




Why Understanding the Brain Stem Matters for Students
The complex organ known as the brain regulates every bodily function, including cognition, memory, emotion, touch, motor skills, vision, respiration, temperature, and hunger. The central nervous system, or CNS, is made up of the spinal cord that emerges from the brain. The human brain, the pinnacle of biological evolution, supports thoughts, memory, movement, and emotions through a complex set of functions. It also serves as the nervous system's command centre. The major goal in pursuing health and longevity is to keep one's brain in good shape for the duration of one's life. In this article, we are going to discuss parts of the brain and how it communicates. There will be other information present in this article which you have to give a thorough read. So let's dive in and learn more about the brain stem.
Brain
Brain Stem Fun Facts
The human brain is composed of 60% fat. This makes the brain the fattest organ in the body, and these fatty acids are essential for the functioning of the brain. Make sure you're providing it with the right kind of nutritious, brain-enhancing food. Your brain hasn't fully matured by the time you're 25. The front of the brain develops first, with the back of the brain starting the process. Your frontal lobes, which govern reasoning and planning, are therefore the last to develop and organise connections.
Your brain has virtually infinite storage space for information. To control balance, breathing, heart rate, and other bodily functions, the brainstem communicates with the rest of your body. According to research, the human brain contains 86 billion neurons. One quadrillion (1,000 trillion) connection between neurons could be formed by each neuron. These neurons may merge over time, expanding the available storage. However, many neurons may suffer damage and cease to function in Alzheimer's disease, impacting memory in particular.
The remarkable speed at which brain information can move is 268 miles per hour. An electrical impulse is produced when a neuron is triggered and it moves from cell to cell. An epileptic seizure may result from an interruption in this usual processing.
Parts of Brain
The largest portion of the brain is the forebrain. The front of the brain is where it is situated. The parts of the frontal lobes are:
Cerebrum
Hypothalamus
Thalamus
Midbrain: The middle and smallest portion of the brain.
The midbrain is made up of:
Tectum
Tegmentum
Lower back of the brain, or hindbrain.
The parts of the hindbrain include:
Cerebellum
Medulla
Pons
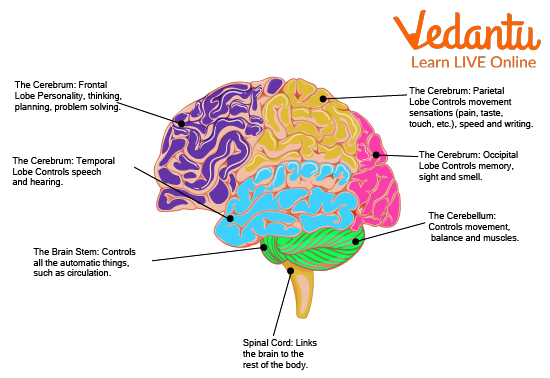
Parts of Brain
Communication of Brain
A signal is delivered to your brain's sneeze centre when something enters your nose, such as bacteria, dust, or pollen. The sections of your body that must cooperate in order to assist you to sneeze receive signals from the sneeze centre. The sneeze centre signals your throat, eyes, and mouth to close tightly. While your throat muscles are relaxed, your chest muscles constrict and squeeze your lungs. All of it causes your nose and mouth to be forced to release air, saliva, and mucus.

Communication of Brain
Brain Stem Interesting Facts
Your brainstem is the stalk-like bottom portion of your brain. It links your spinal cord and brain. The brainstem communicates with the rest of your body in order to regulate balance, respiration, heart rate, and other basic functions. Your brainstem's functionality may be impacted by sudden trauma, heart or brain problems, or both. The basic processes of the brainstem include the control of breathing, eating, sleeping, and heart rate. It contributes to conduction as well. The brainstem is the necessary conduit for all signals travelling from the body to the cerebrum and cerebellum and vice versa.
Summary
To conclude all the conceptual understanding regarding the brain in this article, we can say that the mass of nerve tissue in an organism's head is known as the brain. The brain controls movement, integrates sensory information, and, in higher animals, is the centre of learning. The human brain weighs roughly 1.4 kg and contains billions of neurons (3 pounds). Since we have all the necessary facts about the brain, this information will help you in the further study of Biology. We hope you enjoyed reading this article, in case of any other doubts, feel free to ask in the comments.
FAQs on Essential Facts About the Brain Stem
1. Where is the brain stem located in our body?
The brain stem is located at the very bottom of the brain, right where the brain connects to the spinal cord. You can think of it as the stalk of a flower, where the main part of the brain is the blossom. It sits deep inside your head, protected by the skull.
2. What is the main job of the brain stem?
The main job of the brain stem is to act as the body's automatic control centre. It manages all the essential functions you don't have to think about, such as breathing, your heartbeat, and blood pressure. It also acts as a messenger, passing signals between the brain and the rest of the body.
3. Can you share some fun facts about the brain stem?
Of course! Here are some interesting facts about the brain stem:
- It's one of the oldest parts of the brain in terms of evolution.
- It keeps working even when you are fast asleep, making sure you keep breathing.
- It's only about the size of your thumb but is incredibly powerful and essential for life.
4. What are the different parts of the brain stem and what do they do?
The brain stem is made up of three main parts, each with a special job:
- The Midbrain: Helps control eye movement and processes what we see and hear.
- The Pons: Acts as a bridge, relaying messages between different parts of the brain. It's also involved in sleep and facial movements.
- The Medulla Oblongata: This is the lowest part, controlling vital life functions like breathing, heart rate, and swallowing.
5. Which part of the brain stem connects to the spinal cord?
The medulla oblongata is the part of the brain stem that directly connects to the top of the spinal cord. This connection is crucial because it creates a continuous pathway for messages to travel from the brain down to the body and back again.
6. Why is the brain stem so important for our survival?
The brain stem is absolutely vital for survival because it controls the life-support systems of our body. Without it, we couldn't breathe, our heart wouldn't beat, and we wouldn't be able to swallow. Because it manages these non-stop, automatic tasks, it allows the rest of our brain to focus on higher-level activities like thinking, learning, and feeling.
7. Why is the brain stem sometimes called the 'lizard brain'?
The brain stem is often called the 'lizard brain' or 'reptilian brain' because it controls the same basic survival functions that are found in the brains of reptiles, like lizards. These are the most instinctive and primitive functions, such as breathing, heart rate, and the fight-or-flight response, which have been present for millions of years of evolution.
8. Is the cerebellum part of the brain stem?
This is a common point of confusion! The cerebellum is not part of the brain stem, but it is located very close to it, at the back of the brain. While the brain stem manages automatic functions, the cerebellum is mainly responsible for coordinating movement, balance, and posture. They work together closely, but they are separate structures.
9. Does the brain stem work even when we are asleep?
Yes, absolutely! The brain stem is always active, 24 hours a day. When you are asleep, it continues to manage your breathing and heart rate, which is why you don't have to wake up to remind yourself to breathe. It also plays a key role in managing our sleep-wake cycles.









