




Why Is Division Important in Everyday Life?
In general, kids begin to learn division in-depth in the third grade; however, in the first and second years, kids will be introduced to concepts that lead to long-form division and simple division using methods and games. Kids are expected to work with numbers far greater than those they can physically count as mathematical concepts become more complex. Understanding division will be easier when learned with real-life examples. Let's explore division for year 2 kids in this article.
What is the Definition of Division?
The division is a process of repeated subtraction. It is the inverse action of multiplication. It is considered the formation of equal groups. When we divide numbers, we split them down into smaller numbers so that the multiplication of those smaller numbers equals the larger number taken.
Daily Life Examples
1. Nirmal has 12 Sweets and he wants to share them equally between his three friends. Let's start by creating three groups then add one sweet at a time into each group until all twelve sweets have been shared equally. Let's count how many sweets are in each group to get an answer: Twelve sweets shared equally between friends is 4.
The division is denoted by a mathematical symbol that consists of a small horizontal line with a dot each above and below the line. There are two basic division symbols that represent the division of two numbers.

Symbols for Division
Other words for division are ‘share between’ and ‘divided’. Our solved example can be written as: 12 divided by 3 equals 4.
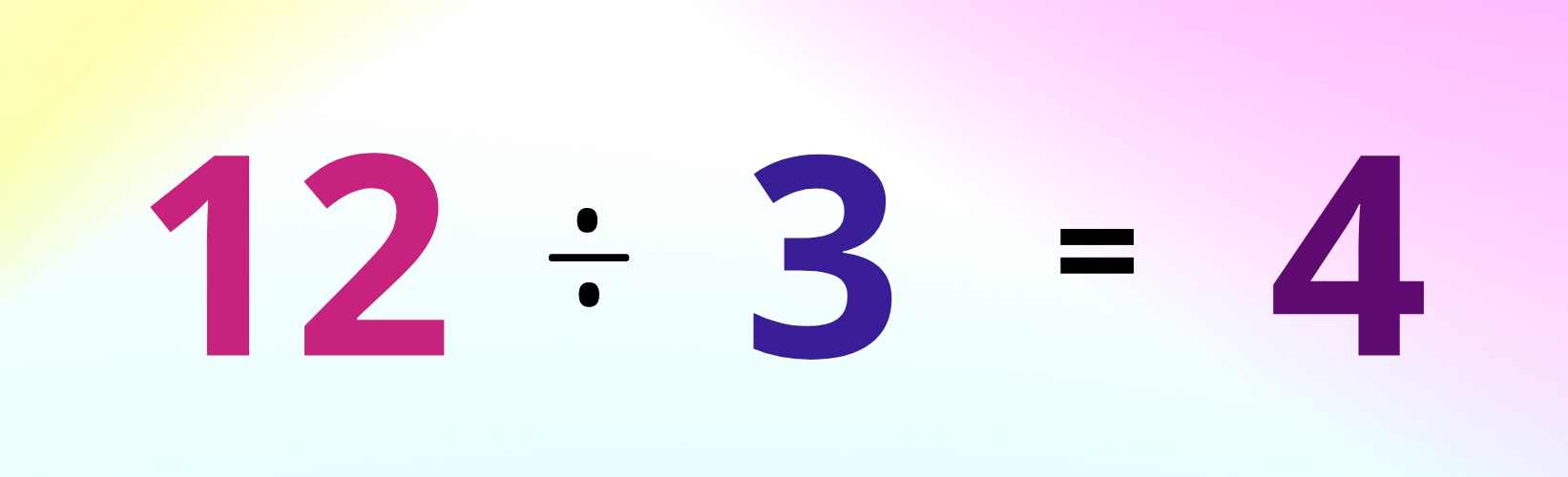
Image Shows the Division 12/3
2. Mahima has 16 apples and wants to divide them equally between her 4 friends. This can be written as 16 divided by 4.

Image Shows the Division 16/4
To find the answer we need to share 16 equally between 4 groups. Let's count how many apples are in each group to get our answer.
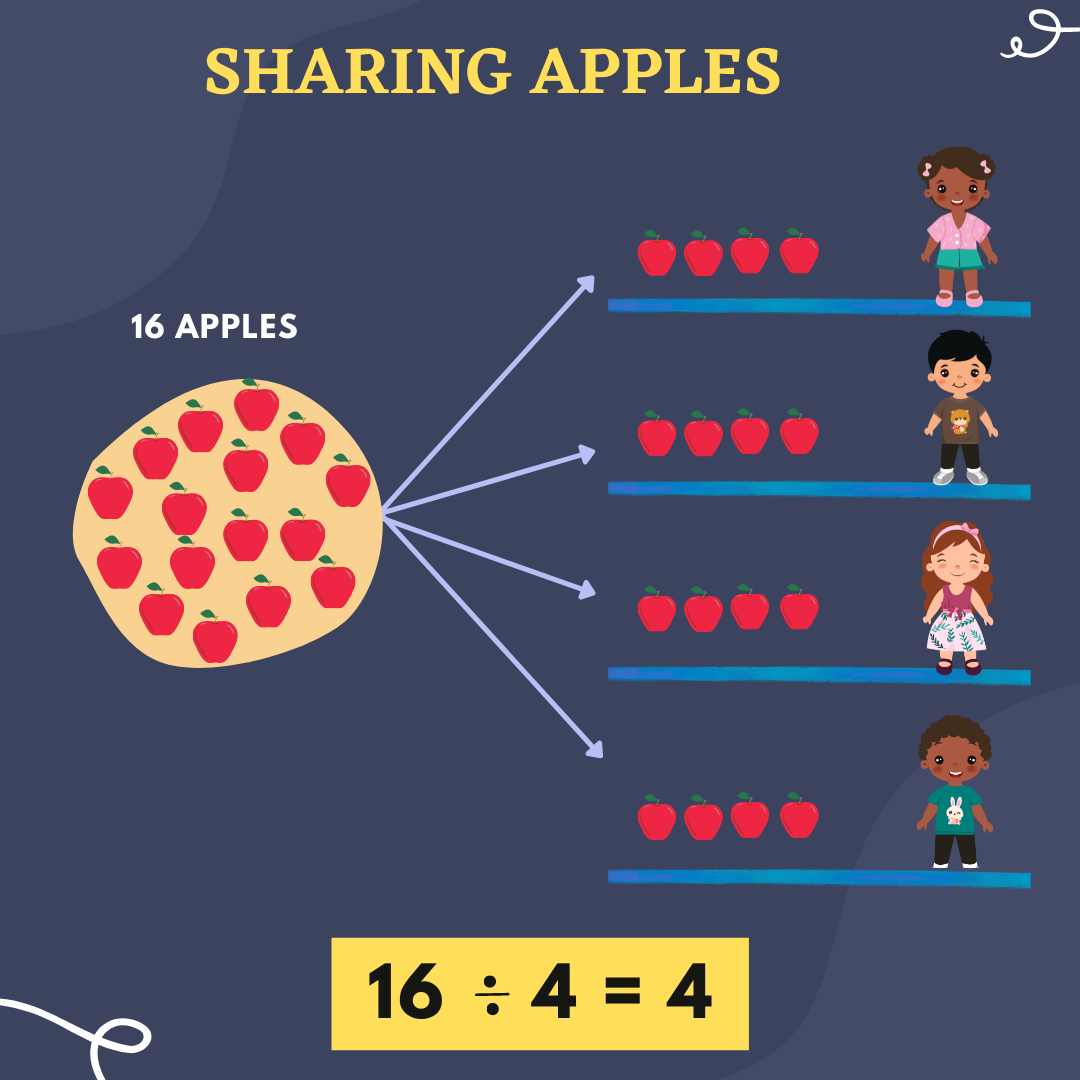
The Image Shows 16 Apples Shared Equally Among 4 People With the Division of 16/4
So, 16 apples shared equally between friends is 4.
3. We can divide by sharing objects into equal groups. So if we make the calculation, for 10 divided by 2, we can work out the answer by sharing ten objects equally into two groups.
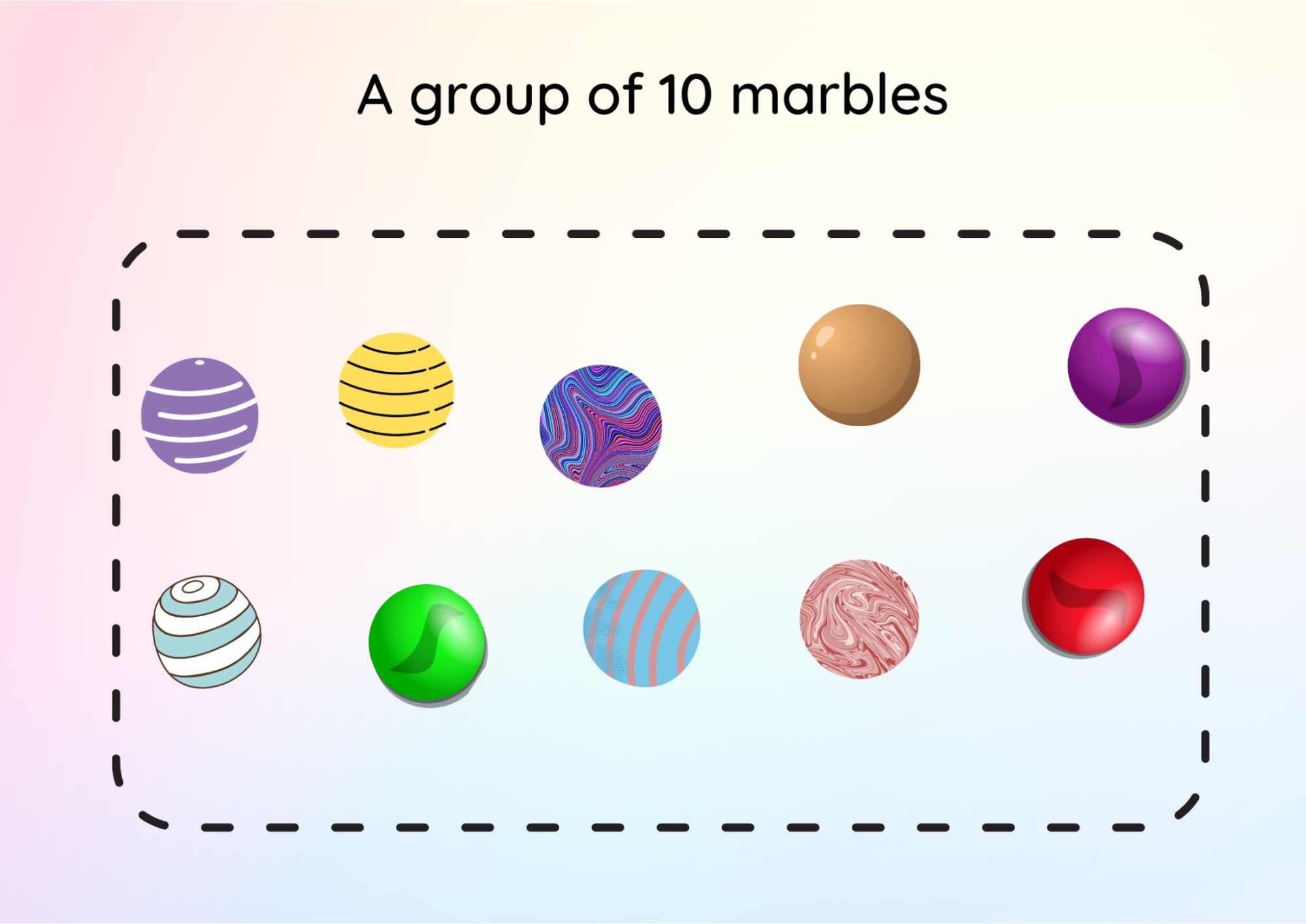
The Image Shows a Group of 10 Objects
There are five marbles in each of the two groups.
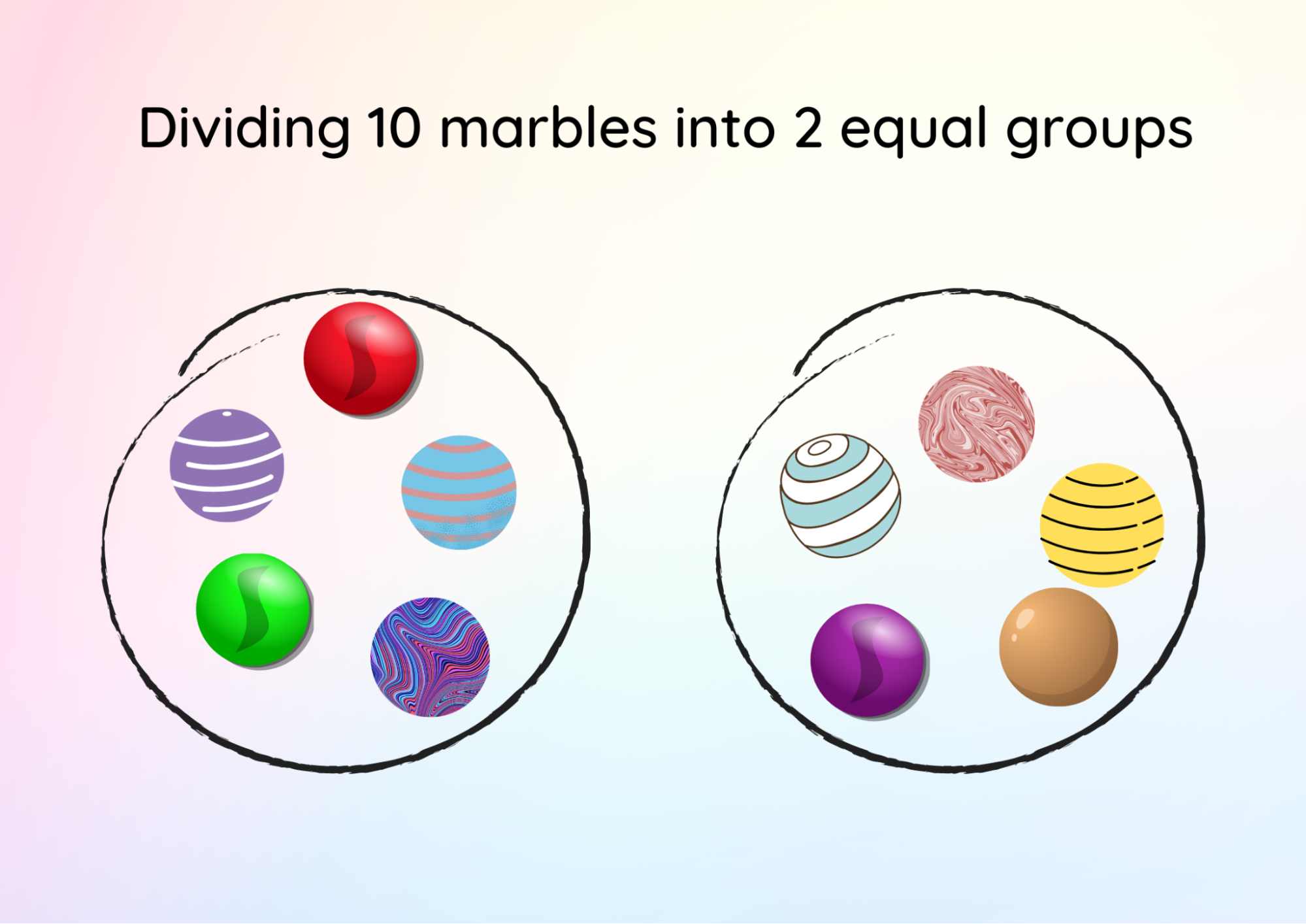
Image Shows 10 Objects Which are Equally Divided Into 2 Groups Each of 5 Objects
So, ten divided by two equals five.
Division by Grouping
Division by grouping looks at how many equal groups there are in a number. So if we take the calculation same as story example 3,
10 divided by 2.
We can look at this as how many groups of 2 there are in 10.
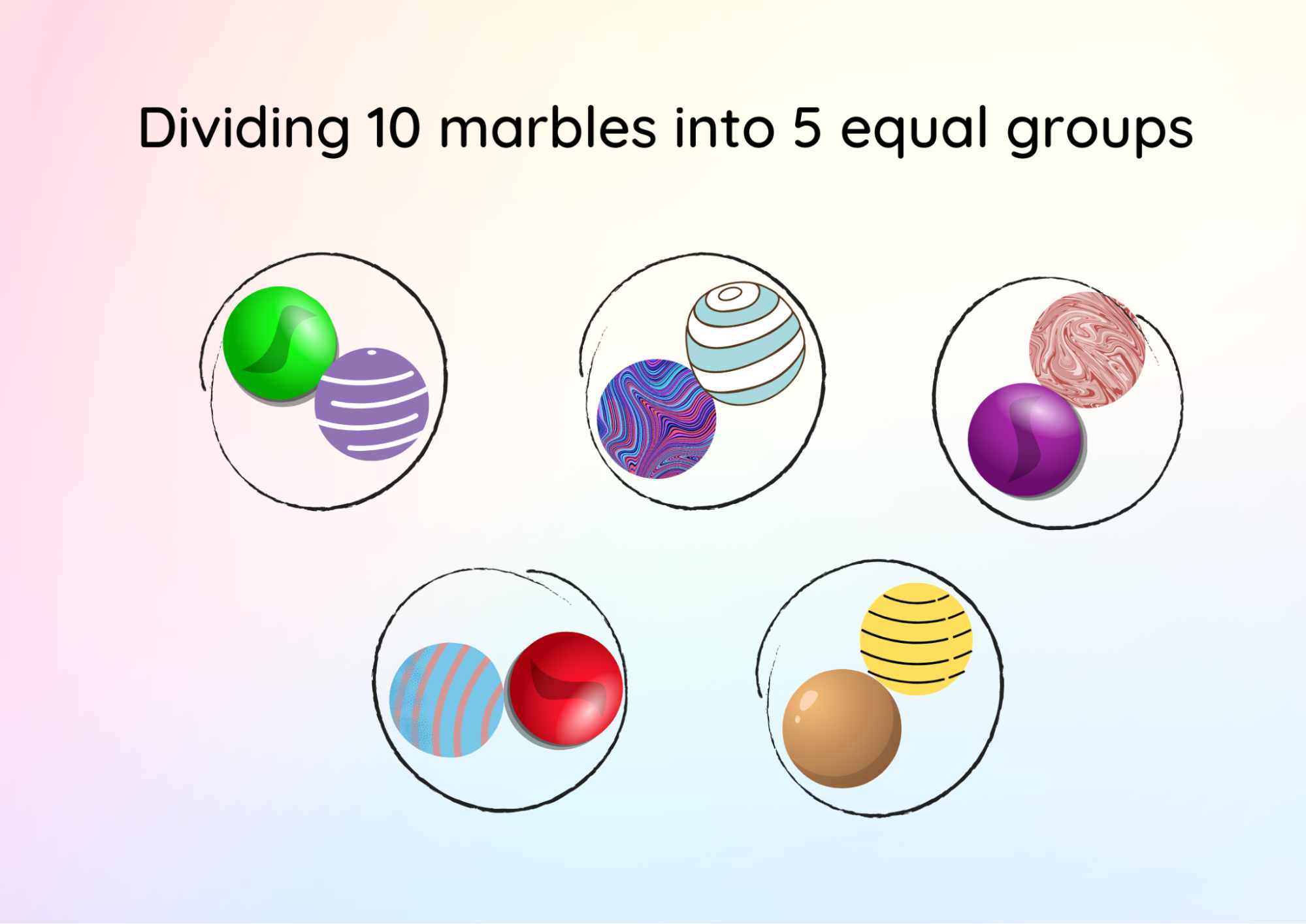
Image Shows 10 Objects Which are Equally Divided Into 5 Groups Each of 2 Objects
Equal groups of 2 in 10 are 5 (Refer to the image above). So 10 divided by 2 equals 5.
Important Terms in Division
The number to be divided in a division sum is referred to as the dividend.
The divisor is the number by which we divide.
The result of division is known as the quotient.

Image Shows the Terms of a Division with an Example
Multiplication and Division
The below picture shows 12 candies arranged in groups of 4.
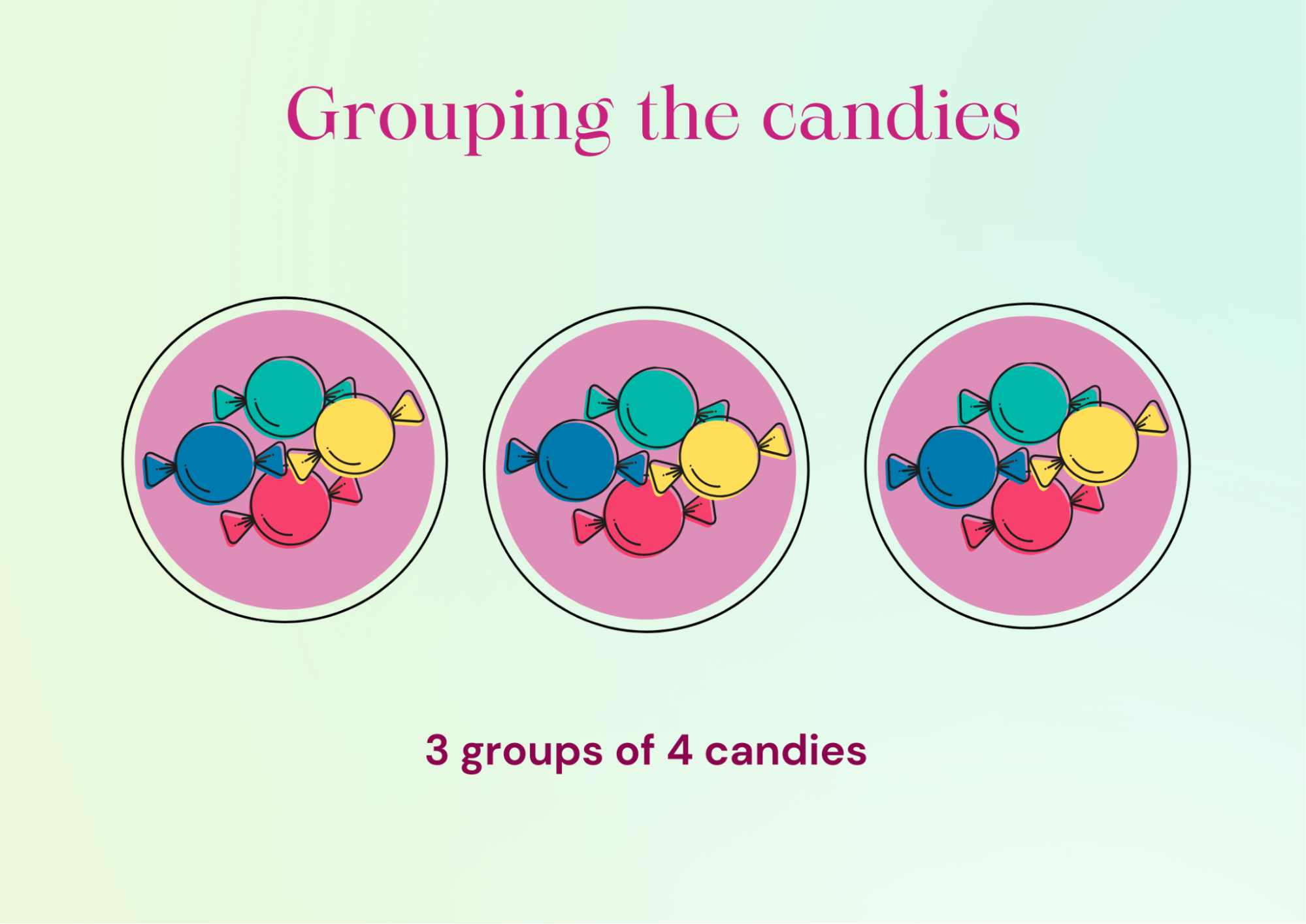
Image Shows Three Groups Each of Four Candies
If we observe, it shows a multiplication fact: 3 x 4 = 12 and also a division fact: 12 ÷ 4 = 3. 12 candies can be arranged in groups of 3 as well. It is shown below.
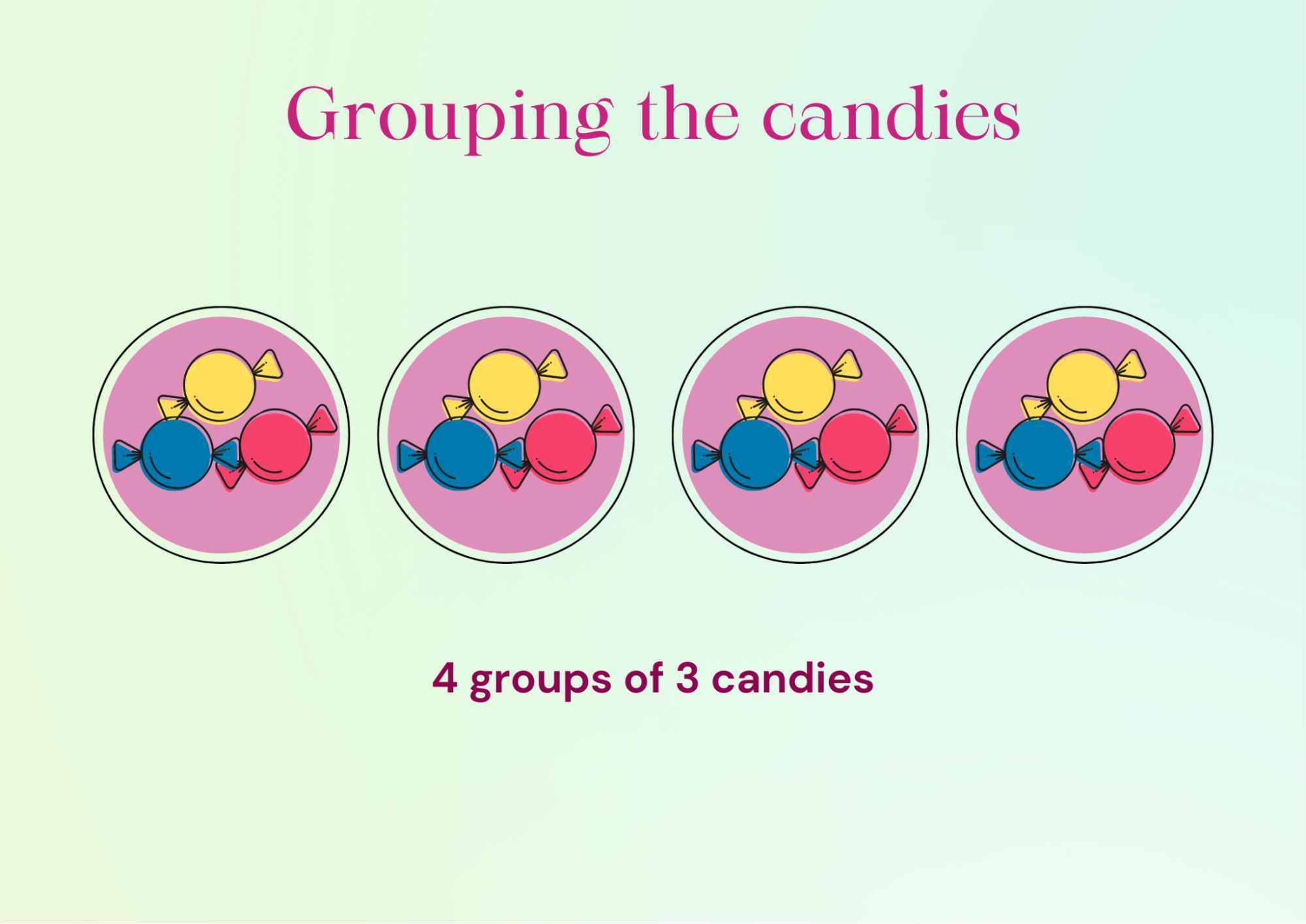
The Image Shows Four Groups Each of Three Candies
Here, we have a multiplication fact: 4 x 3 = 12 and a division fact: 12 ÷ 3 = 4.
Thus, we can observe that,
Multiplication of 3 x 4 = 12 gives us the division fact 12 ÷ 4 = 3.
Multiplication of 4 x 3 = 12 gives us the division fact 12 ÷ 3 = 4.
Helping Kids with Division at Home
Toys, some grapes, paper clips and buttons are all terrific practice items. Ask your child to count the number of objects, to begin with. Can they distribute the items equally between the two of you? Assist them in sharing objects between the two groups one at a time. When all of the objects have been divided, ask your child how many of each group there are. If you have the same number, explain that your child divided the objects equally among two groups, which is equal to dividing by two.
Conclusion
The division is the splitting of a large group into smaller groups so that each group has an equal number of things. In mathematics, it is an operation used for equal grouping and equal sharing. In this article, we have discussed the division process in maths in detail with some examples.
FAQs on Master Division for Grade 2: Real-Life Examples and Solutions
1. What is a real life example of division?
A real life example of division is sharing a group of objects equally among friends. For instance, if you have 12 candies and want to share them with 3 friends, you use division to find out how many each person gets: $12 \div 3 = 4$. So, each friend receives 4 candies. Division helps us split things evenly in everyday situations.
2. What is an example of division for Grade 2?
An example suitable for Grade 2 division is: There are 10 apples, and 2 baskets. How many apples should go into each basket to make it fair? We divide $10 \div 2 = 5$. This means each basket has 5 apples.
- 10 apples divided into 2 sets = 5 apples per set
3. What real life scenarios use division?
Division is used in everyday scenarios such as:
- Splitting a pizza among family members
- Equally grouping students into teams in a classroom
- Measuring ingredients for cooking when using recipes for different numbers of people
4. How is division used in everyday life?
In everyday life, division is used whenever we need to share or distribute items equally. For example:
- When organizing books on shelves so each shelf gets the same number of books
- Sharing snacks among friends to make sure everyone gets an equal amount
5. How can Grade 2 students practice division with real objects at home?
Grade 2 students can practice division using real objects such as:
- Grouping toys into sets of equal numbers
- Distributing cookies or crackers among siblings
- Separating crayons into equal piles for coloring activities
6. What are simple division word problems for Grade 2 students?
Some simple division word problems for Grade 2 include:
- "If 18 pencils are shared equally among 6 students, how many pencils does each student get?" Solution: $18 \div 6 = 3$ pencils each.
- "A teacher arranges 16 chairs into 4 rows. How many chairs are there in each row?" Solution: $16 \div 4 = 4$ chairs each.
7. Why is learning division important for Grade 2 students?
Learning division in Grade 2 builds a foundation for future math skills and problem-solving. It helps students:
- Develop logical thinking
- Understand equal sharing and grouping
- Prepare for more advanced math topics, like fractions and multiplication
8. What strategies can help Grade 2 students understand division better?
To help Grade 2 students understand division, use strategies such as:
- Visual aids like drawing groups or using counters
- Relating division to multiplication as the inverse operation
- Hands-on activities and real-life examples, like sharing objects
9. How does division relate to multiplication for Grade 2 students?
Division and multiplication are related as inverse operations. For example, if $3 \times 4 = 12$, then $12 \div 4 = 3$. Understanding this relationship helps Grade 2 students solve problems more efficiently and improves their overall mathematical reasoning, as encouraged in Vedantu's sessions.
10. What online resources does Vedantu offer for learning division in Grade 2?
Vedantu offers a range of online resources for learning division tailored to Grade 2 students, including:
- Interactive live classes led by expert educators
- Practice worksheets with real-life division examples
- Animated video lessons explaining division concepts
- Engaging math games and quizzes























