




Key Units and Real-Life Examples Explained for Students
Measurement is the numeric value with certain units of measurement. We can measure length, weight, speed , temperature and capacity of a given object with a certain unit and numeric value. We can use standard as well as common units to measure something. E.g To measure time we can use hours, minutes and seconds.
How to measure Length, Time, Weight, Height and Temperature?
Measurement of Length
Length is measured the distance between two points or place, it can be measured in metre (m), centimetre and kilometre.
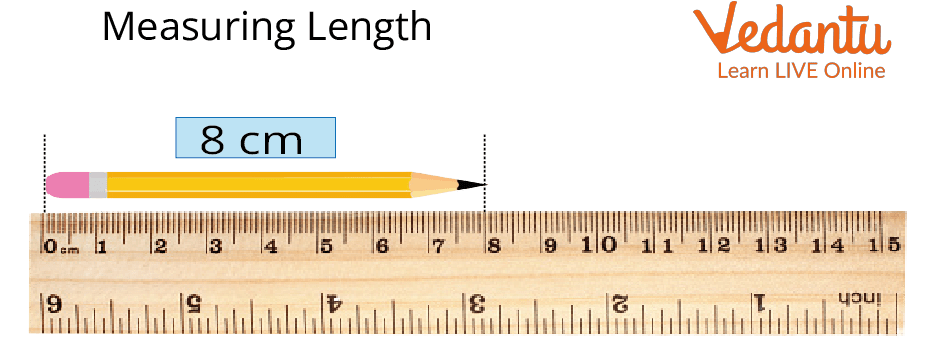
Measuring Length
The metre(m) is equally divided into 100 equal parts, each part known as centimetre or in short (cm).
For Measuring distance between place or city we use kilometre, the kilometre is equally divided into 1000 parts each part as metre (m).
So we can say,
The Relationship Between Different Units of Length.
Measurement of Weight
To measure the weight or mass of the different types of object we can use kilogram in short (kg), gram (gm) and milligram (mg), depending upon the size of the object for small size object we can use milligram or gram and for large size object we will use kilogram (kg). The SI unit of weight is kilogram (kg).
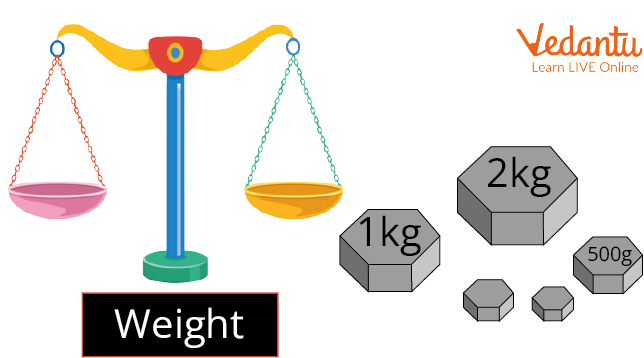
Measuring weight
How To Measure Weight
There are different types of weight scales we can use to measure the weight of an object.
By using Balance equality measures.
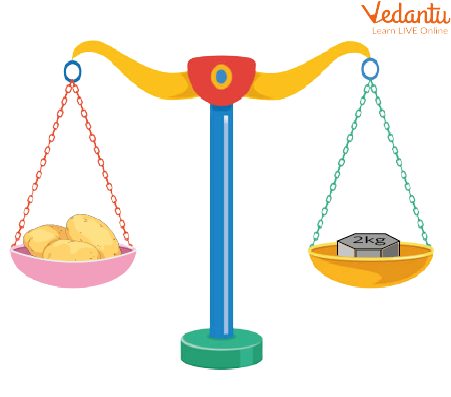
Weighting Balance
Here we have put the potato on one side of the balance and 2 kg of metal on the other side of the balance. If both sides are balanced, then we can say the potato weight is 2 kg.
By using an electronic weighing machine.

Weighting Machine
In this machine we keep the object on the machine plane surface and the weight object will show on a small screen. Here we can measure the weight of objects in different units.
Different Types of Unit to Measure The Weight of an Object And Their Relation With Standard Units.
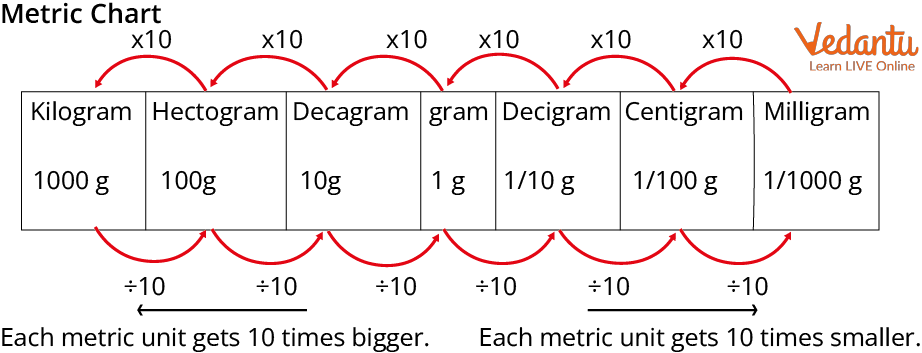
Units of weight
Measurement of Capacity
To measure the capacity or volume of any container can contain we use litre and millilitre. In short we use l for litres and ml for millilitres.
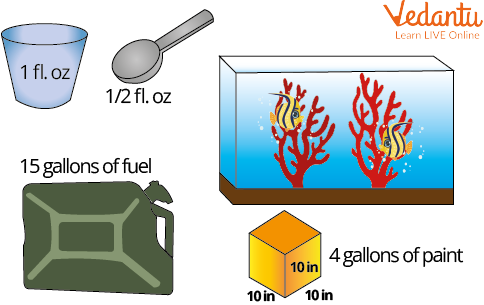
Measurement of capacity
The capacity of an object can be measured by two methods:
1. Customary Units
2. Metric units.
1. Customary units
There are five customary units to measure the capacity or volume of any object.
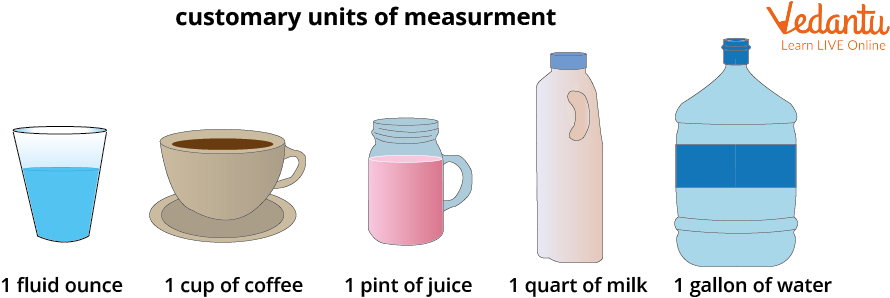
Customary units
Relation between different unitsunit of customary units
1 cup = 8 fluid ounces
1 point = 16 fluid ounces
1 quart = 32 fluid ounces
1 gallon = 128 fluid ounces
2. Metric units
To measure the capacity of any object in a metric unit we use litre, millilitres and kiloliter.
Relation between different units of Metric units
Measurement of Time
Time is measured in different units like hours, minutes, and seconds.
(Image will be uploaded soon)
Time can be measured in various ways like in seconds and minutes which are relatively small units whereas years and decades are relatively large units of time.
(Image will be uploaded soon)
Measurement of Area
The amount covered by the surface of any two-dimensional shape is known as the area. It is also known as the surface covered by the border. The area is measured in square units. It is measured in the square of length units.
(Image will be uploaded soon)
Let’s understand the measurement of area.
(Image will be uploaded soon)
Here we are measuring the area using squares. So the first shape contains 20 squares, therefore, the area is equal to the area of 20 squares similarly the second shape contains 15 squares so the area is equal to the area of 15 squares.
Formulas for Area Measurement
(Image will be uploaded soon)
Solved Examples
Example 1. Convert 100 kilometres in metres.
Sol: As we know that 1 km = 1000 m
So 100 kilometre = 1 km $\times$ 100
Putting the value of 1km = 1000 m
= 1000 m $\times$ 100
= 100000m
Hence, 100 km = 100000 m.
Examples 2. A container with a capacity to hold the liquid is 500 millilitre(ml), convert container capacity in litres(l).
Sol: Here, we have given the capacity of the container in millilitres (ml) and we have to convert it into litres.
Let’s assume container X capacity = 500 millilitres (ml)
Now, As we know that 1 millilitres(ml) = 1/1000 litres (l)
So container X capacity = 500 $\times \dfrac{1}{1000}$
Then container X capacity = 0.5 litre(l).
Examples 3. Express 4 kilometres into metres.
Sol: We know that 1 kilometre = 1000 metres
(Image will be uploaded soon)
So, 4 kilometres = 4 x 1000 metres.
Therefore 4 kilometres = 4000 metres.
Example 4: Express 1 week into hours.
Sol: We know that 1 week = 7 days
1 day = 24 hours
7 days = 7 x 24 hours = 168 hours.
So there are 168 hours in 1 week.
Example 5. Can A contains 2.75 litres of juice and Can B contains 3 ℓ 500 millilitres of juice. If the juice from both cans is mixed then what will be the total volume of juice? Give your answer in ml.
Ans: We know that 1 litre = 1000 millilitres
(Image will be uploaded soon)
Can A contains 2.75 litres = 2750 millilitres
Can B contains 3 ℓ 500 millilitres = 3500 millilitres
(Image will be uploaded soon)
The juice of both cans is mixed then the total quantity of juice = 2750 millilitres + 3500 millilitres
The total quantity of juice = 6250 millilitres
Summary
Measurements are an important part of the skill for kids. They are important topics to learn as kids will remember and carry them with them for higher classes. Allowing kids to measure the object dimension accurately and precisely, measuring the different shapes of the object is fun, engaging, and fundamental to their knowledge of the topics and will help them develop skills not only in this topic, but also in related ones.
Learning By Doing
Find the ? in the figure.
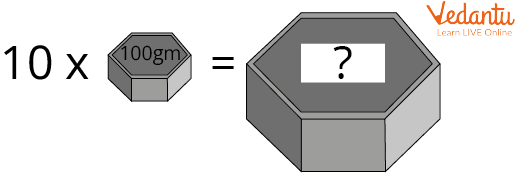
Multiplication of weight























