
A long bar magnet of magnetic moment $6A{m^2}$ & $8A{m^2}$ can be fastened together with their axes horizontal and the centres in a vertical line about which the system is free to oscillate. Compare the time periods in the earth’s field when the axes of magnets are in the same direction, opposite direction and right angles.
A) $1:7:5$
B) $1:\sqrt 7 :\sqrt 5 $
C) $1:\sqrt 7 :\sqrt {\dfrac{7}{5}} $
D) $1:\sqrt {\dfrac{7}{5}} :\sqrt {\dfrac{{14}}{5}} $
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: To solve this problem, we have to consider the quantity magnetic moment as a vector and treat it as a vector when performing the addition operation on them. Different orientations of the magnetic moments of these two bar magnets with respect to each other will yield us different results.
Formula Used:
The time period of oscillation of bar magnet is –
$T = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{I}{{mB}}} $
where $I$= moment of inertia, m = magnetic moment and B = magnetic field.
Complete step by step answer:
When a magnetic material is placed in an external magnetic field, it experiences a moment of force since equal and opposite forces act on both of the poles – North and South. This causes a moment of force which enables the magnetic material to orient itself along the direction of the external applied field.
Here, we can define a quantity called magnetic moment, which is a measure of the tendency of the magnetic material to re-arrange its poles along the direction of the external field.
Mathematically, the magnetic moment is measured as the product of current flowing around the poles and the area,
$M = I \times A$
The SI unit of magnetic moment is $A{m^2}$ and it is a vector quantity whose direction is from South pole to North pole of the magnet.
In the given problem, there are two bar magnets of magnetic moments ${m_1} = 6A{m^2}$ & ${m_2} = 8A{m^2}$. These bar magnets are placed in different orientations. Let us understand the combined magnetic moment in each orientation:
i) Same direction.
The two bar magnets are placed on one another, with North of one magnet placed over the North pole of the other and the same for South poles, as shown:
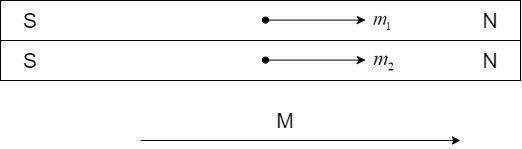
The net moment,
$\overrightarrow M = \overrightarrow {{m_1}} + \overrightarrow {{m_2}} $
Since the moments ${m_1}$ and ${m_2}$ are oriented in the same direction, the magnitude of the net moment is equal to the algebraic sum of the moments.
$M = {m_1} + {m_2}$
Substituting and adding,
$M = 6 + 8 = 14A{m^2}$
ii) Opposite direction.
The two bar magnets are placed on one another, with North of one magnet placed over the South pole of the other and vice-versa, as shown:
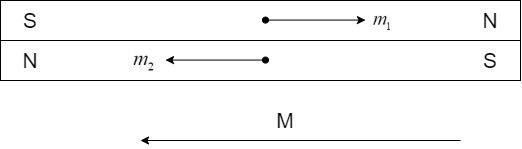
The net moment,
$\overrightarrow M = \overrightarrow {{m_1}} + \overrightarrow {{m_2}} $
Since the moments ${m_1}$ and ${m_2}$ are oriented in the opposite direction, the magnitude of the net moment is equal to the algebraic difference of the moments.
$M = {m_2} - {m_1}$
Substituting and adding,
$M = 8 - 6 = 2A{m^2}$
iii) Right angles
Here, the magnets are so arranged that the axis of one magnet is perpendicular to the axis of another.
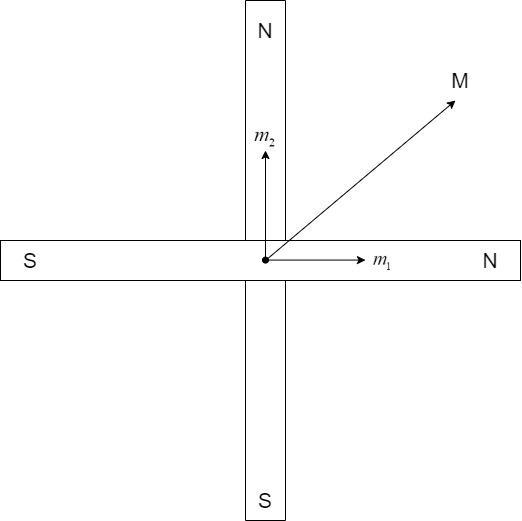
The net moment,
$\overrightarrow M = \overrightarrow {{m_1}} + \overrightarrow {{m_2}} $
Here, the moments are at right angles to each other. Hence, the magnitude of the vector M, is given by –
$M = \sqrt {m_1^2 + m_2^2} $
Substituting,
$M = \sqrt {{6^2} + {8^2}} = \sqrt {36 + 64} = \sqrt {100} = 10A{m^2}$
The time period of oscillation of bar magnet is –
$T = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{I}{{mB}}} $
where $I$= moment of inertia, m = magnetic moment and B = magnetic field.
We can deduce that –
$T \propto \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt m }}$
Let us compare the time periods of the magnets in various orientations as:
Same: Opposite: Right angles = $\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {14} }}:\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}:\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {10} }}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 \sqrt 7 }}:\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}:\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 5 \sqrt 2 }}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 7 }}:1:\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 5 }}$
Multiplying the whole ratio by $\sqrt 7$, we get –
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sqrt 7 }}{{\sqrt 7 }}:\sqrt 7 :\dfrac{{\sqrt 7 }}{{\sqrt 5 }}$
$\Rightarrow 1:\sqrt 7 :\sqrt {\dfrac{7}{5}}$
Hence, the correct option is Option C.
Note: In this problem, the magnitudes were computed directly based on the concept, but however, you can use the direct formula for magnitude of a vector.
If $\overrightarrow K = \overrightarrow A + \overrightarrow B$,
The magnitude of the sum, $\overrightarrow {\left| K \right|} = \sqrt {{A^2} + {B^2} + 2AB\cos \theta }$
where $\theta$= angle between the two vectors, A and B.
Formula Used:
The time period of oscillation of bar magnet is –
$T = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{I}{{mB}}} $
where $I$= moment of inertia, m = magnetic moment and B = magnetic field.
Complete step by step answer:
When a magnetic material is placed in an external magnetic field, it experiences a moment of force since equal and opposite forces act on both of the poles – North and South. This causes a moment of force which enables the magnetic material to orient itself along the direction of the external applied field.
Here, we can define a quantity called magnetic moment, which is a measure of the tendency of the magnetic material to re-arrange its poles along the direction of the external field.
Mathematically, the magnetic moment is measured as the product of current flowing around the poles and the area,
$M = I \times A$
The SI unit of magnetic moment is $A{m^2}$ and it is a vector quantity whose direction is from South pole to North pole of the magnet.
In the given problem, there are two bar magnets of magnetic moments ${m_1} = 6A{m^2}$ & ${m_2} = 8A{m^2}$. These bar magnets are placed in different orientations. Let us understand the combined magnetic moment in each orientation:
i) Same direction.
The two bar magnets are placed on one another, with North of one magnet placed over the North pole of the other and the same for South poles, as shown:

The net moment,
$\overrightarrow M = \overrightarrow {{m_1}} + \overrightarrow {{m_2}} $
Since the moments ${m_1}$ and ${m_2}$ are oriented in the same direction, the magnitude of the net moment is equal to the algebraic sum of the moments.
$M = {m_1} + {m_2}$
Substituting and adding,
$M = 6 + 8 = 14A{m^2}$
ii) Opposite direction.
The two bar magnets are placed on one another, with North of one magnet placed over the South pole of the other and vice-versa, as shown:

The net moment,
$\overrightarrow M = \overrightarrow {{m_1}} + \overrightarrow {{m_2}} $
Since the moments ${m_1}$ and ${m_2}$ are oriented in the opposite direction, the magnitude of the net moment is equal to the algebraic difference of the moments.
$M = {m_2} - {m_1}$
Substituting and adding,
$M = 8 - 6 = 2A{m^2}$
iii) Right angles
Here, the magnets are so arranged that the axis of one magnet is perpendicular to the axis of another.

The net moment,
$\overrightarrow M = \overrightarrow {{m_1}} + \overrightarrow {{m_2}} $
Here, the moments are at right angles to each other. Hence, the magnitude of the vector M, is given by –
$M = \sqrt {m_1^2 + m_2^2} $
Substituting,
$M = \sqrt {{6^2} + {8^2}} = \sqrt {36 + 64} = \sqrt {100} = 10A{m^2}$
The time period of oscillation of bar magnet is –
$T = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{I}{{mB}}} $
where $I$= moment of inertia, m = magnetic moment and B = magnetic field.
We can deduce that –
$T \propto \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt m }}$
Let us compare the time periods of the magnets in various orientations as:
Same: Opposite: Right angles = $\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {14} }}:\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}:\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {10} }}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 \sqrt 7 }}:\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}:\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 5 \sqrt 2 }}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 7 }}:1:\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 5 }}$
Multiplying the whole ratio by $\sqrt 7$, we get –
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sqrt 7 }}{{\sqrt 7 }}:\sqrt 7 :\dfrac{{\sqrt 7 }}{{\sqrt 5 }}$
$\Rightarrow 1:\sqrt 7 :\sqrt {\dfrac{7}{5}}$
Hence, the correct option is Option C.
Note: In this problem, the magnitudes were computed directly based on the concept, but however, you can use the direct formula for magnitude of a vector.
If $\overrightarrow K = \overrightarrow A + \overrightarrow B$,
The magnitude of the sum, $\overrightarrow {\left| K \right|} = \sqrt {{A^2} + {B^2} + 2AB\cos \theta }$
where $\theta$= angle between the two vectors, A and B.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




