




How to Read and Understand Data in Everyday Life
Suppose you are on an aquarium visit, the class saw 10 dolphins, 5 seals, 12 crabs, 15 sharks, and 8 turtles. And according to the data collected from the reviews, sharks are seen the most, and seals are seen the least. But how do you find that out? Data is a collective term for information gathered through observations, measurements, research, or analysis. They could include names, dates, figures, facts, or even descriptions of objects. Data is presented in graphs, charts, or tables. Data scientists are people who collect data and analyze it to understand our world better.
Data is classified into qualitative and quantitative. In other words, displaying and interpreting data is known as data collection.
Types of Data Collection
We represent and interpret data in two forms:
Qualitative Data
Quantitative Data
Quantitative Data
The term 'Quantity' refers to a certain number. Quantitative data collection methods express the data in figures or numbers using traditional or online methods. Once these data are collected, statistical methods and mathematical tools can arrive at the results. Some of the quantitative data collection methods include probability sampling, surveys, and conducting interviews.

Quantitative Data
Qualitative Data
Qualitative data collection methods do not include any mathematical calculations to collect data. It is mainly used for analyzing the quality or understanding the reason behind something. Some of the common methods used for qualitative data collection are discussed below.
Interview Method: As the name suggests, the verbal conversation makes data collection by interviewing people in person or in the telephone or using any computer-aided model.
Questionnaire Method of Collecting Data: The questionnaire method involves surveys with questions targeting quantitative research. These survey questions are easily made using online survey question creation software.
Observation Method: As the word 'observation' suggests, in this method, data is collected directly by observing. This can be achieved by counting the number of people or events that occur in a particular time frame.
The main skill needed here is observing and correctly arriving at the numbers.
Document Review Method: The document review method is a data collection method that is used to collect data from existing documents that have data about the past.
Qualitative Data
Data Collection and Representation in Tables
Let's learn more about data collection and representation in tables:
You must have viewed news channel reports on weather forecasts. They provide measurements, rainfall forecasts, minimum and maximum temperatures, and more. Data collection and representation in tables shown below:
Consider that you are asked to create a table that lists the weight and height of each student in your class. It would look something like this:
The Difference Between Quantitative and Qualitative data
The primary distinctions between quantitative and qualitative data are in what they reveal, how they are obtained, and how they are examined.
Following are the difference:
Solved Examples
Q 1. Which data collection method would you use for the following scenario?
(a) To know the preferred brand of clothing of a certain age group.
Ans: To know the preferred brand of clothing of a certain age group, a primary data collection method, such as a questionnaire survey can be used since we need to know the preference of every individual member of the group.
(b) To know the average rainfall recorded in a year.
Ans: To know the average rainfall recorded in a year, we use the secondary data collection method by looking through the reports that show the statistics of rainfall recorded in previous years.
Q 2. Find the type of data collection method (Qualitative or Quantitative) that could be used for the following.
(i) How well do you recommend an institute to another person to take up a course?
Ans: The first part of the question uses the qualitative data collection method since we will have to analyze the institute's reach, the amount of fee to be paid, and the quality of education received. These factors can only be determined by any of the survey methods.
(ii) To know how many people have attended a training course.
Ans: The second part of the question uses a quantitative data collection method since we will have to get the count by any personal contact method to actually know how many people have attended the training course.
Practice Questions
Q1. Choose the way to represent, and interpret data grade 1 worksheets.
(i) Choose the number of fruit which is most in number
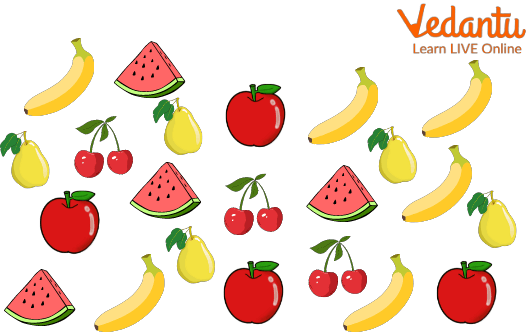
Practice Question
Ans: Banana
(ii) Name the fruit which is the least in number.
Ans. Cherries
Summary
Data represents information collected in the form of numbers and text. Data collection is done after an experiment or an observation. Data collection is useful in planning and estimation, and it also saves a lot of time and resources. Data collection is either qualitative or quantitative. Data collection methods are used in businesses and sales organizations to analyze the outcome of a problem, arrive at a solution, draw conclusions about the performance of a business, and so on. In this article, we have added some solved example which is statement based, this will give more clarity on the topic.
FAQs on Displaying and Interpreting Data for Grade 1 Students
1. What does it mean to display and interpret data in Grade 1 maths?
To display and interpret data means to show collected information in an organised way, such as a table or chart, and to understand what the data shows. For example, students may count how many students like apples, oranges or bananas, then make a picture or table to compare which fruit is liked most or least.
2. Which methods are commonly used for data collection in Grade 1 according to the CBSE 2025–26 maths syllabus?
Common data collection methods for Grade 1 include:
- Observation: Noting or counting items, people, or actions (e.g., number of red cars).
- Interview: Asking classmates questions directly.
- Questionnaire: Using simple survey questions for classmates or family.
- Document Review: Looking at records, such as classroom charts or attendance lists.
3. How can students represent data in a table for Grade 1 maths?
Students can represent data in a table by making rows and columns to list items and their counts. For example, if they count the favourite fruits of classmates, the table will have fruit names in one column and the number of students in the next column. This helps to compare and interpret the data easily.
4. What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative data in simple words for Grade 1?
Qualitative data describes qualities or types, like colours or names (e.g., blue, tall, apple), while quantitative data tells how much or how many, using numbers (e.g., 5 apples, 3 boys).
5. Why is learning to interpret data important in real life for young students?
Learning to interpret data helps students make decisions, solve problems, and understand the world. For example, knowing which toy is most popular can help choose what to bring to school or understanding rain data can help plan outdoor activities.
6. What are some examples of displaying and interpreting data that students can use in class activities?
Examples include:
- Counting and recording the number of each fruit in a fruit basket and making a chart.
- Surveying classmates about their favourite colour and making a bar graph.
- Observing and charting the types of weather over a week.
7. How can Grade 1 students avoid mistakes when collecting and displaying data?
To avoid mistakes, students should:
- Count each item carefully and only once.
- Write numbers clearly in tables or charts.
- Check their data with classmates or teacher.
8. What skills do students develop by working with data in Grade 1 mathematics?
Students develop skills such as observation, counting, recording information, comparing numbers, and reasoning. These skills build a strong foundation for maths and logical thinking.
9. In what ways can data be shown visually to help Grade 1 students understand better?
Data can be shown using tables, pictographs (pictures to represent numbers), and bar graphs with simple bars. Visual representation helps students see patterns and compare information easily.
10. What is a common misconception Grade 1 students may have about interpreting data, and how can it be corrected?
A common misconception is thinking the bigger picture or object always means 'better' or 'more', even if the number is smaller. Teachers can correct this by guiding students to focus on the actual numbers or counts instead of picture size, helping them interpret data accurately.























