




Knowing about the Gigantic Structures on Earth - Mountains
Families begin making travel arrangements to far-off places as soon as the holiday season begins. To enjoy a fantastic holiday together, many families prefer travelling to hill stations and higher up in the mountains. Children adore it because of the beautiful views from the mountaintops and the peaceful, lovely ambiance that is surrounded by nature.

Mountains
For young children, the world is very different, especially in our modern cities, which are essentially dense jungles of concrete blocks with almost any indication of rich greenery or animals. Your child may become enthusiastic about taking another trip and explore their books or the internet for more information if you spark their interest in the development of the mountains and the different shapes the Earth takes. If you wish to introduce your child to mountains, their types and some interesting facts about mountains, keep reading through the following content.
What is a Mountain?

Mountains
A landform that peeks over its surroundings is a mountain. It typically has steep slopes, a rounded or pointed summit, and is taller than a hill. Mountains are typically found in groups. Mountain ranges are collections of mountains. Mountain belts are formed by range lines.
How are Mountains Formed?
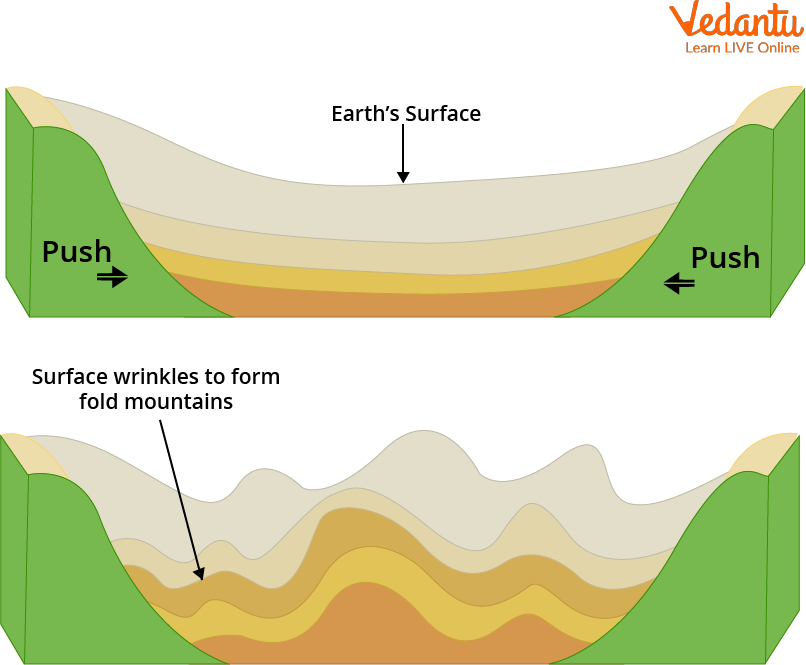
Formation of Mountains
Some mountains were created as a result of volcanic activity. Most volcanic mountains, according to scientists, are composed of rock that melted deep inside the earth.
The crust of the earth's surface was broken by the rock. Then lava began to spill out onto the surface. The lava and volcanic dust gathered to create mountains.
Mountains formed by volcanoes are often steep and cone-shaped.
Examples of volcanic mountains are Mount Fuji in Japan, Mount Kilimanjaro in Africa, and Mount Rainier in the United States.
Other mountains were created by changes in the crust of the earth. This kind of mountain construction is explained by the idea known as plate tectonics. The surface of the earth is divided into massive, slowly moving plates. The continents move with the plates as they pass over them. The rock is occasionally forced upward when the plates clash. This kind of mountain chain is shown in Asia's Himalayas. They were created when an Indian plate and an Asian plate clashed.
Different Types of Mountains

Different Types of Mountains
The following are the different types of the mountain:
Volcanic Mountains- These mountains are created as a result of the eruption of volcanoes and the movement of tectonic plates.
Fold Mountains- When two or more of the tectonic plates of the earth collide, fold mountains are formed.
Block Mountains- Block mountains are created when a fault block is raised.
Residual Mountains- Remaining mountains are created by the erosion of an elevated area. As an alternative, these structures are also referred to as mountains of rifting.
Dome Mountains- Dome mountains are produced when massive magma globules rise from the crust's interior and push up nearby rocks, causing the crust to swell in a spherical shape.
Block Mountain Formation
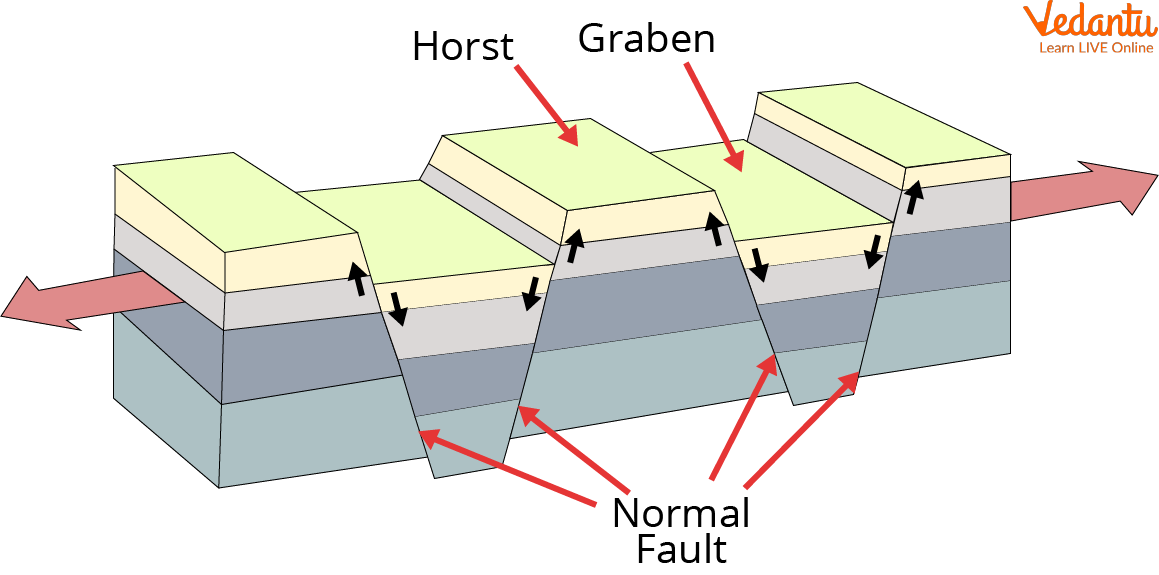
Block Mountain Formation
When two tectonic plates separate from one another, the earth's surface becomes cracked and blocks of mountains are created. Block mountains may emerge when parallel fissures or faults occur due to the raising of the strip or block of land between them. A horst is the name of the upward block. The Black Forest and the Rhineland Vosges are two examples.
Block mountain formation can also happen when two parallel faults cause the earth's crust to sink on both sides. As a result, there is a block mountain situated between two rift valleys. The term "graben" refers to the ground that is sinking. Rift valleys in East Africa are one example.
Facts about Mountains

Mountains View
The following are some amazing facts about mountains:
The majority of the world's highest mountains are found in the Himalayas, including Mount Everest, which is 8,848 metres tall and is the tallest mountain in the world.
The 8,611-metre-high K2, which is situated in Pakistan, holds the record for being the second-highest peak in the world after Mount Everest.
The UN Environmental Program estimates that mountains occupy 24% of the planet's surface.
Summary
Mountains are crucial and beneficial in many ways. It offers a place for animals and other environmentally impacting things. This is a typical item that is available everywhere. This brings our biome's impact on the environment to a close. So the next time you go on a trip to the mountains, try to identify which type of mountain it is and what kinds of plants and animals are present there.
FAQs on Learn How Mountains are Formed and the Types of Mountains
1. What exactly is a mountain?
A mountain is a large natural landform that rises high above the surrounding area. They are much taller and steeper than hills and usually have a pointed top called a peak or summit. To be called a mountain, a landform generally needs to have a significant height and steep slopes.
2. What are the main types of mountains students learn about?
Mountains are mainly classified based on how they are formed. The three main types are:
- Fold Mountains: Created when two of Earth's tectonic plates collide, causing the land to buckle and fold upwards.
- Block Mountains (or Fault-Block): Formed when cracks in the Earth's crust force large blocks of rock up or down.
- Volcanic Mountains: Built from layers of lava, ash, and rock that erupt from a volcano and pile up over time.
3. How are fold mountains, like the Himalayas, formed?
Fold mountains are formed through a powerful process of compression. Imagine pushing the two ends of a rug together—it wrinkles and folds up in the middle. Similarly, when two of the Earth's giant tectonic plates push against each other, the rock layers in between are squeezed and forced to fold upwards, creating massive mountain ranges like the Himalayas and the Alps.
4. What is the difference between how fold mountains and block mountains are created?
The main difference lies in the force that creates them. Fold mountains are formed by a squeezing or compressional force, where tectonic plates collide and push the land upwards into folds. In contrast, Block mountains are formed when the Earth's crust cracks (faults), causing large blocks of rock to be pushed up or to drop down relative to the surrounding land.
5. Are all volcanoes considered mountains?
Yes, most active and dormant volcanoes are a type of mountain called volcanic mountains. They are built up by the eruption of lava and ash which cools and hardens into a cone-like shape. So, while not all mountains are volcanoes, a volcano that rises significantly above its surroundings is indeed a mountain.
6. Why are mountains so important for life on Earth?
Mountains are vital to our planet's ecosystem. They act as natural "water towers," capturing moisture and providing fresh water for rivers that support millions of people. They are also home to a rich biodiversity of plants and animals and play a crucial role in influencing regional weather patterns.
7. How do mountains influence the weather and climate in a region?
Mountains act as large barriers to wind and moisture. When moist air from an ocean is forced to rise over a mountain range, it cools, and the moisture turns into rain or snow. This is why one side of a mountain is often very green and lush, while the other side, known as the rain shadow area, is typically much drier.









