
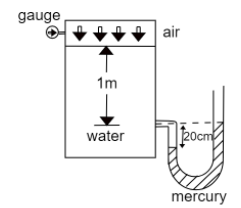
The pressure gauge reading in metre of water column shown in the given figure will be:
(A) $3.20m$
(B) $2.72m$
(C) $2.52m$
(D) $1.52m$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: In the given figure, the air exerts a pressure on the water, which in turn exerts pressure on the mercury, causing it to rise inside the U- tube. The gauge tells the differential pressure in the water column by relating it to the pressure head of the water.
Formula used:
$P = \rho gh$
Where $\rho $ is the density of the fluid.
$g$ is the acceleration due to gravity.
$h$ is the height of the column.
Complete step by step solution:
Here, the height of the column corresponds to the pressure of the different fluids present.
The pressure in the mercury column is equal to the pressure in water column, and is given by-
$P = \rho gh$
Let the pressure in the mercury column be ${P_1}$ and that in the water column be ${P_2}$. Then, assuming no pressure loss we have-
${P_1} = {P_2}$
Which can be written as-
${\rho _1}{h_1}g = {\rho _2}{h_2}g$
Where ${\rho _1}$is the density of mercury at room temperature which is about $13534kg/{m^3}$.
${\rho _2}$is the density of water at room temperature which is about $997.77kg/{m^3}$.
It is given that the height of the mercury column, ${h_1} = 20cm = 0.2m$
On equating both the quantities, we get-
$13534 \times 0.2 = 997.77{h_2}$
Where ${h_2}$ is the height of the water in the column.
${h_2} = \dfrac{{13534}}{{997.77}} \times 0.2$
${h_2} = 2.712m \approx 2.72m$
This reading will be shown by the gauge.
Hence, Option (B) is correct.
Note: Pressure head refers to the representation of pressure in terms of height of fluid raised or fallen. The common pressure measuring term in fluid mechanics, the $mm - Hg$represents pressure head because it tells the height of liquid mercury which would rise in a column provided the same pressure. The gauge here also tells the pressure head, as the meters of water are raised.
Formula used:
$P = \rho gh$
Where $\rho $ is the density of the fluid.
$g$ is the acceleration due to gravity.
$h$ is the height of the column.
Complete step by step solution:
Here, the height of the column corresponds to the pressure of the different fluids present.
The pressure in the mercury column is equal to the pressure in water column, and is given by-
$P = \rho gh$
Let the pressure in the mercury column be ${P_1}$ and that in the water column be ${P_2}$. Then, assuming no pressure loss we have-
${P_1} = {P_2}$
Which can be written as-
${\rho _1}{h_1}g = {\rho _2}{h_2}g$
Where ${\rho _1}$is the density of mercury at room temperature which is about $13534kg/{m^3}$.
${\rho _2}$is the density of water at room temperature which is about $997.77kg/{m^3}$.
It is given that the height of the mercury column, ${h_1} = 20cm = 0.2m$
On equating both the quantities, we get-
$13534 \times 0.2 = 997.77{h_2}$
Where ${h_2}$ is the height of the water in the column.
${h_2} = \dfrac{{13534}}{{997.77}} \times 0.2$
${h_2} = 2.712m \approx 2.72m$
This reading will be shown by the gauge.
Hence, Option (B) is correct.
Note: Pressure head refers to the representation of pressure in terms of height of fluid raised or fallen. The common pressure measuring term in fluid mechanics, the $mm - Hg$represents pressure head because it tells the height of liquid mercury which would rise in a column provided the same pressure. The gauge here also tells the pressure head, as the meters of water are raised.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Derive an expression for maximum speed of a car on class 11 physics JEE_Main

Understanding Elastic Collisions in Two Dimensions

Class 11 JEE Main Physics Mock Test 2025

Other Pages
NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 10 Thermal Properties of Matter (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory (2025-26)

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Define thermal expansion for alpha beta and gamma A class 11 physics JEE_Main

Happy New Year Wishes 2026 – 100+ Messages, Quotes, Shayari, Images & Status in All Languages

Valentine Week 2026 List | Valentine Week Days, Dates & Meaning




