




What Are the Main Uses of Soda Lime in Everyday Life?
The term soda lime has been known to describe all of the mixed drinks, including but not limited to: grapefruit sour, Fresca, seltzer water with fruit juice mixed in it, and club soda. Soda lime is not soda, with the carbonation removed. It has no colour, and is clearer than your average glass of water.
It is estimated that 1 out of every 5 people over the age of 15 consumes at least a litre of carbonated beverage per day. The sale of soda in North America and Europe alone is worth 93 billion annually, representing nearly half of all sugar sales in these two regions. We will read about the medical and experimental uses of soda lime in the article. Let’s start learning!

Soda Lime Drink
What is Soda Lime?
The Soda Lime Transmission Spectrum
Soda lime is a type of limestone that is used in the production of soft drinks. The use of soda lime dates back to the 19th century. It is used to remove excess carbon dioxide from the drink, which is responsible for giving it its fizziness. Soda lime is a chemical compound of calcium hydroxide and sodium bicarbonate that is used in the production of soft drinks. It is an important part of the process that removes impurities from water, especially those found in groundwater.
Soda lime is the substance that is used in the production of soft drinks. It is a type of calcium hydroxide which has been mixed with water and carbon dioxide. The soda lime helps to remove the dissolved carbon dioxide from the drink and it also provides a refreshing taste to it. The drink then becomes fizzy due to the presence of bubbles in it.
Soda Lime Formation
Medical Uses of Soda Lime
It is used in the treatment of caries and dentinal hypersensitivity, as well as in the prevention of dental plaque and tartar. Soda lime is also used for respiratory treatments such as asthma, bronchitis, and emphysema. It is also used to treat infections caused by fungi, viruses or bacteria. Soda lime is a chemical compound with a pH of 8.5-9.5 and is used in water purification. It can also be used to remove odours from water, and it is used as an antacid.
The use of soda lime in the medical field comes in two forms: sodium bicarbonate and calcium hydroxide. Sodium bicarbonate is often used as an antacid when someone has heartburn or indigestion, while calcium hydroxide is commonly used to treat acid reflux or ulcers.
How Soda Lime is Used in Experiments Based on Respiration?
How Chemical Compounds are Used in Experiments
Soda lime is a chemical compound used in experiments based on respiration. It has the ability to remove carbon dioxide from the air and release oxygen. It is a mixture of sodium bicarbonate, calcium hydroxide, and magnesium oxide that has been heated to form a hard white solid. It can be used in experiments such as measuring the rate of respiration in small animals or determining how much carbon dioxide is produced by yeast.
Soda lime is a chemical compound used in experiments based on human respiration. It is an alkaline substance that reacts with acid to form carbon dioxide and water.
The chemical reaction between soda lime and acid can be represented as follows:
Na2CO3 + HCl → NaCl + H2O + CO2
It is used in experiments based on human respiration because it helps to remove carbon dioxide from the air.
Benefits of Soda Lime

Chemical Compound
Soda lime is a chemical compound, which is a mixture of sodium bicarbonate, sodium carbonate and calcium hydroxide. It is used in the water treatment process to remove impurities from water. Soda lime has many benefits like:
It removes the odour and taste of chlorine.
It helps in reducing the corrosion of metal pipes.
Soda lime is a chemical compound that is used in the process of water purification. It is also used in other industries as well.
Soda lime has many benefits for various industries in which it is used. For example, it can be used to remove any odour from water, and it can also be used to remove any chemicals from water, such as chlorine. It can also remove any hardness minerals from water such as calcium and magnesium. Soda lime has many different uses and benefits for the various industries that use it.
Summary
In this article, we learned that soda lime is a chemical compound that is used in the process of absorption of gaseous substances. Soda lime has a number of industrial applications due to its ability to adsorb both gases and water vapour. Soda lime is a chemical compound that is used to remove CO2 from natural gas, or to absorb and remove CO2 from the air.
We already have learnt the uses of soda lime in detail in the above article. We discussed soda lime in the article above, and now we know almost all the information about soda lime. It is used in the food industry as an acid regulator, including in carbonated drinks. Isn’t it interesting that we use soda lime in our drinks? We hope you enjoyed reading this article.
FAQs on Uses of Soda Lime: Applications and Importance
1. What is soda lime and what are its main components?
Soda lime is not a single chemical compound but a granular mixture of chemicals, primarily used as a carbon dioxide absorbent. Its composition is typically:
- Calcium Hydroxide (Ca(OH)₂): The main component, making up about 75% of the mixture.
- Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH): Acts as a catalyst to speed up the reaction with carbon dioxide, comprising about 3%.
- Water (H₂O): Present in small amounts (around 20%) to facilitate the chemical absorption.
- pH Indicator: Medical-grade soda lime often includes an indicator like ethyl violet that changes colour as the material is exhausted.
You can learn more about its properties in detail on the page about Soda Lime.
2. What are the most common uses of soda lime?
Soda lime is highly effective at absorbing acidic gases, which leads to its use in several critical applications:
- Medical Anaesthesia: It removes exhaled carbon dioxide (CO₂) from breathing circuits, allowing anaesthetic gases to be safely re-breathed by the patient.
- Scuba Diving and Submarines: Used in rebreather systems to scrub CO₂ from the air supply, extending the time a person can stay underwater or in a sealed environment.
- Gas Masks: Deployed in some respiratory protection systems to filter out poisonous acidic gases.
- Chemistry Labs: Used as a drying agent for gases and as a reagent in decarboxylation reactions to produce alkanes like methane.
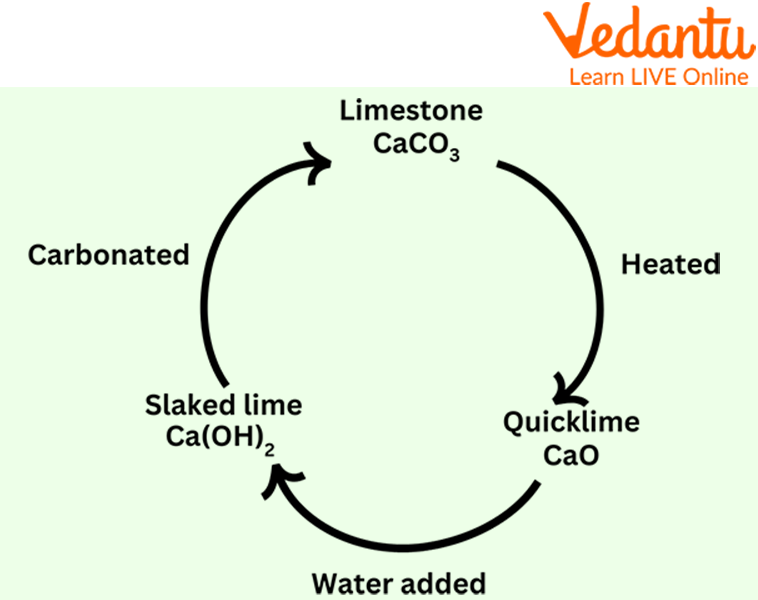
3. What is the difference between soda lime and soda-lime glass?
Although they sound similar, soda lime and soda-lime glass are completely different materials with different purposes.
- Soda Lime: A granular chemical mixture (calcium hydroxide and sodium hydroxide) used to absorb gases like carbon dioxide.
- Soda-Lime Glass: The most common type of glass, used for windows and bottles. It is made by melting sand (silica), soda (sodium carbonate), and lime (calcium oxide) together at high temperatures.
In short, one is a gas absorbent used in breathing systems, while the other is a solid, transparent material used for everyday items. For more details on glass, see the composition of glass.
4. How is soda lime used to test for nitrogen in an organic compound?
Soda lime is used in Lassaigne's test, a method for the qualitative analysis of elements in an organic compound. When the organic compound containing nitrogen is strongly heated with soda lime, the nitrogen is converted into ammonia gas (NH₃). The presence of ammonia, which has a characteristic pungent smell and turns moist red litmus paper blue, indicates that nitrogen was present in the original sample.
5. Why does medical-grade soda lime change colour as it gets used up?
The colour change is a crucial safety feature. Medical-grade soda lime contains a special pH indicator dye, such as ethyl violet. Soda lime is alkaline (basic), but as it absorbs acidic carbon dioxide (CO₂), its pH level drops. This chemical change triggers the indicator dye to change colour, typically from white or pink to deep violet. This visual cue instantly alerts medical staff that the soda lime is exhausted and has lost its ability to absorb CO₂, signalling that it must be replaced immediately.
6. Is soda lime a dangerous substance?
Yes, soda lime is considered a hazardous substance and must be handled with care. Its corrosive nature comes from its sodium hydroxide (caustic soda) content. Direct contact can cause severe chemical burns to the skin and eyes. Inhaling the dust can also damage the respiratory tract. Therefore, when handling soda lime, it is essential to wear personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, safety goggles, and a dust mask, and to work in a well-ventilated area.
7. Why is a mixture like soda lime used to absorb CO₂, instead of just pure sodium hydroxide?
While pure sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is a powerful CO₂ absorbent, it has significant drawbacks. The reaction is intensely exothermic (produces a lot of heat) and NaOH is highly corrosive. Adding calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)₂) to create soda lime offers several advantages:
- Safety: It moderates the chemical reaction, making it less aggressive and generating less heat.
- Durability: The lime provides a hard, porous granular structure that prevents the mixture from clumping or becoming a paste, ensuring consistent airflow.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Calcium hydroxide is less expensive than sodium hydroxide.
This makes the mixture safer, more stable, and more efficient for practical applications like anaesthesia.
8. How does soda lime help in the preparation of methane gas?
Soda lime is a key reagent in the laboratory preparation of methane through a process called decarboxylation. In this reaction, a sodium salt of a carboxylic acid (like sodium acetate) is heated with soda lime. The soda lime facilitates the removal of a carboxyl group (-COO) from the molecule. The overall reaction is:
CH₃COONa + NaOH (in presence of CaO) → CH₄ (Methane) + Na₂CO₃
Here, the sodium hydroxide part of soda lime reacts, while the calcium oxide (CaO) acts as a high-temperature stabilizer, preventing the molten NaOH from corroding the glass apparatus. This decarboxylation reaction is a standard method for producing alkanes.









