




What Makes a Material a Good or Bad Conductor?
Every material is unique and has unique qualities and traits. Electrons, which are charged electrically, are present in some materials. Specific locations on the material are charged with electrons, which cause the electrons to travel and cause electricity to flow through it. Conductivity is the property of a material that allows electricity to flow through it. Materials are categorised as conductors, insulators, or superconductors based on their conductivity.
Materials with high electron mobility are known as conductors, while those with low electron mobility are referred to as insulators. A good conductor of electricity is characterised as having a relatively simple electron flow. Let's learn about the characteristics of the most outstanding electrical conductor in this post.
Good and Bad Conductors
What is an Electrical Conductor?
The simplest definition of an electrical conductor is a material that makes it easy for electricity to go through it. A substance is said to be a good conductor of electricity when the substance is compared to another type of material, the first one permits a better flow of electricity through it.
Several types of electrical conductors include the following:
Copper
Aluminium
Silver
Gold
Graphite
Platinum
Water
People
Electric charges can easily pass through an electrical conductor. Conductivity is the ability of conductors to "conduct" electricity. Such materials provide less barrier to the movement of charges. Due to the unrestricted flow of electrons through them, conducting materials make it simple to transfer charges.
Bad Conductors of Electricity
Materials known as insulators have the exact opposite effect on the movement of electrons as do conductors. They make it difficult for electrons to move smoothly between atoms. Materials that have strongly bonded electrons in their atoms are called insulators. These electrons can't just go around and share space with nearby atoms.
Examples of Bad Conductors
Materials like glass, plastic, rubber, air, and wood are used as insulators.
We are shielded by insulators from the potentially harmful effects of electricity passing through conductors. Electrical circuits can occasionally have dangerously high voltage levels. Even materials that aren't typically thought of as good conductors can be made to conduct electricity when the voltage is high enough.
Several types of electrical bad conductors include the following:
Plastic
Rubber
Cloth
Polythene
Wood
Our Body as a Conductor
Our bodies will be electrically conductive and you might have already had this happen to you when you got an electrical shock. Generally, electricity hurts and is unpleasant to flow through the body. A powerful electrical shock and the current it produces can both impair the function of our hearts and can result in burns. Consequently, we must protect our bodies from the conductors, which transport electricity.
The rubbery layer on wires acts as an insulator to keep us from being exposed to the conductor inside. You can see the insulator in any lamp cord if you look closely. It's probably time to replace the cord if you can see the conductor.
Summary
Silver in particular makes metals excellent electrical conductors. Since copper is less expensive than silver, electrical wiring covering millions of kilometres is produced using it every year. Glass and plastic are examples of insulators since they are poor electrical conductors. They are employed to prevent electricity from passing into areas of our bodies where it is unsafe or unnecessary. The plastic covering on cables allows us to handle them safely.
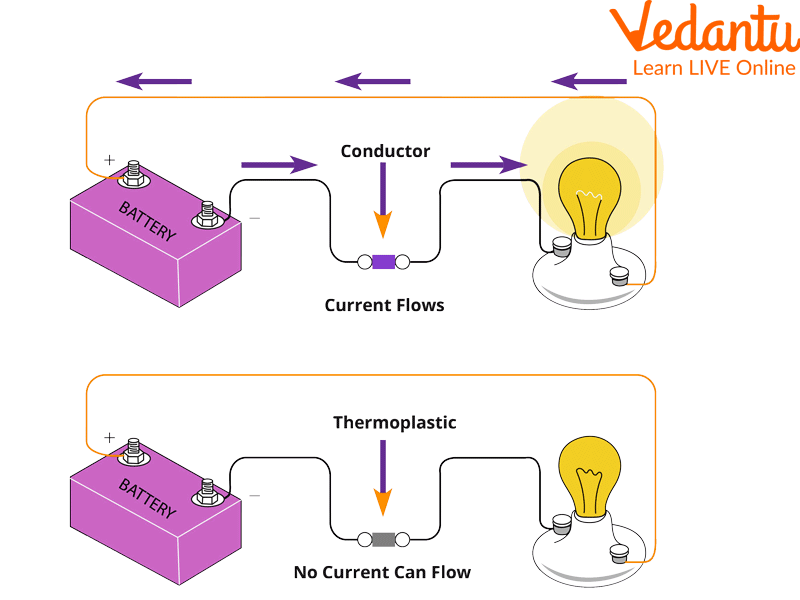
Bulb Experiment
FAQs on Good and Bad Conductors of Electricity Made Simple
1. What are good and bad conductors of electricity?
Materials that allow electric current to pass through them easily are known as good conductors of electricity. This is because they have free-moving charged particles, typically electrons. In contrast, materials that do not allow electric current to pass through them easily are called bad conductors or insulators. Their electrons are tightly bound to atoms and cannot move freely.
2. What are some common examples of good and bad conductors?
Examples of good conductors and bad conductors (insulators) are commonly found in everyday life.
- Good Conductors: Most metals are excellent conductors, including copper, silver, aluminium, gold, and iron. Graphite (a form of carbon) and tap water are also good conductors.
- Bad Conductors (Insulators): Common examples include rubber, plastic, wood, glass, cloth, and pure (distilled) water.
3. What is the main difference between good and bad conductors at the atomic level?
The primary difference lies in their atomic structure and the behaviour of their valence electrons (the outermost electrons). In good conductors like metals, these electrons are loosely held and form a 'sea of delocalised electrons' that can move freely throughout the material. When a voltage is applied, these free electrons flow, creating an electric current. In bad conductors or insulators, the valence electrons are tightly bound to their individual atoms and are not free to move, thus preventing the flow of electricity.
4. Why are metals generally good conductors of electricity?
Metals are good conductors due to their unique metallic bonding. The atoms in a metal lattice readily release their outermost electrons, which become delocalised and form a collective 'sea of electrons'. These electrons are not tied to any single atom and are free to move throughout the entire metal structure. This high mobility of free electrons allows metals to efficiently carry an electric charge when a potential difference is applied.
5. Why is pure water a bad conductor, but tap water conducts electricity?
This difference is due to the presence of dissolved impurities. Pure water (H₂O) is a very poor conductor because it has an extremely low concentration of free ions. However, tap water contains dissolved salts and minerals from its source. These substances dissociate into positive and negative ions (like Na⁺, Ca²⁺, Cl⁻) in the water. These mobile ions act as charge carriers, allowing tap water to conduct electricity effectively.
6. What is the only non-metal that is a good conductor of electricity?
The only non-metal that is a good conductor of electricity is graphite, which is an allotrope (a specific structural form) of carbon. Its conductivity is due to its unique layered structure. Within each layer, carbon atoms are strongly bonded, and there are delocalised electrons that are free to move along the layers, similar to electrons in a metal. This allows graphite to conduct electricity.
7. Why is our body considered a conductor and what are the safety implications?
Our body is considered a conductor because it is composed of approximately 70% water containing dissolved salts and electrolytes, which form ions. These ions allow electric current to flow through our tissues. The key safety implication is that touching a live electrical source can cause a dangerous current to pass through the body, resulting in electric shock, severe burns, or disruption of vital functions like heartbeat. This is why electrical wires are covered with insulators like plastic or rubber to prevent accidental contact.
8. Can a material act as both a conductor and an insulator?
Yes, certain materials called semiconductors can behave as both. Materials like silicon and germanium act as insulators at very low temperatures because their electrons are not free to move. However, their conductivity can be significantly increased by adding specific impurities (a process called doping) or by increasing the temperature. This ability to control their conductive properties makes them fundamental components in electronic devices like transistors and diodes.









