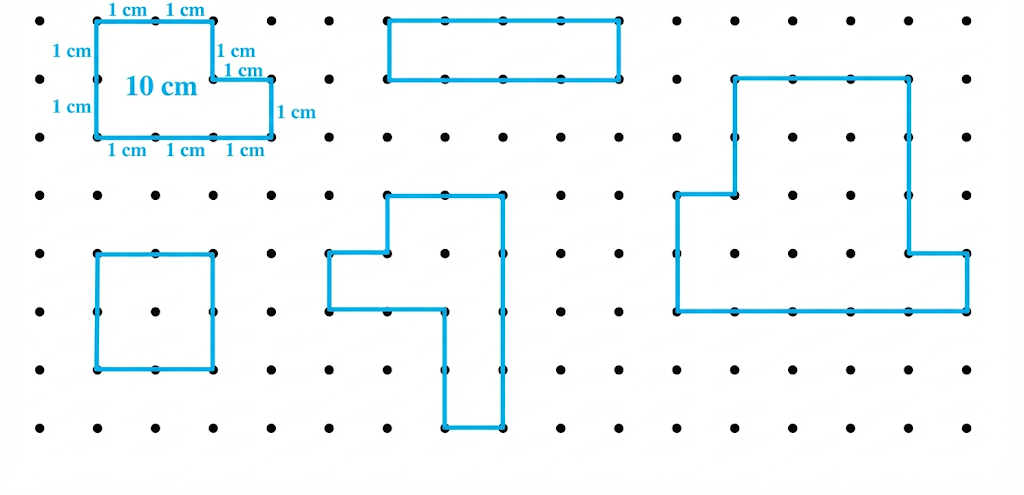
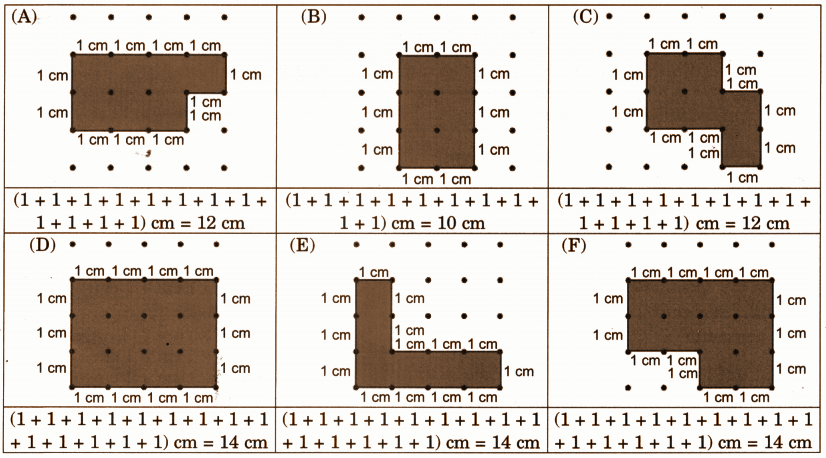
Exercise-wise Step-by-Step Answers for Measuring Length (Class 4 Maths)
FAQs on Class 4 Maths Chapter 6: Measuring Length NCERT Solutions
1. What is the easiest way to master measuring length in Class 4 Maths?
The most effective way to master measuring length in Class 4 Maths is by practising NCERT Solutions Class 4 Maths Chapter 6 step by step.
- Consistently solve exercise-wise questions for better understanding.
- Use key formulae and diagrams provided in the solutions for clarity.
- Revise with short notes and chapter summary to help with quick recall before the exam.
2. Are NCERT Solutions enough for Class 4 Maths exams?
NCERT Solutions for Class 4 Maths are usually sufficient for most CBSE school exams.
- They cover all intext and back exercise questions as per the CBSE 2025–26 syllabus.
- Regular practice helps students understand key concepts and definitions thoroughly.
- Use them along with exemplar and revision notes for additional practice.
3. How to write stepwise NCERT answers to score full marks?
To score full marks, always write clear and stepwise solutions for each problem in Class 4 Maths Chapter 6.
- Start with the formula or method used.
- Show all calculation steps neatly.
- Draw diagrams wherever required and label them properly.
- Highlight the final answer.
- Follow the CBSE marking scheme to include all required parts of the answer.
4. Are diagrams or definitions mandatory in answers?
Including diagrams and definitions wherever asked is essential for full marks in most CBSE Class 4 Maths questions.
- Neat, well-labelled diagrams help explain measurement problems clearly.
- Definitions of terms like centimetre, metre, length show your understanding to the examiner.
5. How can I structure long answers for better marks in measuring length chapter?
To structure long answers in Measuring Length Class 4 for maximum marks:
- Start with a brief introduction or definition if needed.
- Write stepwise working for every calculation.
- Insert diagrams with proper labels if relevant.
- Conclude with the final answer and units (cm, m, etc.).
- Follow the marking scheme for pointwise explanation.
6. Where can I download the NCERT Solutions Class 4 Maths Chapter 6 PDF?
You can download the Class 4 Maths Chapter 6 solutions PDF for free from trusted educational platforms.
- Look for a "Free PDF Download" option on the solution page.
- Use the PDF for offline study and quick revision before exams.
7. Which questions are most important from Class 4 Maths Chapter 6 for exams?
The most important questions from Class 4 Maths Chapter 6 Measuring Length are:
- Problems on converting units (cm to m, m to cm).
- Sum and difference of lengths.
- Application of measurement in real-life scenarios.
- Drawing and labelling diagrams for measurement activities.
8. How does practicing step-by-step NCERT solutions help in exams?
Practising stepwise NCERT Solutions helps in scoring higher marks as it:
- Ensures you follow the correct method for each question.
- Helps avoid common mistakes in calculations and diagrams.
- Makes your answers easy to check for examiners following the CBSE marking scheme.
9. What are the key formulae and definitions in Measuring Length Class 4?
The key formulae and definitions in NCERT Solutions for Class 4 Maths Chapter 6 include:
- 1 metre (m) = 100 centimetres (cm)
- Length: Measurement of something from end to end.
- Centimetre, metre, kilometre: Units of length measurement.
10. Do examiners award partial marks for correct steps even if the final answer is wrong?
Yes, in CBSE exams, examiners often give partial marks for correct methods and steps even if the final answer is wrong.
- Writing stepwise solutions in Class 4 Maths Chapter 6 helps secure marks for your approach.
- Always show all working clearly, even if you are unsure about the final answer.
11. How to learn diagrams for Class 4 Maths Chapter 6?
To learn diagrams for Class 4 Maths Chapter 6 Measuring Length:
- Practice drawing and labelling measuring instruments (scale, tape, etc.).
- Refer to stepwise solutions with diagrams in the NCERT solutions.
- Maintain neatness and correct labels to earn easy marks in exams.
12. What is covered in NCERT Solutions Class 4 Maths Chapter 6 Measuring Length?
The Class 4 Maths Chapter 6 NCERT Solutions cover:
- Stepwise solutions to all intext and back exercise questions.
- Key definitions, measurement units, and conversion problems.
- Diagram drawn questions and application-based questions.
- Summary and formulae for revision aligned with the CBSE 2025–26 syllabus.