




What is a Catfish?
Catfish is a type of fish that has one or more than one pair of whiskers like feelers around its mouth which are known as barbels that help the organism to feel and taste. To date, we have discovered around 2500 different species of catfish. These organisms are related to other organisms like crap, minnows, etc.
Catfish are present on almost all continents, most of the species can survive in both freshwater and seawater, but they are mainly found in freshwater. In this article we will study about these amusing organisms in a little detail, throwing special light on what they feed on.

Catfish Picture

Catfish Picture; A Different Species of Catfish
Helicopter Catfish
Wallago attu is a species of catfish that is exclusively found in freshwater and is also known as the helicopter catfish or wallago catfish.
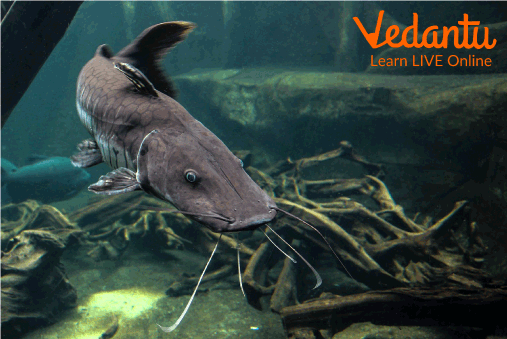
Helicopter Catfish
The helicopter Catfish is a native of South and Southeast Asia. It is relatively the larger size among the various different species of catfish, it is mostly one metre in length and is usually found in large and widespread water bodies. It can be differentiated from the other species of catfish by its characteristically long and narrow head and its dorsal fin which is high and sharp, unlike the other species.
The helicopter catfish is one of the many species which has been used as a source of food in south Asia for many decades.
What Do Catfish Eat?
Catfish are scavengers or decomposers thus they are always looking for food as they swim around in their natural habitat. The barbels on their mouth help them locate their food, they usually prefer fresh food but they can also eat dead animals or plants. The barbels help them sense and smell the food as well as they help them taste the food.

A Catfish Eating a Small Fish
They mainly eat a variety of small fishes, crayfish, snails, calms, and even frogs. They can also eat algae and dead plants or fish floating in the water.
Their predators include us humans, crocodiles, some large birds, etc.
Getting Catfished Meaning
The term getting catfished or catfishing refers to a scam or malicious activity on any online platform. Catfishing means posing as someone else or identifying yourself as someone else on an online platform. It comes from the fact that a catfish is actually a fish but because of its barbels, it looks like a cat thus its name.
Sample Questions
1. Explain briefly the growth pattern of a catfish.
Ans: Just like plants, catfish continue to grow throughout their lives.
2. Name some species of catfish.
Ans:
Channel Catfish
Blue Catfish
Flathead Catfish
Learn by Doing
Complete the statements that follow by filling in the blanks:
1. The _______ of a catfish gives it a cat-like appearance.
Ans: barbels
2. The barbel on their mouth helps them to ______ and _______
Ans: smell, taste.
3. Catfish are ________.
Ans: Scavengers
4. The scientific name of helicopter catfish is ________.
Ans: Wallago Attu
5. Catfish are natives of ______ and _________ Asia.
Ans: South, South East.
Summary
A Catfish is a type of fish that is mainly found in freshwater but can also survive in seawater. To date, more than 2500 different species of catfish have been discovered. One such species is the helicopter catfish which is a native of south and southeast Asia and is majorly found in large and widespread water bodies. Catfish is a scavenger or a decomposer that can eat a variety of things like some small fish, snails, calms, frogs, algae dead plants, and dead fishes. Catfishing means posing as somebody else other than your actual self on some online platform.
FAQs on What Do Catfish Eat?
1. What do catfish generally eat in the wild?
Catfish are omnivores, which means they eat a variety of both plants and animals. Their diet in the wild is very diverse and depends on what is available in their habitat. Common food items include:
Small fish and fish eggs
Insects, worms, and snails
Aquatic plants and algae
Crustaceans like crayfish
They are not picky eaters and will consume almost anything they can find at the bottom of a river, lake, or pond.
2. What is the importance of the 'whiskers' or barbels on a catfish?
The long, whisker-like feelers around a catfish's mouth are called barbels. They are a vital sensory organ for feeding and navigation. They do not sting; instead, they function like a combination of fingers and taste buds, helping the catfish to:
Smell and taste for food in dark or muddy water where visibility is poor.
Navigate and feel their surroundings along the bottom of the water body.
Locate prey such as insects and small fish that may be hiding in the mud.
3. Do different types of catfish, like those in rivers and oceans, eat different things?
Yes, a catfish's diet is highly dependent on its habitat. Freshwater catfish, found in rivers and lakes, primarily eat insects, worms, snails, and smaller fish native to those environments. In contrast, saltwater catfish, which live in the ocean, consume marine life such as small crabs, shrimp, and different types of ocean fish. They are excellent examples of how animals adapt their feeding habits to their surroundings.
4. Are catfish more active during the day or at night to find food?
Most species of catfish are nocturnal or crepuscular, which means they are most active during the night, dawn, or dusk. Their excellent sense of smell and taste, powered by their barbels, makes them highly effective hunters in low-light conditions. During the day, they often prefer to rest in darker, sheltered spots like under rocks, logs, or in deep holes.
5. Can catfish eat plants or human food like rice?
As omnivores, many catfish species do eat aquatic plants and algae as a natural part of their diet. Regarding human food, while wild catfish do not encounter rice, some farmed catfish are fed specially made pellets that can contain plant-based ingredients like corn or rice byproducts. However, their preferred diet in a natural setting is typically live or decaying animal matter.
6. Why are catfish known as 'bottom-feeders' and what does that mean for their diet?
Catfish are called bottom-feeders because they primarily live and search for food at the bottom of lakes, rivers, and ponds. Their bodies, especially their downward-facing mouths and sensory barbels, are adapted for this lifestyle. This means their diet largely consists of organisms and matter found on the floor of the water body, such as insects hiding in the mud, worms, molluscs, crustaceans, and decaying organic material (detritus).
7. Do catfish really 'clean' a pond or tank by eating poop?
This is a common misconception. While catfish are excellent scavengers that help keep their environment clean by eating leftover fish food, dead plants, and other decaying matter, they do not eat poop (fish waste). They are valuable for managing uneaten food that would otherwise rot, but they do not eliminate the need for cleaning or filtering fish waste in a tank or pond.
8. How does a catfish's diet change as it grows from a baby to an adult?
A catfish's diet evolves significantly throughout its life cycle. The change reflects its growing size and energy needs:
Baby Catfish (Fry): When very small, they feed on microscopic organisms like plankton and tiny insect larvae.
Young Catfish (Fingerlings): As they grow, they move on to larger food sources like aquatic insects, worms, and the eggs of other fish.
Adult Catfish: A fully grown catfish has a much broader diet that can include larger fish, frogs, crayfish, and clams, enabling it to be a dominant predator or scavenger in its habitat.
9. Besides their barbels, what other senses do catfish use to find food in muddy water?
While barbels are their primary tool, catfish have other highly developed senses for hunting in low-visibility conditions. They possess an acute sense of hearing to detect the vibrations and movements of prey. Furthermore, their entire body is covered in taste receptors. This allows them to effectively 'taste' the water around them, helping them to locate a source of food even before their barbels make contact with it.
10. How long can a catfish live, and how does its diet affect this?
The lifespan of a catfish varies widely by species, ranging from a few years for smaller types to over 20 years for larger ones like the blue catfish. A healthy and consistent diet is a critical factor for longevity. Access to a nutritious and abundant food source allows a catfish to grow to its full potential, maintain a strong immune system, and live a longer, healthier life. A poor diet or scarcity of food can lead to stunted growth and a significantly shorter lifespan.





















