
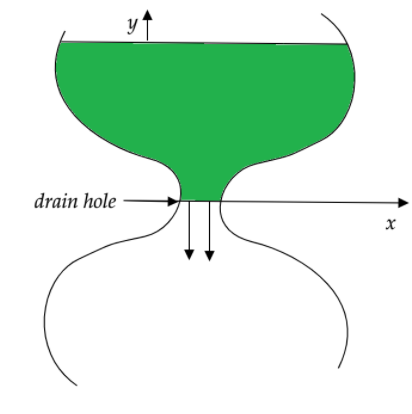
The shape of an ancient water clock jug is such that water level descends at a constant rate at all times. If the water level falls by \[4cm\] every hour, determine the shape of the jar, i.e., specify \[x\] as a function of \[y\] . The radius of the drain hole is \[2mm\] and can be assumed to be very small compared to \[x\] .
Answer
167.7k+ views
Hint: If the water in the jug is at a certain height, it will cause the water to flow through the hole with a certain velocity and as a result, the height will decrease at a certain rate. The volume of water flowing out through the orifice will be proportional to the decrease in height of water in the jug. We will make use of this property to find our answer.
Formula Used: \[{{v}_{y}}=\sqrt{2gy}\] , \[V={{v}_{y}}\times A\]
Complete step by step solution:
Let the height of the water column in the jug at a certain instant of time, say \[t=0\] , is \[y\]
The velocity of the water through the drain hole will be \[\sqrt{2gy}\]
Radius of the drain hole \[(r)=2mm=2\times {{10}^{-3}}m\left[ \because 1mm={{10}^{-3}}m \right]\]
Hence area of the drain hole \[(A)=\pi {{r}^{2}}\]
Substituting the values, we get
\[\begin{align}
& A=\pi \times {{(2\times {{10}^{-3}})}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow A=\pi \times 4\times {{10}^{-6}} \\
& \Rightarrow A=1.26\times {{10}^{-5}}{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
The volume of the water flowing through the orifice will be equal to the product of the velocity of the water through the drain hole and the area of the drain hole, that is
Volume of water flown \[(V)=A.\sqrt{2gy}\]
Now, the corresponding decrease in the water in the mug can be given as \[\pi {{x}^{2}}\times \left( -\dfrac{dy}{dt} \right)\] where \[\dfrac{dy}{dt}\] is the infinitesimal decrease in the height of the water column and is the area of the open surface of water in the jug at that instant in time.
Rate of fall of water level (per second) \[\left( -\dfrac{dy}{dt} \right)=\dfrac{4cm}{3600s}=\dfrac{4\times {{10}^{-2}}m}{3600s}=1.11\times \times {{10}^{-5}}m/s\left[ \because 1cm={{10}^{-2}}m;1hr=3600s \right]\]
As already discussed, the water flowing out must be equal to the corresponding decrease in the water from the jug, that is
\[A.\sqrt{2gy}=\pi {{x}^{2}}\times \left( -\dfrac{dy}{dt} \right)\]
We have our variables in the above equation and the other quantities are known to us, hence substituting the values, we will get
\[\begin{align}
& 1.26\times {{10}^{-5}}\times \sqrt{2\times 9.8\times y}=\pi \times {{x}^{2}}\times 1.11\times \times {{10}^{-5}} \\
& \Rightarrow \sqrt{19.6\times y}=2.77{{x}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Squaring both sides and simplifying further, we have
\[y=0.4{{x}^{2}}\]
This is the equation for the shape or the curve of the jar.
Note: We were given the rate of fall of water level for an hour, but we always consider the rate of change in terms of seconds, so we had to convert it into seconds. Some students directly put the value of the rate of fall of water level given to us in hours and reach the wrong answer even after using the correct approach. So always make sure that you’re analytically as well as logically correct. Also, note that the negative sign with the rate of change of water level only indicates that the level is falling.
Formula Used: \[{{v}_{y}}=\sqrt{2gy}\] , \[V={{v}_{y}}\times A\]
Complete step by step solution:
Let the height of the water column in the jug at a certain instant of time, say \[t=0\] , is \[y\]
The velocity of the water through the drain hole will be \[\sqrt{2gy}\]
Radius of the drain hole \[(r)=2mm=2\times {{10}^{-3}}m\left[ \because 1mm={{10}^{-3}}m \right]\]
Hence area of the drain hole \[(A)=\pi {{r}^{2}}\]
Substituting the values, we get
\[\begin{align}
& A=\pi \times {{(2\times {{10}^{-3}})}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow A=\pi \times 4\times {{10}^{-6}} \\
& \Rightarrow A=1.26\times {{10}^{-5}}{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
The volume of the water flowing through the orifice will be equal to the product of the velocity of the water through the drain hole and the area of the drain hole, that is
Volume of water flown \[(V)=A.\sqrt{2gy}\]
Now, the corresponding decrease in the water in the mug can be given as \[\pi {{x}^{2}}\times \left( -\dfrac{dy}{dt} \right)\] where \[\dfrac{dy}{dt}\] is the infinitesimal decrease in the height of the water column and is the area of the open surface of water in the jug at that instant in time.
Rate of fall of water level (per second) \[\left( -\dfrac{dy}{dt} \right)=\dfrac{4cm}{3600s}=\dfrac{4\times {{10}^{-2}}m}{3600s}=1.11\times \times {{10}^{-5}}m/s\left[ \because 1cm={{10}^{-2}}m;1hr=3600s \right]\]
As already discussed, the water flowing out must be equal to the corresponding decrease in the water from the jug, that is
\[A.\sqrt{2gy}=\pi {{x}^{2}}\times \left( -\dfrac{dy}{dt} \right)\]
We have our variables in the above equation and the other quantities are known to us, hence substituting the values, we will get
\[\begin{align}
& 1.26\times {{10}^{-5}}\times \sqrt{2\times 9.8\times y}=\pi \times {{x}^{2}}\times 1.11\times \times {{10}^{-5}} \\
& \Rightarrow \sqrt{19.6\times y}=2.77{{x}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Squaring both sides and simplifying further, we have
\[y=0.4{{x}^{2}}\]
This is the equation for the shape or the curve of the jar.
Note: We were given the rate of fall of water level for an hour, but we always consider the rate of change in terms of seconds, so we had to convert it into seconds. Some students directly put the value of the rate of fall of water level given to us in hours and reach the wrong answer even after using the correct approach. So always make sure that you’re analytically as well as logically correct. Also, note that the negative sign with the rate of change of water level only indicates that the level is falling.
Recently Updated Pages
Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties | Trends, Notes & FAQs

Difference Between Orbit and Orbital in Chemistry Explained (With Table & Diagram)

Difference Between Intensive and Extensive Properties in Chemistry

Difference Between Evaporation and Boiling: Key Concepts, Table & Examples

Difference Between CNG and LPG: Explained with Table, Properties & Uses

Difference Between Cell and Battery – Key Differences, Diagram, and Examples

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2025 Session 2: Application Form (Out), Exam Dates (Released), Eligibility, & More

Uniform Acceleration

Displacement-Time Graph and Velocity-Time Graph for JEE

JEE Main 2025: Derivation of Equation of Trajectory in Physics

Atomic Structure - Electrons, Protons, Neutrons and Atomic Models

Learn About Angle Of Deviation In Prism: JEE Main Physics 2025

Other Pages
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 Units and Measurements

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics Chapter 2 Motion In A Straight Line

Units and Measurements Class 11 Notes: CBSE Physics Chapter 1

Motion in a Straight Line Class 11 Notes: CBSE Physics Chapter 2

Important Questions for CBSE Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 - Units and Measurement




