
Chlorobenzene is extremely less reactive towards a nucleophilic substitution reaction. Give two reasons for the same.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: We know that, in nucleophilic substitution reactions, a nucleophile attacks the positively charged atom. A nucleophile is a species, which is electron rich in nature. Some examples of nucleophiles are hydroxide ion, cyanide ion etc.
Complete step by step answer:
Resonance is the phenomenon in which delocalization of electrons occurs that causes stabilization of molecules.
We first draw the resonance in chlorobenzene. The lone pair of chlorine atoms delocalized in the benzene ring.
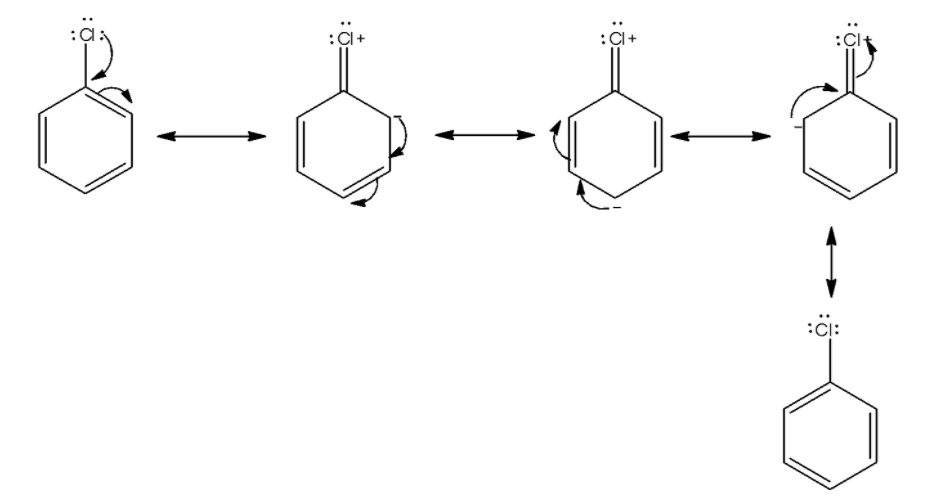
From the above structure we see a lone pair of electrons delocalized in the benzene ring and four resonating structures present. This causes stabilization of the molecule. So, activation energy for displacement of halogen from benzene is very much higher than displacement of alkyl halide.
In chlorobenzene, the halogen atom is bonded to the highly electronegative $sp^2$ hybridised carbon atom. So, nucleophilic substitution reaction is not possible.
Hence, two reasons for less reactivity of chlorobenzene towards nucleophilic substitution reactions are resonance in chlorobenzene and $sp^2$ hybridised nature of carbon atom bonded to chlorine atom.
Additional Information:
In a chemical reaction, replacement of one group by another is termed as substitution reaction. Substitution reactions are of three types, radical, electrophilic and nucleophilic substitution. Electrophile is a chemical species possessing electron deficient nature and nucleophile is a species possessing electron rich nature. Some examples of electrophiles are hydronium ion, bromine etc.
Note:
Students might get confused about nucleophilic and electrophilic substitution. In electrophilic substitution, an electrophile generally displaces hydrogen atom from a compound and in nucleophilic substitution, nucleophile attacks positively charged carbon.
Complete step by step answer:
Resonance is the phenomenon in which delocalization of electrons occurs that causes stabilization of molecules.
We first draw the resonance in chlorobenzene. The lone pair of chlorine atoms delocalized in the benzene ring.

From the above structure we see a lone pair of electrons delocalized in the benzene ring and four resonating structures present. This causes stabilization of the molecule. So, activation energy for displacement of halogen from benzene is very much higher than displacement of alkyl halide.
In chlorobenzene, the halogen atom is bonded to the highly electronegative $sp^2$ hybridised carbon atom. So, nucleophilic substitution reaction is not possible.
Hence, two reasons for less reactivity of chlorobenzene towards nucleophilic substitution reactions are resonance in chlorobenzene and $sp^2$ hybridised nature of carbon atom bonded to chlorine atom.
Additional Information:
In a chemical reaction, replacement of one group by another is termed as substitution reaction. Substitution reactions are of three types, radical, electrophilic and nucleophilic substitution. Electrophile is a chemical species possessing electron deficient nature and nucleophile is a species possessing electron rich nature. Some examples of electrophiles are hydronium ion, bromine etc.
Note:
Students might get confused about nucleophilic and electrophilic substitution. In electrophilic substitution, an electrophile generally displaces hydrogen atom from a compound and in nucleophilic substitution, nucleophile attacks positively charged carbon.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




