




Key Principles and Everyday Uses of Electromagnets Explained
Electromagnets are magnets whose magnetic field is generated by electricity. The magnets used for decoration on your refrigerator are different from this type. It is made from metal materials that are permanently magnetized. These magnets are used in refrigerators because they continuously generate magnetic fields.
A permanent magnet does not create a magnetic field when it is required, like electromagnets. Scrap iron and steel are also moved and picked up using electromagnets in industry.
Electric currents produce electromagnetism. An electric wire moved near a metal compass needle in 1819, a discovery made by Danish scientist Hans Oersted.
Science considered electricity and magnetism to be separate phenomena before his discovery. The first helpful electromagnet was developed by a physicist named William Sturgeon in 1825 that could lift 9 pounds of iron.
Electricity and Magnetism
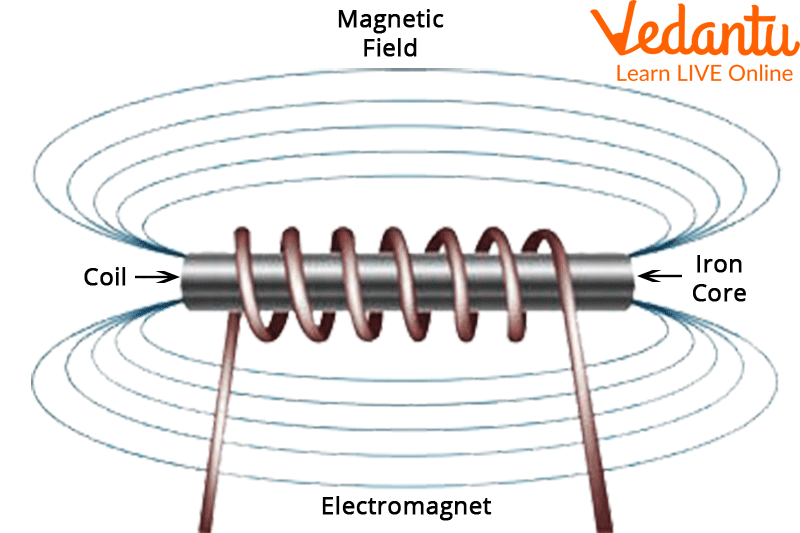
Working of Electromagnets
Permanent magnets differ from electromagnets. Electricity passes through coils of wire in electromagnets. An electromagnet behaves like a magnet when it has electric current flowing through its coils, which creates magnetic fields. Electronic devices often use electromagnets when magnetic forces are only applied for a short time.
Electromagnets work by creating a magnetic field around a wire as electricity flows through it. By Fleming's right-hand rule, if the thumb, first finger, and second finger are perpendicular to each other (right angle), the thumb represents magnetic thrust, the first finger represents a moving particle, and the second finger represents an induced magnetic field.
There are two names for this rule: dynamo rule or generator rule. The right-hand rule can be used to determine the magnetic field's direction. One wire produces a weak magnetic field. Wires are wrapped in loops to combine the magnetic fields of each to create an electromagnet with a stronger magnet.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Electromagnets
Advantages:
A magnet is very useful when poles need to change and magnetic fields need to be interrupted. Electromagnets are used effectively in magnetic separators. By magnetizing scrap metal, it attracts scrap iron from a pile, and when the current is stopped, it drops the scrap at another location.
To get iron scrap, we use a magnetic separator. Another advantage of electromagnets is their affordability and ease of construction. Their lightweight design avoids damaging the electromagnet's test piece. The use of electromagnets daily is diverse.
Large cranes used in waste yards, for instance, use electromagnets. Electronic and electromechanical devices also use electromagnets.
Disadvantages:
A disadvantage of electromagnets is that they heat up very quickly, which results in a very high loss of energy. Maintaining a constant magnetic field is necessary for a continuous power supply.
Maintaining a constant magnetic field is essential for a continuous power supply. Coils of copper wire are required to generate a strong magnetic field, which requires large amounts of space. Small spaces are not suitable for electromagnets. Because electromagnets generate magnetic fields, short-circuits can damage them and cause serious harm to operators.
Is There a Perfection to be Produced between a Perpetual Attraction and an Electromagnet?
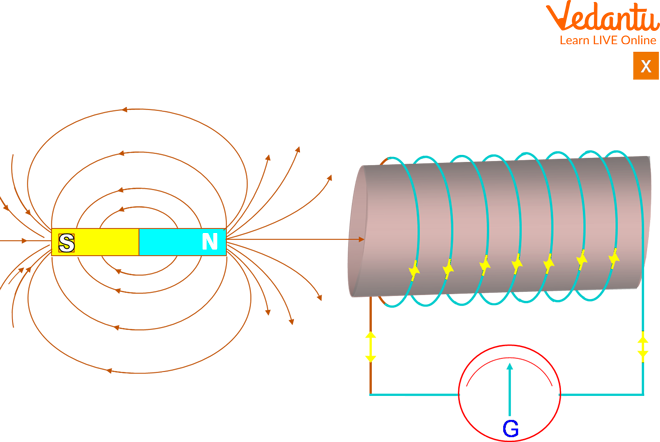
Electromagnet and Permanent Magnet
Permanent Attraction:
There is always a magnetic field present around a permanent magnet. Magnetic materials maintain their magnetic properties for an extended time. Some rare earth alloys, for example, contain iron, nickel, cobalt, etc.
The South-North opposition to an endless attraction is fixed. It can not be changed.
Its energy can not be remade.
Electromagnet:
The South-North opposition of an electromagnet can be altered by changing the direction of the current in the coil.
Its strength can be remade by changing the usual run through it or by changing the number of ranges in it.
The Electromagnetic Field and the Right-Hand Rule
When electricity flows in a long straight line, it creates an indirect or spherical glamorous field around the line according to the right-facet rule, which means the galettes show the direction of the electromagnetic field generated, and the thumb points to the direction of electrons or current flowing in.
Uses of Electromagnetism
Permanent attractions produce much more glamorous fields than electromagnets.
The power of the electromagnets can be acclimated by changing the quantum of current flowing through them.
Electromagnets find their use in numerous effects that we use in our everyday lives.
They're used in cell phones that work on the commerce between the phone signals and raising weighty loads.
Summary
Electromagnets are truly simple to make, and they can be contained. They aren’t dangerous. They're more useful than regular attractions, and they work with electricity. The glamorous material is made of soft iron and we want them all the time. After conducting all the trials, Faraday eventually concluded that if the relative movement was between a captain and a glamorous field, the flux relation with a coil was remade and this change in fluctuation produced a voltage across a coil.
FAQs on How Does an Electromagnet Work?
1. What is an electromagnet in simple terms?
An electromagnet is a type of magnet where the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. Unlike a regular fridge magnet, it is temporary and can be switched on or off simply by controlling the flow of electricity.
2. How does an electromagnet work?
An electromagnet works on the principle that electricity in motion creates magnetism. Here’s a simple breakdown:
- An insulated wire, usually made of copper, is wrapped tightly to form a coil.
- An electric current from a source like a battery is passed through this coil.
- This moving current generates a magnetic field around the wire, turning the coil into a magnet.
- Placing a piece of iron (called a core) inside the coil makes this magnetic field much stronger.
3. What is the main difference between a permanent magnet and an electromagnet?
The biggest difference is control. A permanent magnet has a constant magnetic field that is always on. An electromagnet is temporary; its magnetism only exists when an electric current is flowing. You can turn it on, turn it off, and even change its strength, which is not possible with a permanent magnet.
4. How can I make a simple electromagnet at home?
You can create a basic electromagnet with an iron nail, insulated copper wire, and a battery. First, wrap the copper wire tightly around the iron nail many times, leaving both ends of the wire free. Then, connect one end to the positive (+) terminal and the other to the negative (-) terminal of the battery. The nail will become a magnet and can attract small metal items like paper clips.
5. What factors can make an electromagnet stronger?
You can increase the strength of an electromagnet in three main ways:
- Increase the current: More electricity flowing through the wire creates a stronger magnetic field.
- Add more coils: The more times you wrap the wire around the core, the stronger the magnet becomes.
- Use a soft iron core: Placing a soft iron core inside the coil significantly boosts the magnet's power.
6. Why does an electromagnet stop being a magnet when the electricity is turned off?
The magnetic field of an electromagnet is entirely created by the moving electric current. When you turn off the power, the current stops. Without the current, there is nothing to align the magnetic domains inside the core material, so it almost instantly loses its magnetism.
7. What are some common examples of electromagnets used in daily life?
Electromagnets are essential in many everyday devices. You can find them in electric bells, speakers, computer hard drives, and medical equipment like MRI machines. They are also used in large industrial cranes that lift heavy scrap metal.
8. Why is a soft iron core used inside an electromagnet instead of steel?
A soft iron core is ideal because it magnetises strongly when the current is on but loses its magnetism very quickly when the current is turned off. Steel, however, tends to stay magnetised even after the power is cut. This property makes steel unsuitable for devices that need to be switched on and off reliably.
9. Why do we use a coil of wire instead of a straight wire to make an electromagnet?
A single straight wire creates a very weak magnetic field. By winding the wire into a coil, the magnetic fields from each individual loop add together. This concentration of magnetic field lines creates a much stronger and more useful magnet, especially in the area inside the coil.









