
Ethene when treated with Br2 in the presence of CCl4 which compound is formed.
(a) 1, 2-dibromoethane
(b) 1-bromo-2-chloroethane
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) 1, 1, 1 - tribromoethane
Answer
231.3k+ views
Hint: Bromine (\[B{r_2}\]) is a reddish-brown colour liquid. When it is treated with an alkene in the presence of carbon tetrachloride (\[CC{l_4}\]) the reddish-brown colour disappears with the formation of vicinal-dibromo (a colourless compound). This reaction is used for the detection of double bonds in organic compounds.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
When the unsaturated hydrocarbon like ethene is treated with bromine and chlorine in the presence of a non-nucleophilic solvent such as \[CC{l_4}\]this led to the isolation of vicinal dibromo or dichloroalkene respectively.
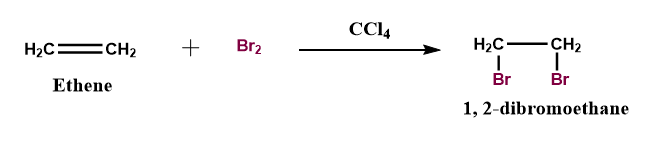
Figure 1: Bromination of alkene via bromine in the presence of carbon tetrachloride (\[CC{l_4}\]) as a solvent.
The solvent carbon tetrachloride (\[CC{l_4}\]) is used because of its non-reactive nature i.e., it does not interfere in the reaction pathway unlike other solvents such as., water and alcohol, etc.
During the bromination, the alkene is activated by the attack of the bromonium (\[B{r^ + }\]) ion, which is later attacked by the bromide (\[B{r^ - }\]) ion, hence, as a result, the formation of a trans-dibromo compound is occurs. Therefore, we can say bromination delivers bromine in the trans fashion to the alkene, or on the other hand the bromination of alkene is an anti-addition.
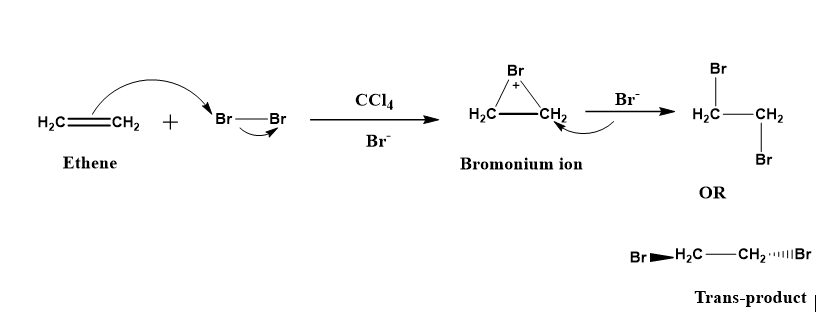
Figure 2: Reaction mechanism of bromination of an alkene.
In the question, option (b), (c), and (d) will be the incorrect option because the bromination of ethene do not involve the formation of 1-bromo-2-chloro or 1-bromo-2-chloro and 1, 2-dibromoethane together.
Therefore, from the above discussion, it is quite clear that option (a) will be the correct answer.
Note: The alkane, alkene and alkyne are saturated (alkane) and unsaturated (alkene and alkyne) hydrocarbons. Alkane is a saturated hydrocarbon, in which the carbon atoms contain the single bonds Alkene and alkyne belong to the family of unsaturated hydrocarbons in which the double and triple bond is present between the carbon atoms.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
When the unsaturated hydrocarbon like ethene is treated with bromine and chlorine in the presence of a non-nucleophilic solvent such as \[CC{l_4}\]this led to the isolation of vicinal dibromo or dichloroalkene respectively.
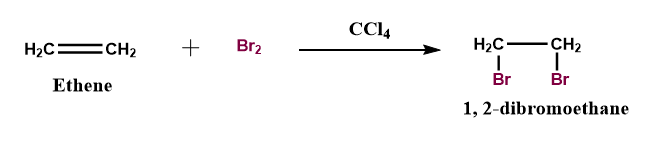
Figure 1: Bromination of alkene via bromine in the presence of carbon tetrachloride (\[CC{l_4}\]) as a solvent.
The solvent carbon tetrachloride (\[CC{l_4}\]) is used because of its non-reactive nature i.e., it does not interfere in the reaction pathway unlike other solvents such as., water and alcohol, etc.
During the bromination, the alkene is activated by the attack of the bromonium (\[B{r^ + }\]) ion, which is later attacked by the bromide (\[B{r^ - }\]) ion, hence, as a result, the formation of a trans-dibromo compound is occurs. Therefore, we can say bromination delivers bromine in the trans fashion to the alkene, or on the other hand the bromination of alkene is an anti-addition.

Figure 2: Reaction mechanism of bromination of an alkene.
In the question, option (b), (c), and (d) will be the incorrect option because the bromination of ethene do not involve the formation of 1-bromo-2-chloro or 1-bromo-2-chloro and 1, 2-dibromoethane together.
Therefore, from the above discussion, it is quite clear that option (a) will be the correct answer.
Note: The alkane, alkene and alkyne are saturated (alkane) and unsaturated (alkene and alkyne) hydrocarbons. Alkane is a saturated hydrocarbon, in which the carbon atoms contain the single bonds Alkene and alkyne belong to the family of unsaturated hydrocarbons in which the double and triple bond is present between the carbon atoms.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Amino Acids and Peptides Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Electricity and Magnetism Explained: Key Concepts & Applications

Algebra Made Easy: Step-by-Step Guide for Students

JEE Energetics Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Admit Card Out, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




