
Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Light Reflection and Refraction Questions and Answers: Free PDF Download
Class 10 Science Chapter 9: Light Reflection and Refraction focuses on understanding the behaviour of light as it reflects off surfaces and refracts through different media. The chapter introduces concepts like laws of reflection, refraction, and refractive index that explain how light behaves in our daily lives. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 provide comprehensive answers, breaking down complex ideas into simple, understandable steps.
 Table of Content
Table of ContentBy solving Class 10 Science Chapter 9 question answers, students will understand how to apply these concepts in real-world scenarios. The solutions include detailed steps that help students approach tricky questions and prepare for the CBSE exams. With Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 covered in the solutions, students can gain confidence in solving related problems and achieve better marks in exams.
NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Light Reflection And Refraction (2025-26)
Access NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 – Light Reflection and Refraction
1. What is the principal focus of a concave mirror?
Ans: The light rays parallel to the principal axis converge at a point on the principal axis after reflecting from the concave mirror.
The point of convergence on the principal axis of a concave mirror is called the principal focus of a concave mirror.
2. What is the focal length of a spherical mirror whose radius of curvature is $20cm$?
Ans: It is given that,
Radius of curvature of a spherical mirror, $R=20cm$
It is known that,
Radius of curvature is twice the focal length.
$R=2f$
$\Rightarrow f=R/2$
$\Rightarrow f=\frac{20}{2}$
$\Rightarrow f=10cm$
Therefore, the focal length of a spherical mirror with the radius of curvature equal to $20cm$ is $f=10cm$.
3. Which mirror gives an erect and enlarged image of an object?
Ans: If the object is placed between pole and the principal focus of a concave mirror the image formed is virtual, erect and enlarged.
Erect and enlarged images are not possible in case of convex or plane mirrors.
4. Why is convex mirror preferred as a rear-view mirror in vehicles?
Ans: If the objects are placed in front of a convex mirror, then the image formed is an erect and diminished image.
In vehicles we need erect images and we need to see as many areas as possible behind the vehicles.
So, a convex mirror is preferred as a rear-view mirror in vehicles.
5. What is the focal length of a convex mirror whose radius of curvature is $32cm$?
Ans: It is given that,
Radius of curvature of a convex mirror, $R=32cm$
It is known that,
Radius of curvature is twice the focal length.
$R=2f$
$\Rightarrow f=R/2$
$\Rightarrow f=\frac{32}{2}$
$\Rightarrow f=16cm$
Therefore, the focal length of a convex mirror with the radius of curvature equal to $32cm$ is $f=16cm$.
6. Find the location of image for a concave mirror that produces three times magnified (enlarged) real image of the object placed at $10cm$ in front of it.
Ans: It is given that,
Distance of object in front of mirror, $u=-10cm$ (negative sign due to the location of the object in front of the mirror)
Distance of image from mirror, $v=?$
It is known that,
Magnification of a spherical mirror,$m=\frac{{{h}_{i}}}{{{h}_{o}}}=-\frac{v}{u}$
where,
${{h}_{i}}$ is the height of the image
${{h}_{o}}$ is the height of the object
Let, ${{h}_{o}}=h$
It is given that three times the enlarged real image of the object is produced.
So, ${{h}_{i}}=-3h$ ($-$ due to real image formation)
$\Rightarrow m=-\frac{3h}{h}=-\frac{v}{u}$
$\Rightarrow 3=\frac{v}{-10}$
$\Rightarrow v=-30cm$(negative sign due to the formation of inverted image)
Therefore, the location of image from the mirror is at a distance of $30cm$ and the nature of the image is inverted.
7. When a light ray travelling in the air enters obliquely into the water, how does it bend towards the normal or away from the normal? State reason.
Ans: When a light ray is travelling from the rarer medium to denser medium, it refracts towards the normal.
Here, the light ray bends towards the normal because the light ray is moving from air(rarer) to water(denser) medium.
8. Find the speed of light in glass if the light enters from air to glass having a refractive index of $1.50$. Take the speed of light in vacuum, $c=3\times {{10}^{8}}m{{s}^{-1}}$ .
Ans: It is given that,
Refractive index of glass,$\mu =1.50$
Speed of the light in vacuum, $c=3\times {{10}^{8}}m{{s}^{-1}}$
Speed of the light in glass,${{v}_{g}}=?$
It is known that,
$\mu =\frac{c}{{{v}_{g}}}$
$\Rightarrow 1.5=\frac{3\times {{10}^{8}}m{{s}^{-1}}}{{{v}_{g}}}$
$\Rightarrow {{v}_{g}}=\frac{3\times {{10}^{8}}}{1.5}$
$\Rightarrow {{v}_{g}}=2\times {{10}^{8}}m{{s}^{-1}}$
Therefore, the speed of light in glass is ${{v}_{g}}=2\times {{10}^{8}}m{{s}^{-1}}$ .
9. From the table, find the medium having the highest optical density and the lowest optical density.
Material medium | Refractive Index | Material medium | Refractive Index |
Air | 1.0003 | Crown glass | 1.52 |
Ice | 1.31 | Canada Balsam | 1.53 |
Water | 1.33 | Rock salt | 1.54 |
Alcohol | 1.36 | Carbon disulphide | 1.63 |
Kerosene | 1.44 | Dense flint glass | 1.65 |
Fused quartz | 1.46 | Ruby | 1.71 |
Turpentine oil | 1.47 | Sapphire | 1.77 |
Benzene | 1.50 | Diamond | 2.42 |
Ans: To find the materials of highest and lowest optical densities check for its refractive index. The one with the highest refractive index will have the highest optical density and the one with lowest refractive index will have the lowest optical density.
The highest optical density is for Diamond i.e., $\mu =2.42$
The lowest optical density is for Air i.e.,$\mu =1.0003$
10. Among kerosene, turpentine oil and water in which medium does the light travel fastest? Refer to the table for refractive index.
Material Medium | Refractive Index | Material Medium | Refractive Index |
Air | 1.0003 | Crown Glass | 1.52 |
Ice | 1.31 | Canada Balsam | 1.53 |
Water | 1.33 | Rock Salt | 1.54 |
Alcohol | 1.36 | Carbon Disulphide | 1.63 |
Kerosene | 1.44 | Dense Flint Glass | 1.65 |
Fused Quartz | 1.46 | Ruby | 1.71 |
Turpentine Oil | 1.47 | Sapphire | 1.77 |
Benzene | 1.50 | Diamond | 2.42 |
Ans: It is known that,
Absolute refractive index,$\mu =\frac{c}{{{v}_{m}}}$
where,
$c$ is the speed of light in vacuum$=3\times {{10}^{8}}m{{s}^{-1}}$
${{v}_{m}}$ is the speed of light in medium
$\Rightarrow \mu \propto \frac{1}{{{v}_{m}}}$ ($c$ is constant)
To compare the speed of light we compare the refractive index. Speed of light and refractive index are inversely proportional i.e., if the refractive index is more than the speed of light is less.
The order of refractive index among kerosene, turpentine oil and water is${{\mu }_{\ker osene}}>{{\mu }_{turpentineoil}}>{{\mu }_{water}}$ .
The order of speed of light becomes ${{\mu }_{\ker osene}}<{{\mu }_{turpentineoil}}<{{\mu }_{water}}$ .
Therefore, the speed of light is fastest in water.
11. What is the meaning of the statement “The refractive index of diamond is $2.42$”?
Ans: It is known that,
Refractive index of a medium,$\mu =\frac{c}{{{v}_{m}}}$
where,
$c$ is the speed of light in vacuum
${{v}_{m}}$ is the speed of light in medium
$2.42=\frac{c}{{{v}_{d}}}$
“The refractive index of diamond is $2.42$” means that the speed of light in vacuum is $2.42$ times the speed of light in diamond or the speed of light in diamond is $\frac{1}{2.42}$ times the speed of light in vacuum.
12. What is $1$ dioptre of power of a lens?
Ans: When $f$ is the focal length in metres of a lens with power $P$ then$P=\frac{1}{f(metres)}$ .
Dioptre is the S.I. unit of power of a lens and is denoted by $D$.
The power of a lens of focal length $1$ metre is defined as $1$ dioptre.
13. Image formed by a convex lens is real and inverted and at a distance of $50cm$from the lens. Find the position of the needle in front of the convex lens when the image is equal to the size of the object. Also, calculate the power of the lens.
Ans: It is given that,
Distance of image from convex lens,$v=50cm$
Distance of object in front of lens,$u=?$
The image formed is real and inverted. So, the magnification of the lens is $-1$.

Image source: Self-created
It is known that,
Magnification of a convex lens,$m=\frac{v}{u}$
$\Rightarrow -1=\frac{v}{u}$
$\Rightarrow -1=\frac{50}{u}$
$\Rightarrow u=-50cm$
Lens formula:$\frac{1}{v}-\frac{1}{u}=\frac{1}{f}$
$f$ is the focal length of the lens.
$\Rightarrow \frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{50}-\frac{1}{(-50)}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{50}+\frac{1}{50}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{1}{f}=\frac{2}{50}$
$\Rightarrow f=\frac{50}{2}$
$\Rightarrow f=25cm=0.25m$
It is known that,
Power of the lens,$P=\frac{1}{f(metres)}$
$\Rightarrow P=\frac{1}{(+0.25)}$
$\Rightarrow P=+4D$
Therefore, the object distance from the lens is $u=-50cm$ and power of the lens is $P=+4D$.
14. What is the power of a concave lens of focal length$2m$?
Ans: It is given that,
Focal length of a concave lens is,$f=-2m$
Power of the concave lens,$P=\frac{1}{f(metres)}$
$\Rightarrow P=\frac{1}{(-2)}$
$\Rightarrow P=-0.5D$
Therefore, the power of a concave lens is $P=-0.5D$.
15. Which one of the following materials cannot be used to make a lens?
Water
Glass
Plastic
Clay
Ans: d) Clay can’t be used to make a lens because it is opaque.
16. The image formed by a concave mirror is observed to be virtual, erect and larger than the object. Where should the position of the object be?
Between the principal focus and the centre of curvature
At the centre of curvature
Beyond the centre of curvature
Between the pole of the mirror and its principal focus.
Ans: d) The object is placed between the pole of the mirror and its principal focus when the image formed is virtual, erect and larger than the object in the concave mirror.
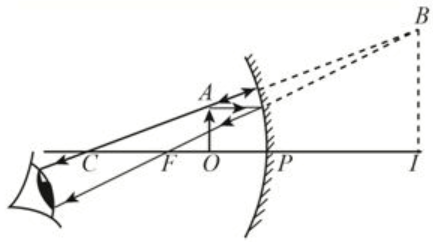
17. Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens to get a real image of the size of the object?
At the principal focus of the lens
At twice the focal length
At infinity
Between the optical centre of the lens and its principal focus
Ans: b) An object should be placed at a distance of twice the focal length of a convex lens to get a real image of the size of the object.

18. A spherical mirror and a thin spherical lens have each a focal length of $-15cm$ . The mirror and the lens are likely to be
Both concave
Both convex
The mirror is concave and the lens is convex
The mirror is convex, but the lens is concave
Ans: a) For a concave lens the primary focus is on the same side as the object and is negative. In the case of a concave mirror, the focus is in front of the mirror and negative. Therefore, the mirror and lens are likely to be concave.
19. No matter how far you stand from a mirror, your image appears erect. The mirror is likely to be
Plane
Concave
Convex
Either plane or convex
Ans: d) Erect images are produced by both plane and convex mirrors for objects at any position.
20. Which of the following lenses would you prefer to use while reading small letters found in a dictionary?
A convex lens of focal length \[\mathbf{50}\text{ }\mathbf{cm}\]
A concave lens of focal length \[\mathbf{50}\text{ }\mathbf{cm}\]
A convex lens of focal length \[\mathbf{5}\text{ }\mathbf{cm}\]
A concave lens of focal length \[\mathbf{5}\text{ }\mathbf{cm}\]
Ans: a) When the object is placed between focus and optic centre, magnified and erect images are formed in a convex lens. So, while reading small letters a convex lens is preferred.
21. We wish to obtain an erect image of an object, using a concave mirror of focal length \[\mathbf{15}\text{ }\mathbf{cm}\]. What should be the range of distance of the object from the mirror? What is the nature of the image? Is the image larger or smaller than the object? Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
Ans: To obtain an erect image in a concave mirror the object should be placed between Focus and the Optic centre.
Here, the focal length of the concave mirror is given as $15cm$.
Therefore, the range of distance of the object from the mirror is from $0cm$ to$15cm$.
The nature of the image is virtual.
The image is larger than the object.
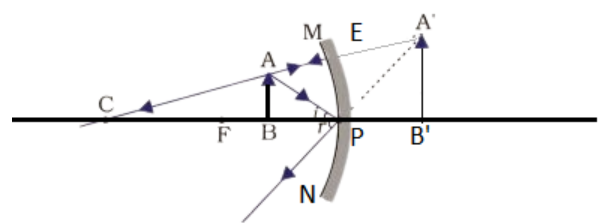
A virtual, erect and magnified image is formed.
22. Name the type of mirror used in the following situations and support your answer with reason.
Headlights of a car
Ans: In the headlights of a car, a concave mirror is used. Because in concave mirrors a parallel beam of light is produced if the bulb is placed at the focus.
Side/Rear-View Mirror of a Vehicle
Ans: In a side/rear-view mirror of a vehicle , a convex mirror is used. Because when objects are placed in front of the convex mirror, erect and diminished images are formed which gives a wider field of view.
Solar Furnace
Ans: In solar furnaces, Concave mirrors are used. They converge sunlight to a point and produce high temperatures because of their converging properties.
23. One-half of a convex lens is covered with a black paper. Will this lens produce a complete image of the object? Verify your answer experimentally. Explain your observations.
Ans: Yes, the lens produces a complete image of the object with less intensity.
Consider the following two cases:

In the first case the lower half of the lens is covered with black paper. Light rays coming from the object are refracted only from the upper half and the image is formed, whereas in the lower half the light rays are blocked.

In the second case the upper half of the lens is covered with black paper. Light rays coming from the object are refracted only from the lower half and the image is formed, whereas in the upper half the light rays are blocked.
Therefore, change in intensity of the image is observed i.e., the intensity of the image is less and the complete image is formed.
24. An object of \[\mathbf{5}\text{ }\mathbf{cm}\] in length is held \[\mathbf{25}\text{ }\mathbf{cm}\] away from a converging lens of focal length \[\mathbf{10}\text{ }\mathbf{cm}\] . Draw the ray diagram and find the position, size and the nature of the image formed.
Ans: It is given that,
Height of the object,${{h}_{o}}=5cm$
Distance of object in front of lens,$u=-25cm$
Distance of image from lens,$v=?$
Focal length of the lens,$f=+10cm$
From lens formula:$\frac{1}{v}-\frac{1}{u}=\frac{1}{f}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{1}{v}=\frac{1}{f}+\frac{1}{u}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{1}{v}=\frac{1}{10}-\frac{1}{25}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{1}{v}=\frac{25-10}{250}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{1}{v}=\frac{15}{250}$
$\Rightarrow v=\frac{250}{15}$
$\Rightarrow v=16.66cm$
The positive value of $v$ indicates that the image and the object are on opposite sides.
It is known that,
Magnification ,$m=\frac{{{h}_{i}}}{{{h}_{o}}}=-\frac{v}{u}$
Height of the image, ${{h}_{i}}=?$
$\Rightarrow m=\frac{{{h}_{i}}}{5}=-\frac{16.66}{25}=-0.66$
$\Rightarrow {{h}_{i}}=-0.66\times 5$
$\Rightarrow {{h}_{i}}=-3.3cm$
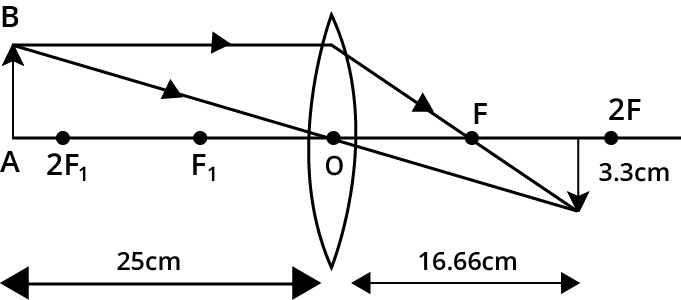
As the magnification is $-0.66$, the negative sign indicates that the object is inverted and less than $1$ indicates that the image is smaller than the object.
Therefore, the position of the image is $16.66cm$ from the lens. The height of the object is $3.3cm$. The nature of the image is real, inverted and diminished.
25. A concave lens of focal length \[\mathbf{15}\text{ }\mathbf{cm}\] forms an image \[\mathbf{10}\text{ }\mathbf{cm}\] from the lens. Find the distance of an object from the lens? Draw the ray diagram.
Ans: It is given that,
Focal length of the lens,$f=-15cm$
Distance of image from lens,$v=-10cm$
Distance of object in front of lens,$u=?$
From lens formula:$\frac{1}{v}-\frac{1}{u}=\frac{1}{f}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{1}{u}=\frac{1}{v}-\frac{1}{f}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{1}{u}=\frac{1}{(-10)}-\frac{1}{(-15)}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{1}{u}=\frac{-1}{10}+\frac{1}{15}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{1}{u}=\frac{-5}{150}$
$\Rightarrow u=-\frac{150}{5}$
$\Rightarrow u=-30cm$
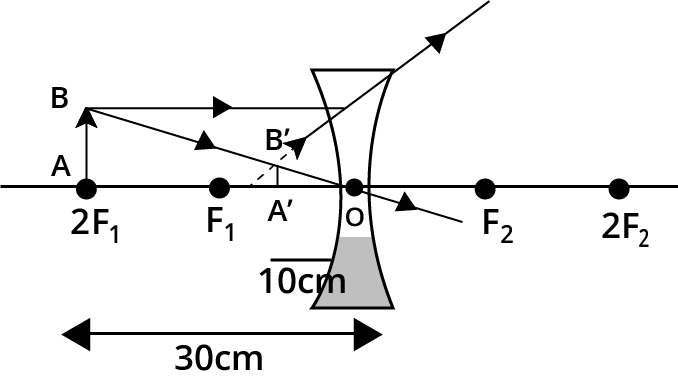
Thus, the object is at a distance of $30cm$ from the lens.
26. An object is placed at a distance of \[\mathbf{10}\text{ }\mathbf{cm}\] from a convex mirror of focal length \[\mathbf{15}\text{ }\mathbf{cm}\] . Find the position and nature of the image.
Ans: It is given that,
Focal length of the convex mirror,$f=+15cm$
Distance of object in front of convex mirror,$u=-10cm$
Distance of image from convex mirror,$v=?$
From mirror formula:$\frac{1}{v}+\frac{1}{u}=\frac{1}{f}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{1}{v}=\frac{1}{f}-\frac{1}{u}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{1}{v}=\frac{1}{15}-\frac{1}{(-10)}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{1}{v}=\frac{1}{15}+\frac{1}{10}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{1}{v}=\frac{25}{150}$
$\Rightarrow v=\frac{150}{25}$
$\Rightarrow v=6cm$
The positive value of $v$ indicates that the image is formed behind the mirror and virtual.
It is known that,
Magnification ,$m=\frac{{{h}_{i}}}{{{h}_{o}}}=-\frac{v}{u}$
$\Rightarrow m=\frac{-6}{-10}=+0.6$
The positive magnification indicates that the image is erect. As magnification is less than $1$ it indicates that the image is smaller than the object.
Therefore, the position of image is $6cm$ behind the mirror. Nature of image is virtual, erect and diminished.
27. What does “The magnification produced by a plane mirror is \[+1\] ” mean?
Ans: It is known that,
Magnification produced by a plane mirror is,$m=\frac{{{h}_{i}}}{{{h}_{o}}}=-\frac{v}{u}$
where,
${{h}_{i}}$ is the height of the image
${{h}_{o}}$ is the height of the object
$u$ is the distance of the object in front of lens
$v$ is the distance of image from lens
Magnification produced by a plane mirror is $+1$ means that ${{h}_{i}}={{h}_{o}}$ that is the size of the image is the same as the size of the object. The positive size indicates that the image is erect.
Therefore, magnification equal to $+1$ means that the size of the image is the same as object and erect.
28. An object \[\mathbf{5}\text{ }\mathbf{cm}\] in length is placed at a distance of \[\mathbf{20}\text{ }\mathbf{cm}\]in front of a convex mirror of radius of curvature\[\mathbf{30}\text{ }\mathbf{cm}\] . Find the position of the image, its nature and size.
Ans: It is given that,
Distance of object in front of the mirror,$u=-20cm$
Distance of image from the mirror,$v=?$
The radius of curvature of the mirror,$R=30cm$
The focal length of the mirror,$f=?$
It is known that,
Radius of curvature is equal to twice the focal length.
$\Rightarrow R=2f$
$\Rightarrow 30=2f$
$f=\frac{30}{2}=15cm$
From mirror formula:$\frac{1}{v}+\frac{1}{u}=\frac{1}{f}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{1}{v}=\frac{1}{f}-\frac{1}{u}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{1}{v}=\frac{1}{15}-\frac{1}{(-20)}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{1}{v}=\frac{1}{15}+\frac{1}{20}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{1}{v}=\frac{20+15}{300}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{1}{v}=\frac{35}{300}$
$\Rightarrow v=\frac{60}{7}$
$\Rightarrow v=8.57cm$
The positive value of $v$ indicates that the image is formed behind the mirror.
It is known that,
Magnification ,$m=\frac{{{h}_{i}}}{{{h}_{o}}}=-\frac{v}{u}$
Height of the object, ${{h}_{o}}=5cm$
Height of the image, ${{h}_{i}}=?$
$\Rightarrow {{h}_{i}}=-\frac{v}{u}\times {{h}_{o}}$
$\Rightarrow {{h}_{i}}=-\frac{8.57}{(-20)}\times 5$
$\Rightarrow {{h}_{i}}=2.14cm$
Therefore, the image is formed at a distance of \[8.57cm\]behind the mirror. The nature of the image is virtual, erect and diminished.
29. An object of size \[\mathbf{7}.\mathbf{0}\text{ }\mathbf{cm}\] is placed at \[\mathbf{27}\text{ }\mathbf{cm}\] in front of a concave mirror of focal length \[\mathbf{18}\text{ }\mathbf{cm}\] . At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed, so that a sharp focused image can be obtained? Find the size and the nature of the image.
Ans: It is given that,
Distance of object in front of mirror,$u=-27cm$
Distance of image from the mirror,$v=?$
Focal length of the mirror,$f=-18cm$
From mirror formula:$\frac{1}{v}+\frac{1}{u}=\frac{1}{f}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{1}{v}=\frac{1}{f}-\frac{1}{u}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{1}{v}=\frac{1}{-18}-\frac{1}{(-27)}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{1}{v}=-\frac{1}{18}+\frac{1}{27}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{1}{v}=\frac{-3+2}{54}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{1}{v}=-\frac{1}{54}$
$\Rightarrow v=-54cm$
The negative value of $v$ indicates that the screen should be placed at a distance of $54cm$ in front of the mirror and the image is real.
It is known that,
Magnification ,$m=\frac{{{h}_{i}}}{{{h}_{o}}}=-\frac{v}{u}$
Height of the object, ${{h}_{o}}=7cm$
Height of the image, ${{h}_{i}}=?$
$\Rightarrow {{h}_{i}}=-\frac{v}{u}\times {{h}_{o}}$
$\Rightarrow {{h}_{i}}=-\frac{-54}{(-27)}\times 7$
$\Rightarrow {{h}_{i}}=-14cm$
The height of image is \[14cm\].
Therefore, the image is formed at a distance of \[54cm\]in front of the mirror. Nature of image is real, inverted and enlarged.
30. Find the focal length of a lens of power\[-\mathbf{2}.\mathbf{0}\text{ }\mathbf{D}\] . What type of lens is this?
Ans: It is given that,
Power of a lens,$P=-2.0D$
Focal length of a lens, $f=?$
Power of a lens,$P=\frac{1}{f(metres)}$
$\Rightarrow -2=\frac{1}{f}$
$\Rightarrow f=-\frac{1}{2}=-0.5m$
Negative $f$ indicates concave lens.
Therefore, the focal length of lens is $f=-0.5m$and the lens is concave.
31. A doctor has prescribed a corrective lens of power \[+\mathbf{1}.\mathbf{5}\text{ }\mathbf{D}\]. Find the focal length of the lens. Is the prescribed lens diverging or converging?
Ans: It is given that,
Power of a lens,$P=+1.5D$
Focal length of a lens, $f=?$
Power of a lens,$P=\frac{1}{f(metres)}$
$\Rightarrow 1.5=\frac{1}{f}$
$\Rightarrow f=\frac{1}{1.5}=0.66m$
Positive $f$ indicates a convex lens.
Therefore, the focal length of lens is $f=0.66m$ and the lens prescribed is a diverging lens.
Topics Covered In Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Light Reflection and Refraction
List of Topics Covered in Science Chapter 9 Class 10 | |
Topics | Subtopics |
Reflection of Light | |
Spherical Mirrors | Image formation by spherical mirrors, Representation using Ray Diagrams, Sign Convention, Mirror Formulas and Magnification |
Refraction of Light | Reflection through a rectangular glass slab, The Refractive Index, Refraction by spherical lenses, Image formation using Ray diagrams, Sign convention, Lens formula, and magnification. Power of a Lens |
Key Features of Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 NCERT Solutions
Class 10th science chapter 9 question answer offers great opportunities for students to achieve maximum marks. To do so, students must have a good understanding of the concepts of this chapter, which is duly sufficient by NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9. The main benefits of these NCERT Solutions are given below:
Light reflection and refraction class 10 questions and answers PDF are given by faculties who are specialists in this field and have excellent experience. The solutions they created are exact and will help you get good test marks.
The solutions to various questions in this chapter are clarified with charts and viable diagrams with regard to an easy understanding of students.
Step-by-step derivation and application of the mirror formula for concave and convex mirrors.
The solutions are designed and created keeping in mind one of the main objectives of helping students in obtaining high marks.
Detailed steps and diagrams explain light's refraction through a glass slab and the concept of lateral displacement.
Explanation of the working principles of optical instruments such as microscopes and telescopes.
The solutions are available for free download in PDF format, allowing students to access them offline at their convenience. The user-friendly format ensures easy navigation through the document.
Important Study Material Links for Class 10 Science Chapter 9
S. No | Study Material Links for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 |
1 | |
2 | |
3 |
Conclusion
Class 10 science chapter 9 question-answer solutions provide students with simple and detailed definitions and explanations of each concept covered in the chapter. Therefore, it is highly recommended that students download and refer to our comprehensive and expert-curated light class 10 NCERT solutions to get a gist of the chapter before the exam and to know how to answer the questions in the exam. Students can also refer to our plethora of other study resources related to this chapter, which are available for free on our website and mobile app.
FREE PDF Links for Other Chapter-wise NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science
You can also access chapter-wise NCERT Solutions for all other chapters of Class 10 Science from the links below and kick-start your preparation for Class 10 Board exams.
S.No. | Links to NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science All Chapters |
1. | |
2. | |
3. | |
4. | |
5. | |
6. | |
7. | |
8. | |
9. | Chapter 10 - The Human Eye and the Colourful World Solutions |
10. | |
11. | |
12. |
Related Links for Class 10 Science
S.No. | Related Links for Class 10 Science |
1. | |
2. | |
3. | |
4. | |
5. |
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Light Reflection And Refraction (2025-26)
1. Are Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Light Reflection and Refraction NCERT Solutions enough to score well in board exams?
Yes, practising all questions using Class 10 Science Chapter 9 NCERT Solutions on Vedantu is sufficient to score well, as board questions are directly based on NCERT problems.
2. How many marks does Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Light Reflection and Refraction usually carry in the board exam?
Class 10 Science Chapter 9 contributes numerical and diagram-based questions, making it a scoring chapter when prepared using Vedantu NCERT Solutions.
3. What common mistakes do students make in Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 Chapter 9?
Common mistakes include incorrect sign convention, wrong ray diagrams, and calculation errors, which can be avoided by checking step-by-step solutions on Vedantu.
4. Are ray-diagram questions from Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Light Reflection and Refraction compulsory?
Ray-diagram questions from Class 10 Science Chapter 9 are frequently asked in exams, and practising them through Vedantu NCERT Solutions improves accuracy.
5. Can Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Light Reflection and Refraction NCERT Solutions PDF be downloaded for offline study?
Yes, students can access and download the Class 10 Science Chapter 9 NCERT Solutions PDF from Vedantu for offline revision.
6. Do numericals from Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 repeat in exams?
Yes, numericals based on mirror and lens formulas from Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 are often repeated with similar values, as seen in NCERT-based practice on Vedantu.
7. Are Class 10 Science Chapter 9 NCERT Solutions helpful for avoiding calculation errors?
Yes, Vedantu NCERT Solutions show the correct step order and formula usage, which helps reduce calculation and sign-convention mistakes.
8. Is Class 10 Science Chapter 9 more scoring compared to other physics chapters?
Yes, Class 10 Science Chapter 9 is considered scoring due to direct formula-based questions when prepared thoroughly using Vedantu.
9. Can Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 solutions be used for last-minute revision offline?
Yes, the PDF versions of Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 solutions from Vedantu are suitable for quick offline revision before exams.
10. How do Vedantu NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 improve answer accuracy?
They improve accuracy by clearly explaining diagram steps, formula substitution, and final presentation as expected in CBSE exams.














 Watch Video
Watch Video

















