
When a person uses a convex lens as a simple magnifying glass, the object must be placed at a distance
A. less than one focal length
B. more than one focal length
C. less than twice the focal length
D. more than twice the focal length
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint A magnifying is an optical device that uses a converging lens (such as a convex lens) to form a virtual, upright and magnified image. The only condition is that the object should be placed between the optical centre and the focus of the lens. The distance between the optical centre and the focus is called focal length of the lens.
Complete step by step answer
Let us first discuss magnifying glass.
A magnifying is an optical device that uses a converging lens (such as a convex lens) to form a virtual, upright and magnified image. The only condition is that the object should be placed between the optical centre and the focus of the lens.
So, if we want a magnified, virtual and erect image, we have to place the object not beyond the focal length of the convex lens. The distance between the optical centre and the focus is called focal length of the lens.
A ray diagram of formation of a magnified virtual and erect image using a convex lens is shown in the figure.
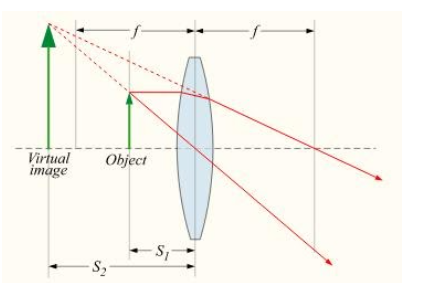
Here, ${S_1}$ is the distance of the object from the optical centre, ${S_2}$ is the distance of the image formed and $f$ is the focal length of the lens.
It is clearly seen from the ray diagram that the image formed is virtual, erect and has size larger than the object. It is formed behind the lens.
Therefore, when a person uses a convex lens as a simple magnifying glass, the object must be placed at a distance less than one focal length.
Hence, option A is correct.
Note Apart from the location of the object, the magnifying power or magnification of a magnifying glass also depends upon the place it is placed between the observer's eye and the object being viewed, and the total distance between them. The magnifying power is also equivalent to the angular magnification which is the ratio of the size of the image formed on the observer's retina with and without the lens.
Complete step by step answer
Let us first discuss magnifying glass.
A magnifying is an optical device that uses a converging lens (such as a convex lens) to form a virtual, upright and magnified image. The only condition is that the object should be placed between the optical centre and the focus of the lens.
So, if we want a magnified, virtual and erect image, we have to place the object not beyond the focal length of the convex lens. The distance between the optical centre and the focus is called focal length of the lens.
A ray diagram of formation of a magnified virtual and erect image using a convex lens is shown in the figure.

Here, ${S_1}$ is the distance of the object from the optical centre, ${S_2}$ is the distance of the image formed and $f$ is the focal length of the lens.
It is clearly seen from the ray diagram that the image formed is virtual, erect and has size larger than the object. It is formed behind the lens.
Therefore, when a person uses a convex lens as a simple magnifying glass, the object must be placed at a distance less than one focal length.
Hence, option A is correct.
Note Apart from the location of the object, the magnifying power or magnification of a magnifying glass also depends upon the place it is placed between the observer's eye and the object being viewed, and the total distance between them. The magnifying power is also equivalent to the angular magnification which is the ratio of the size of the image formed on the observer's retina with and without the lens.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Why does capacitor block DC and allow AC class 12 physics JEE_Main

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

CBSE Class 12 Physics Set 2 (55/2/2) 2025 Question Paper & Solutions

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Units and Measurements Mock Test for JEE Main 2025-26 Preparation

Chemistry Question Papers for JEE Main, NEET & Boards (PDFs)




