




What Are the Key Geometry Shapes Every Year 2 Child Should Know?
We can see different shapes in everything around us. Have you ever seen the model of the earth i.e. globe? It is round in shape. Have you ever thought about the shape of an egg? It is oval. Do you know the shape of a pizza? It is circular. But, what is the shape of the slices that we cut out from a pizza? It is triangular. What about a chessboard? Do you know its shape? They are square-shaped. Similarly, there are other different shapes that we can observe in our everyday life.
Read the article below to know what exactly the shapes are.
What are Shapes in Geometry?
Shapes, also known as geometric shapes or figures, are made up of fixed lines and curves. The name of different shapes describes the number of sides that exist in the given shape. For example, a triangle is a shape with three sides whereas a rectangle is a shape with four sides and many more.
In Geometry, shapes are classified as open shapes, closed shapes, two-dimensional shapes, and three-dimensional shapes.
What are Open Shapes?
Open shapes are shapes whose line segments or curves do not meet. Open shapes do not start and end at one point. In other words, they start at one point and end at another point.
Here are some examples of open shapes.
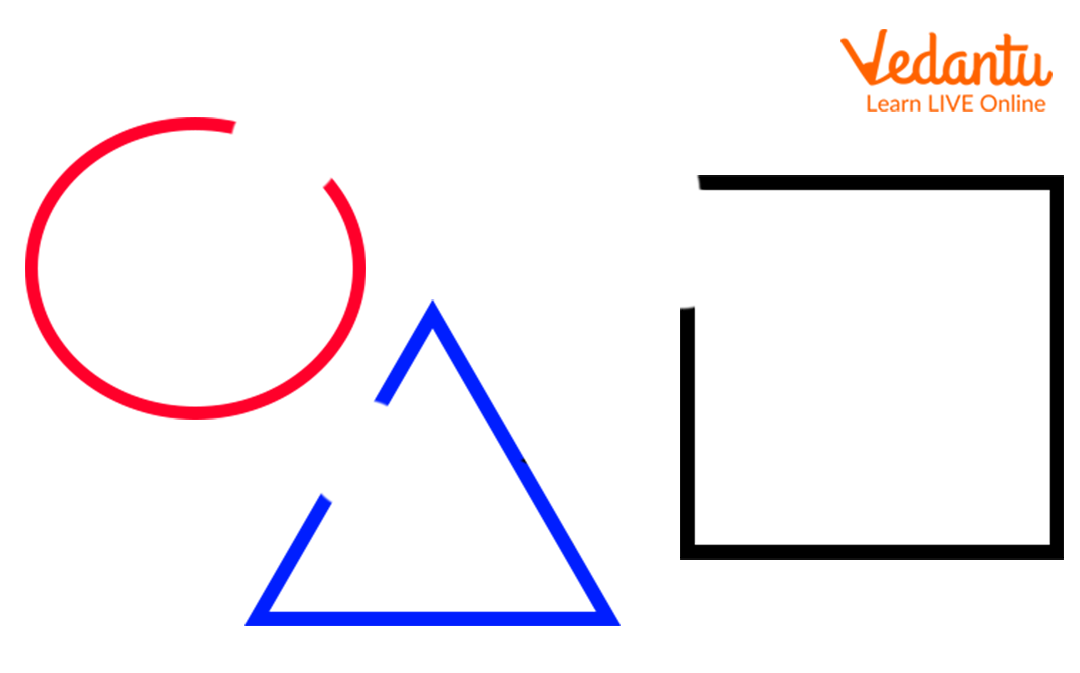
Open shapes
What are Closed Shapes?
The closed shapes are shapes whose line segments or curves are connected or meet. The closed shapes start and end at the same point. Here are some examples of closed shapes.
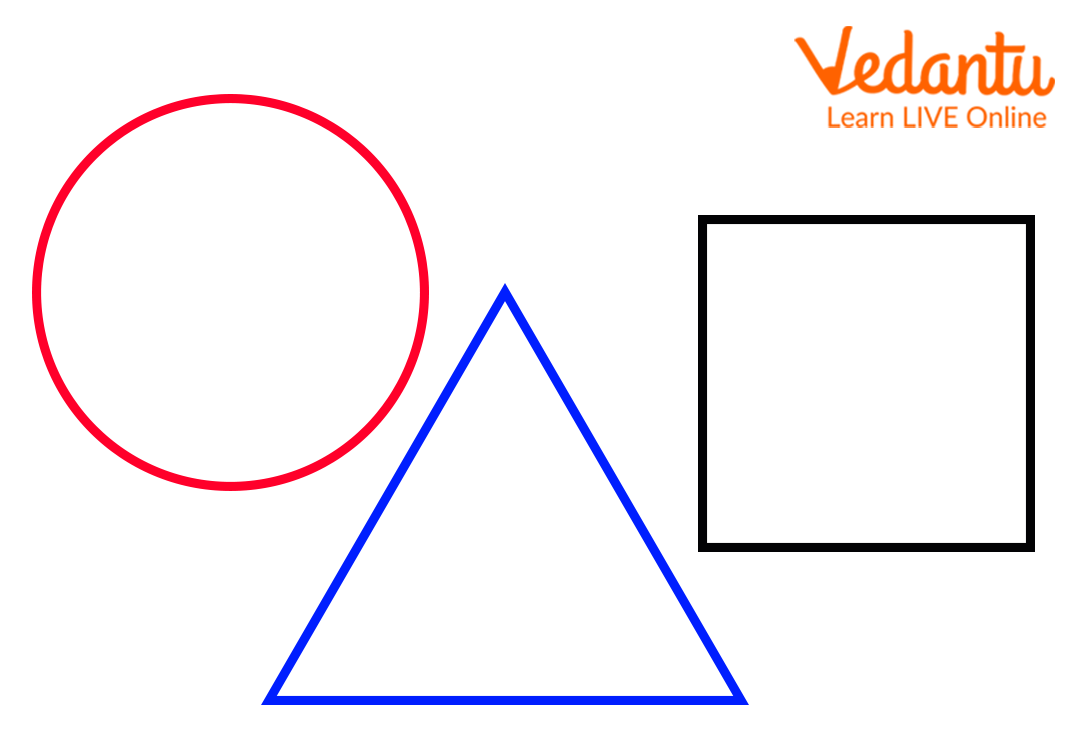
Closed shapes
Real Life Example of Open and Closed Shape
Following are the real-life examples of open and closed shapes.
An Open Shape Real-life Example
A skipping rope is an open shape. You can jump on it.

Two kids skipping ropes
A Closed Shape Real-life Example
A bangle is a closed shape. You can easily wear it on your wrist.

A hand wearing a bangle
What Are 2-D Shapes?
2-D shapes, also known as two-dimensional shapes, are flat and have only two dimensions i.e. length and width. 2-D shapes do not have depth. 2-D shapes include squares, rectangles, circles, etc.
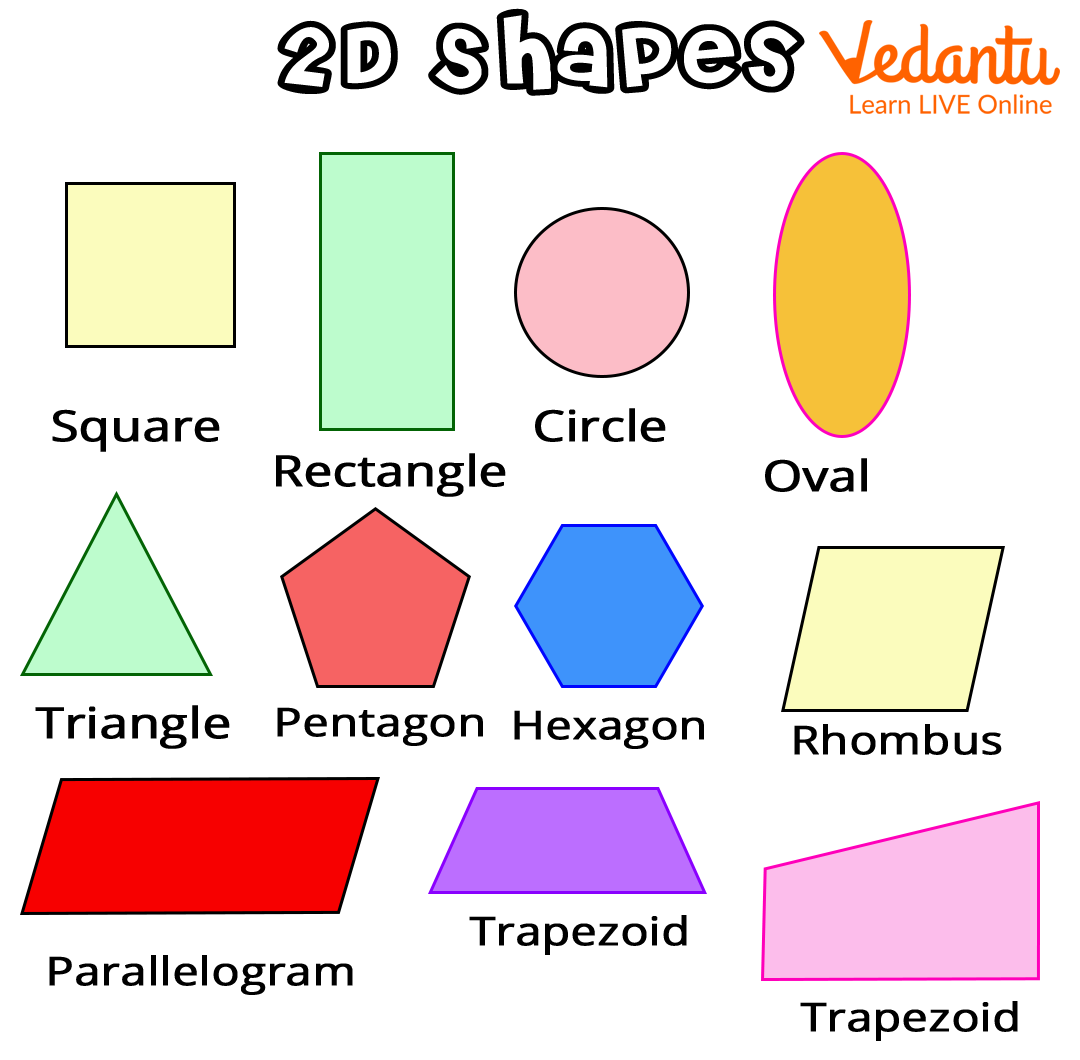
2-D shapes
Names of 2-D Shapes
The different names of 2-D shapes children of Year 2 should know include the following:
What are 3-D Shapes?
3-D shapes, also known as three-dimensional shapes, are solid shapes with three dimensions such as length, width, and depth. Boxes, balls, and packets are of 3-D shapes. Unlike 2- D shapes, 3-D shapes are not flat because these shapes have depth.
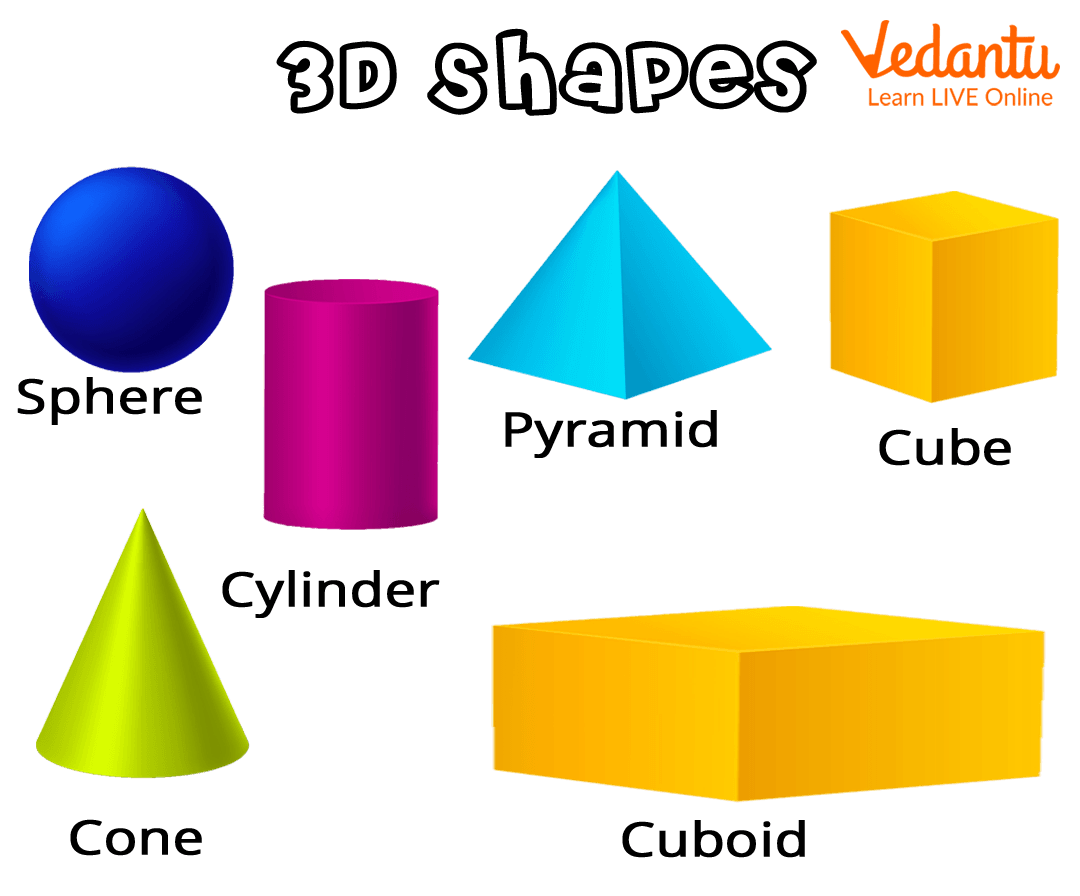
3-D shapes
Names of 3-D Shapes
The different names of 3-D shapes children of Year 2 should know include the following:
Properties of 3-D Shapes
The three important properties of 3-D shapes are faces, edges, and vertices or corners.
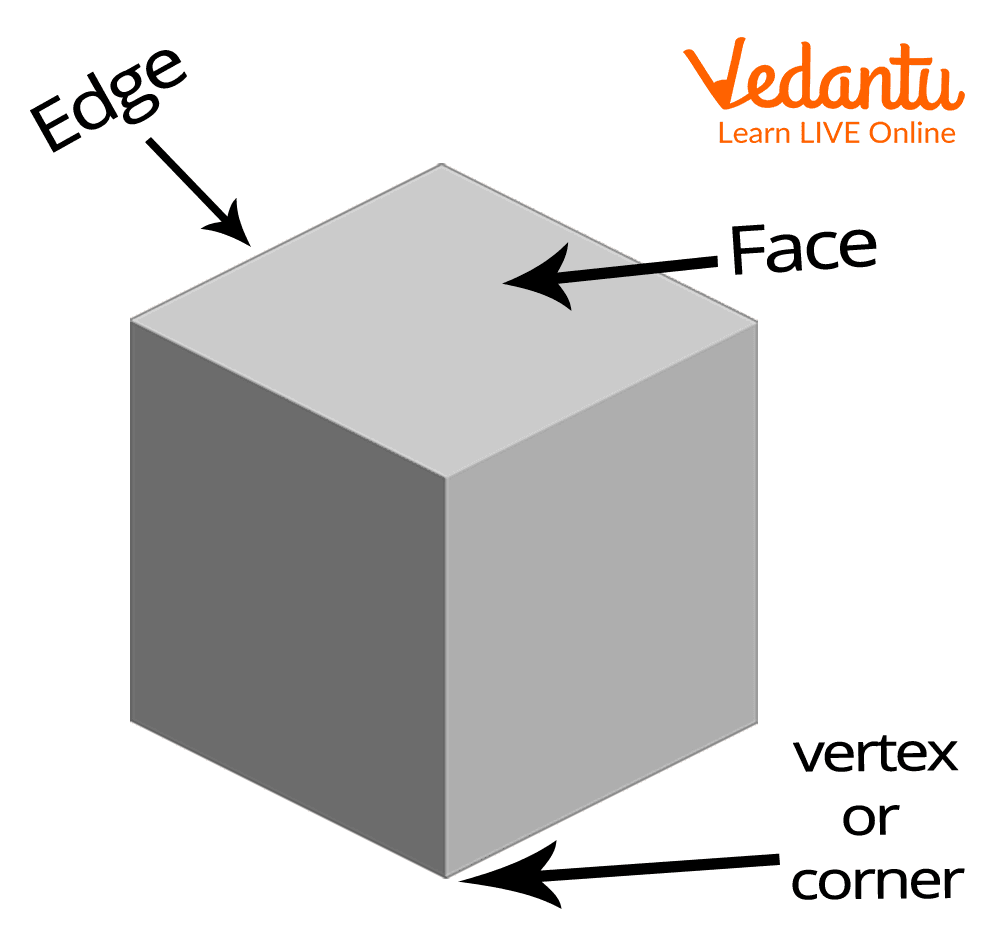
A cube - 3-D shape
Let’s understand the properties of 3-D shapes in brief.
Face: A face is defined as the flat surface of 3-D shapes. For example, the geometric shape cube has 6 faces.
Edge: Edges are lines where two faces of 3-D shape meet. For example, the geometric shape cube has 12 edges.
Vertex Or Corners: A vertex is a corner where edges of 3-D shapes meet. For example, the geometric shape cube has 8 vertices. Remember, the plural form of vertex is vertices.
Conclusion
In short, geometric shapes are enclosed figures made by joining two or more points, lines, and curves. For example, a geometric figure formed by a three-line segment is known as a triangle. Similarly, a geometric shape, circle is formed using a curve. Remember, shapes are classified as 2-D shapes and 3-D shapes based on the number of dimensions they have. 2-D shapes have two dimensions, whereas 3-D shapes have three dimensions.
FAQs on Geometry Shapes for Year 2 Kids: Easy Guide to 2D & 3D Shapes
1. What are 2D and 3D shapes for a Class 2 student?
2D shapes are flat shapes that you can draw on paper. They only have two dimensions: length and width. Examples include circles and squares. 3D shapes are solid objects that you can hold. They have three dimensions: length, width, and height. Examples include a ball (sphere) or a box (cube).
2. What is the main difference between 2D and 3D shapes?
The main difference is that 2D shapes are flat, like a picture, and have only length and width. You cannot hold them. 3D shapes are solid objects that take up space, have length, width, and height (or depth), and you can pick them up and hold them.
3. Can you give some real-world examples of 2D and 3D shapes?
Yes! You can find shapes all around you.
- 2D Shape Examples: A coin (circle), a page of a book (rectangle), a slice of pizza (triangle), and a checkerboard square (square).
- 3D Shape Examples: A cricket ball (sphere), a dice (cube), a party hat (cone), and a can of juice (cylinder).
4. What are the properties of basic 2D shapes like squares and circles?
Basic 2D shapes have simple properties that you can see and count.
- A square has 4 equal straight sides and 4 corners.
- A circle is one continuous curved line and has no sides or corners.
- A triangle has 3 straight sides and 3 corners.
- A rectangle has 4 straight sides (opposites are equal) and 4 corners.
5. Is a circle a 2D or a 3D shape?
A circle is a 2D shape. It is completely flat and has only length and width. The 3D version of a circle is a sphere, like a ball, which is solid and has depth.
6. Why is learning about shapes important for young students?
Learning about 2D and 3D shapes is important because it helps students develop problem-solving skills and spatial awareness. It allows them to understand the world around them by identifying and categorizing objects, which is a fundamental skill in maths and science.
7. How are the faces of a 3D shape like a cube related to 2D shapes?
3D shapes are often made up of 2D shapes. For example, a cube is a 3D shape whose flat surfaces, called faces, are all squares. A cube has six square faces. This shows how flat 2D shapes come together to build solid 3D objects.
8. Why is a ball considered a sphere (3D) and not just a circle (2D)?
A ball is a sphere because you can hold it and it takes up space in all directions; it has depth. A circle is the flat, 2D outline you would draw if you traced the ball on paper. The key difference is that a sphere is solid and a circle is flat.
9. What is the difference between corners (vertices) and edges on a 3D shape?
On a 3D shape like a cube, there is a clear difference:
- Edges are the straight lines where two flat faces meet. You can trace them with your finger. A cube has 12 edges.
- Corners (or vertices) are the sharp points where three or more edges meet. A cube has 8 corners.























