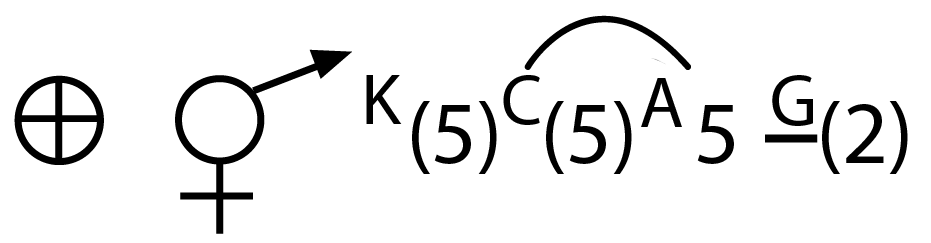How Are Morphology Of Flowering Plants Class 11 Questions and Answers Helpful for Exam Preparation
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Biology Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering Plants (2025-26)
1. What does the morphology of flowering plants class 11 NCERT chapter cover?
The morphology of flowering plants chapter covers the external structure and form of angiosperms, including roots, stems, leaves, inflorescence, flowers, fruits, and seeds. This chapter forms the foundation for understanding plant identification and classification in botanical studies.
2. How do NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 5 help students understand plant morphology?
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 5 provide step-by-step explanations of morphological concepts with labeled diagrams and detailed answers to all textbook questions. These solutions clarify complex terminology and help students visualize different plant parts systematically.
3. What are the main types of root systems discussed in flowering plant morphology?
Flowering plants have two main root systems: taproot system with a prominent main root and lateral branches, and fibrous root system with numerous thin roots of similar size. These systems determine how plants anchor themselves and absorb nutrients from soil.
4. How can students access morphology of flowering plants questions and answers PDF for free?
Students can access free PDF of morphology of flowering plants questions and answers through educational platforms like Vedantu, which provide comprehensive study materials aligned with NCERT curriculum. These PDFs contain solved examples, practice questions, and detailed explanations of morphological concepts.
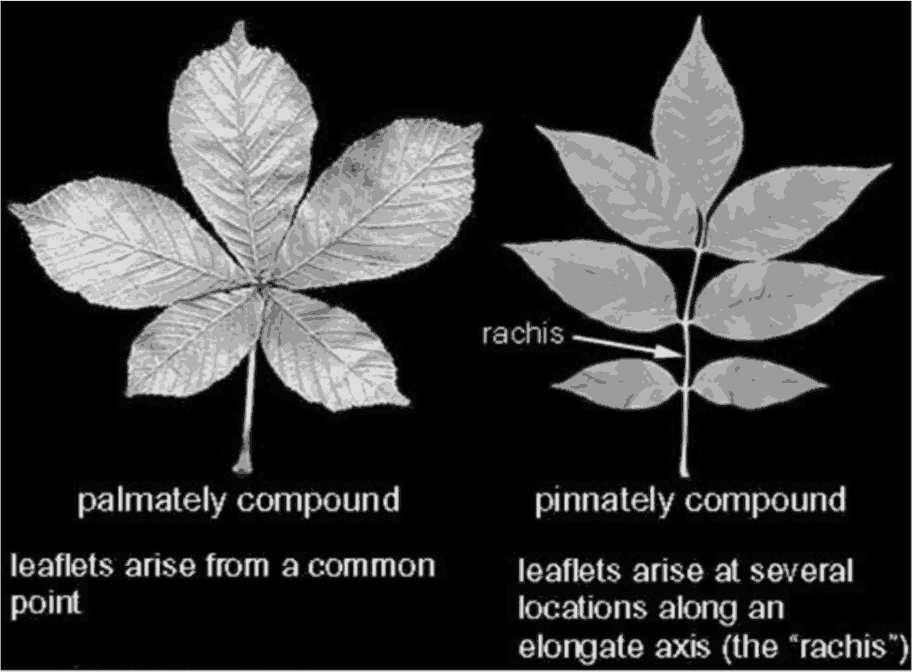
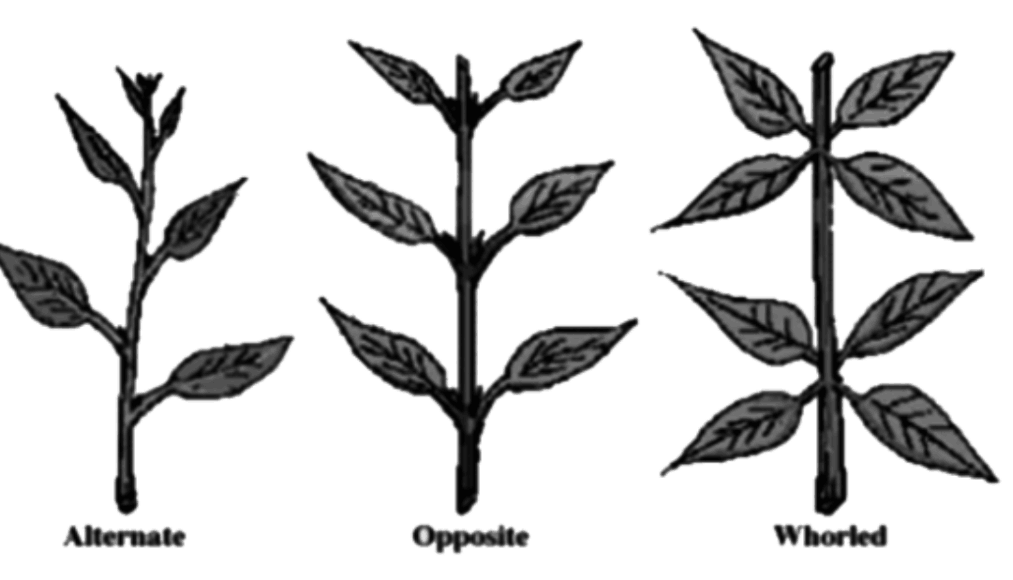
5. What are the different types of leaf arrangements found in flowering plants?
Flowering plants show three main leaf arrangements: alternate (one leaf per node), opposite (two leaves per node), and whorled (more than two leaves per node). These phyllotactic patterns optimize light capture and space utilization for photosynthesis.
6. How do morphology of flowering plants class 11 notes help in exam preparation?
Class 11 morphology notes provide structured summaries of plant parts, terminology, and classification systems essential for board exams and competitive tests. These notes consolidate complex morphological concepts into easily reviewable formats with key diagrams and examples.
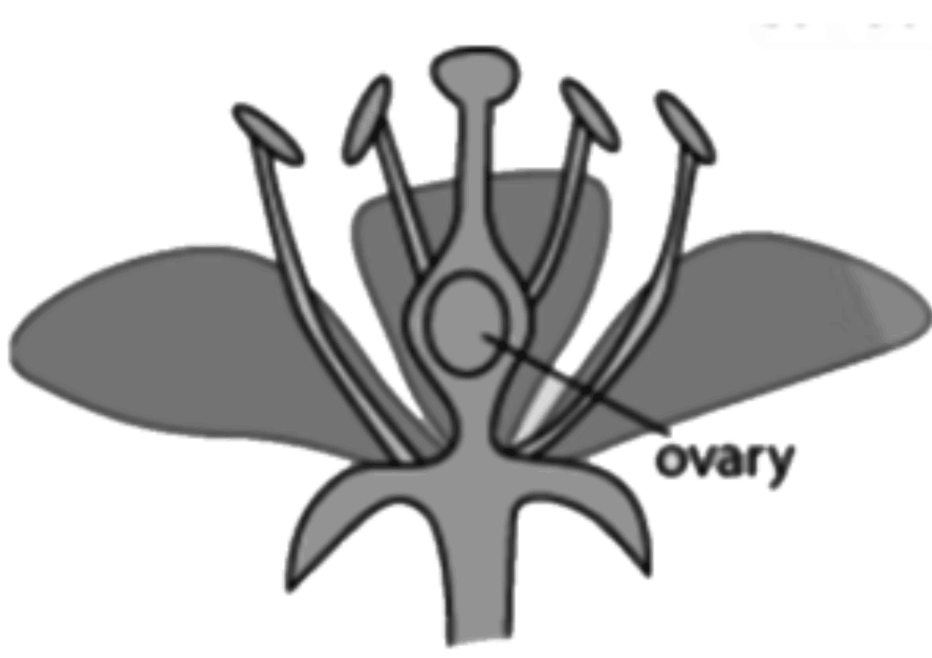
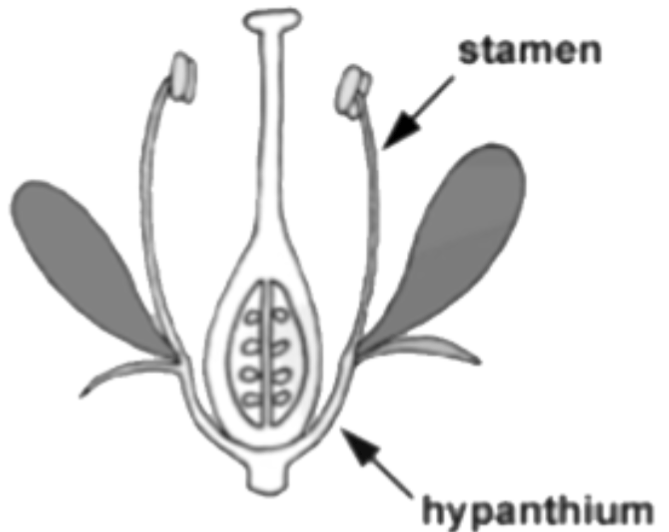
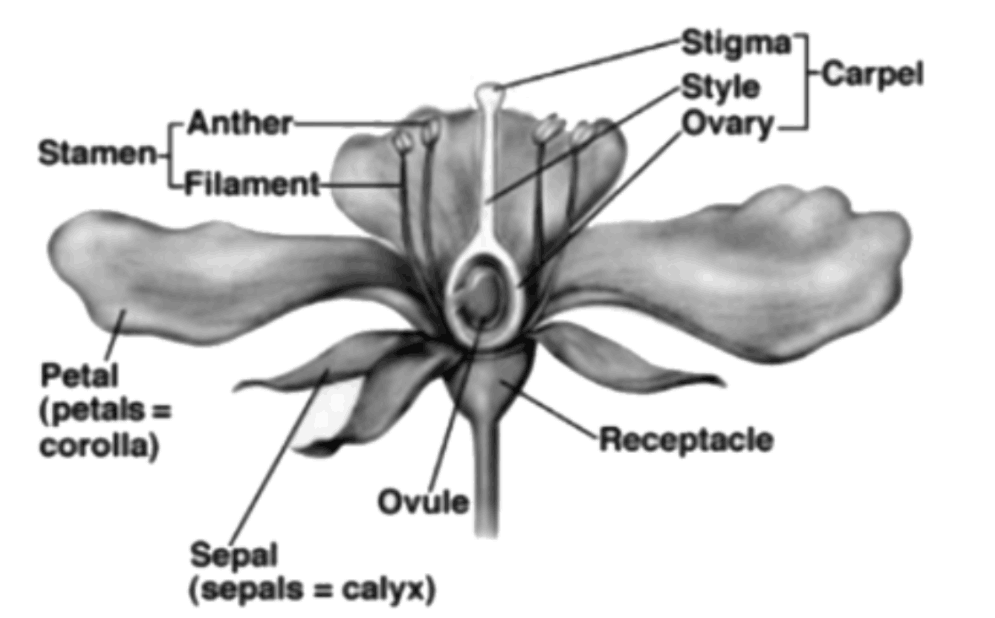
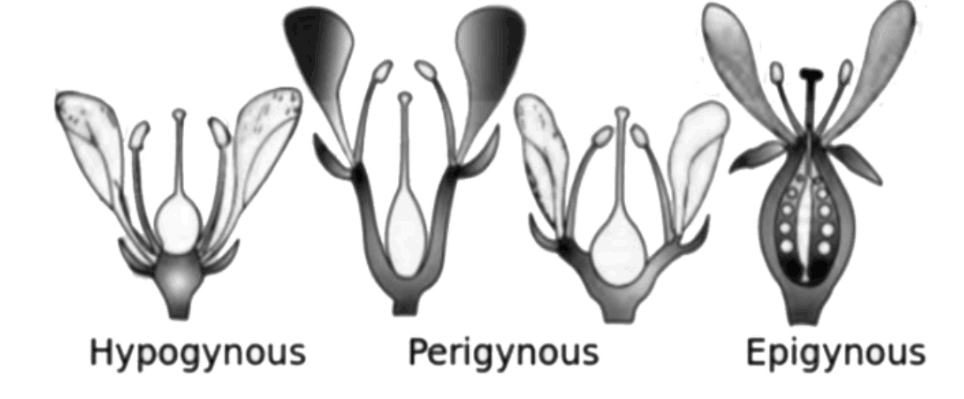
7. What is the significance of flower morphology in plant classification?
Flower morphology serves as the primary basis for angiosperm classification because floral structures show consistent patterns within related plant groups. Characters like petal number, symmetry, and ovary position help identify plant families and genera accurately.
8. How are stem modifications classified in flowering plant morphology?
Stem modifications are classified into underground (rhizome, tuber, bulb, corm), subaerial (runner, sucker, stolon), and aerial modifications (tendril, thorn, cladophyll) based on their location and function. These adaptations help plants survive different environmental conditions and perform specialized functions.
9. What role do fruit and seed morphology play in plant reproduction?
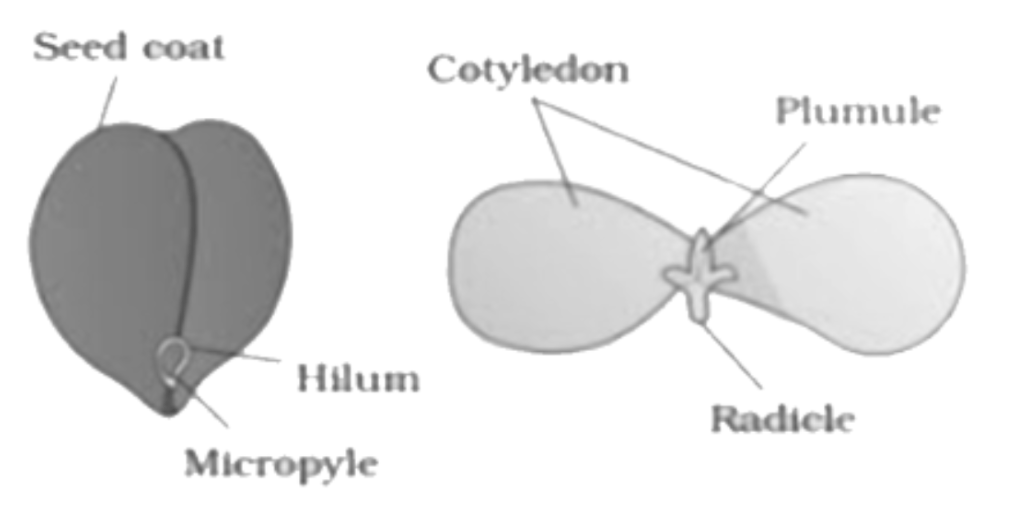
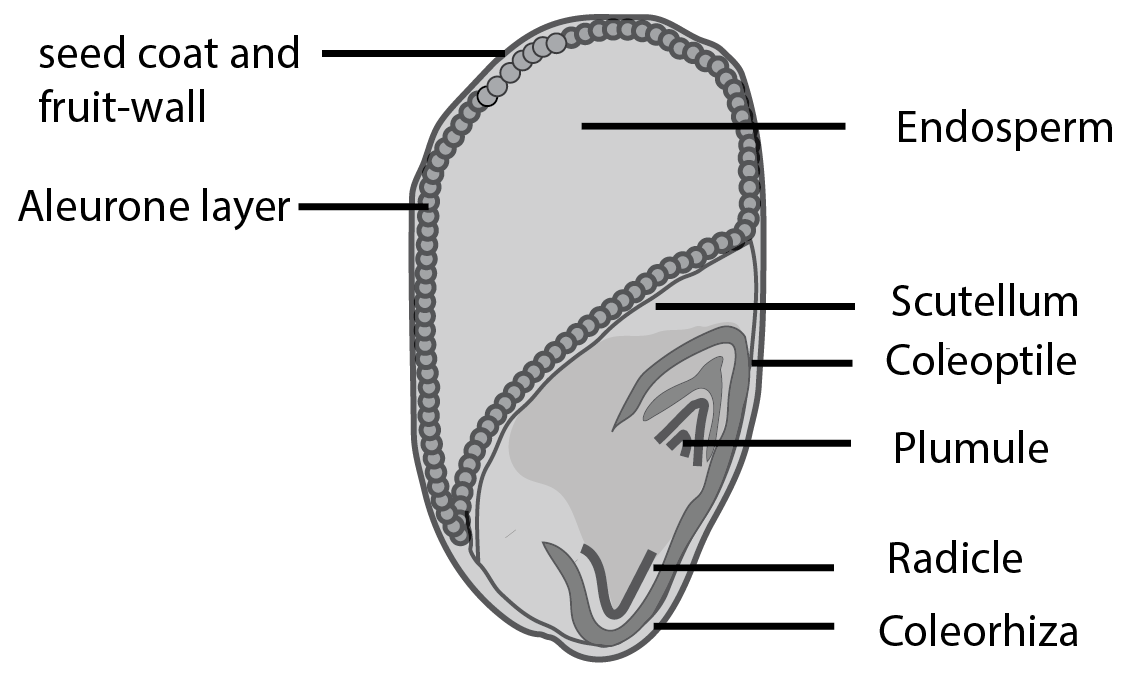
Fruit and seed morphology determines dispersal mechanisms and germination strategies, ensuring species survival and distribution across different habitats. Different fruit types like drupes, berries, and capsules have evolved specific structures for effective seed dispersal.
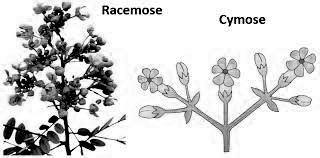
10. How do inflorescence types affect flowering and pollination in plants?
Different inflorescence types like raceme, spike, umbel, and capitulum determine flowering sequence and pollination efficiency by arranging flowers in specific patterns. These arrangements optimize pollinator visits and reproductive success through strategic flower positioning and timing.