
The magnetic lines of force inside a bar magnet:
(A) Are from north-pole to south-pole of the magnet
(B) Do not exist
(C) Depends upon the area of cross-section of the bar magnet
(D) Are from south-pole to north-pole of the magnet
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: - The magnetic forces around the area of a magnet is known as a magnetic field. In a bar magnet, the magnetic fields are durable at either pole of the magnet. It is also just as strong at the north-pole when compared with the south-pole. At the center of the magnet and in between the poles, the force is weaker.
Complete Step-by-step solution:
General properties of magnetic field lines:
(1) The magnetic lines of force always make closed loops.
(2) When going from an area of higher permeability to an area of lower permeability the field lines tend to bulge out i.e. when going from the surface of the magnet to the air density of the field line decreases.
(3) Every field line has the same strength.
(4) They never cross each other.
(5) By convention, these field lines seem to originate from the north pole & end into the south pole of a bar magnet.
(6) The direction inverses inside the magnet i.e. they appear to move from the south pole towards the north pole.
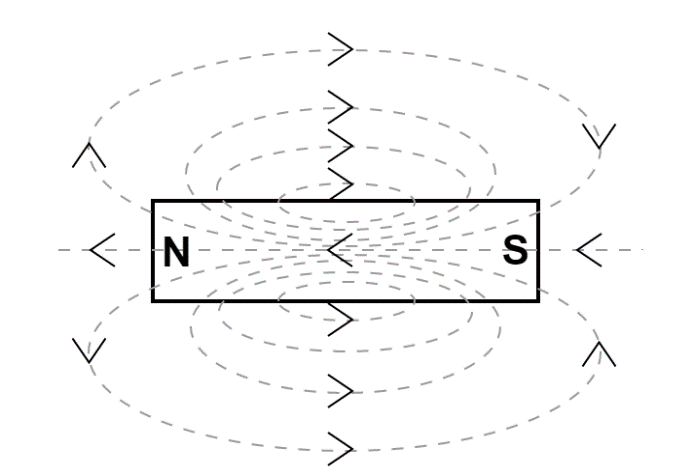
For that reason, the magnetic lines of forces inside a bar magnet are from south-pole to north-pole of the magnet.
Thus, the correct option is (D) Are from south-pole to north-pole of the magnet.
Additional Information: Magnetic lines of force are imaginary lines to indicate their magnetic field. It helps to understand the density of the magnetic field lines; hence magnetism will be easier to understand. Magnetic flux is the term used to define the number of lines of force passing through the unit area.
Note: The magnetic field lines are almost parallel to each other, as the bar magnet is made up of uniform ferromagnetic material with constant permeability throughout its length & bulge out as the lines move reverse to the poles & pass through air. Inside the bar magnet, the magnetic lines are ongoing their journey to the opposite end.
Complete Step-by-step solution:
General properties of magnetic field lines:
(1) The magnetic lines of force always make closed loops.
(2) When going from an area of higher permeability to an area of lower permeability the field lines tend to bulge out i.e. when going from the surface of the magnet to the air density of the field line decreases.
(3) Every field line has the same strength.
(4) They never cross each other.
(5) By convention, these field lines seem to originate from the north pole & end into the south pole of a bar magnet.
(6) The direction inverses inside the magnet i.e. they appear to move from the south pole towards the north pole.

For that reason, the magnetic lines of forces inside a bar magnet are from south-pole to north-pole of the magnet.
Thus, the correct option is (D) Are from south-pole to north-pole of the magnet.
Additional Information: Magnetic lines of force are imaginary lines to indicate their magnetic field. It helps to understand the density of the magnetic field lines; hence magnetism will be easier to understand. Magnetic flux is the term used to define the number of lines of force passing through the unit area.
Note: The magnetic field lines are almost parallel to each other, as the bar magnet is made up of uniform ferromagnetic material with constant permeability throughout its length & bulge out as the lines move reverse to the poles & pass through air. Inside the bar magnet, the magnetic lines are ongoing their journey to the opposite end.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




