




How Does Energy Transformation Work? Understanding Through Real-Life Scenarios
Energy is all around us, but how do we transform it? One of the ways that energy is transformed is through what we call a power plant. As electrical energy flows from the plant through the transmission lines to our homes and businesses, it continually undergoes transformation until it reaches its final form as usable electricity. Energy Transformation is a process in which one form of energy is transformed into another. Find out in this article about various instances of the transformation of energy around us and how they are transformed!
What is Transformation of Energy?
An energy transformation is the change of energy from one form to another. Energy transformations occur everywhere every second of the day. There are many different forms of energy such as electrical, thermal, nuclear, mechanical, electromagnetic, sound, and chemical. A coal-fired power plant involves these energy transformations: Chemical energy in the coal is converted into thermal energy in the exhaust gases of combustion. Thermal energy of the exhaust gases converted into thermal energy of steam through heat exchange.
Electrical Energy
The types of energy can generally be divided into two types - kinetic energy and implicit energy. Movement results in kinetic energy, which is the energy that an object has. Energy is the capability to do work. It's the power that exists far and wide in numerous forms. A major source of energy is light, which is composed of light, chemical, mechanical, nuclear, electrical, and sound components.
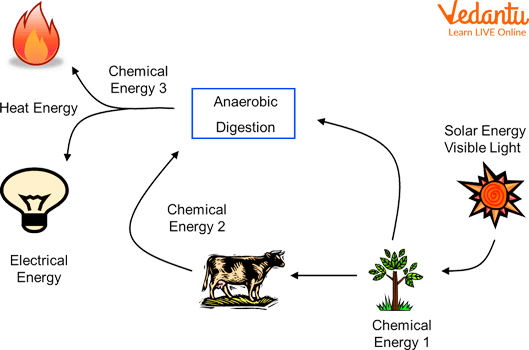
Energy Conservation
Energy is used up! Energy isn't created or destroyed. It just changes into a different form. This is called Energy Transformation. Some energy is stored in batteries.
Natural Energy
The Sun is Earth’s primary source of energy. In addition to nuclear energy, solar electromagnetic energy is constantly being converted into light energy. This energy peregrination enters through space.
Engineered Energy Transformations
People have constructed numerous ways to beget energy metamorphoses. For example, people control how electrical energy is formed and where it goes so that it can be changed into light energy.
Light and heat are generated by electrical energy entering a light bulb. Energy wasted as a result of heat is considered wasteful.

Sun
These are remains of ancient trees and shops that grew hundreds of millions of times ago. They turn into coal, oil painting, and gas.

Coal, Gas, and Water
Reactionary energies produce heat energy when we burn them.
Reactionary Energies
That makes hot water turn into brume. The heat energy of the brume turns into stir energy.
Electricity Energy
Electricity Energy:
It also comes into our places through cables.
In a heater, it turns into warm energy.
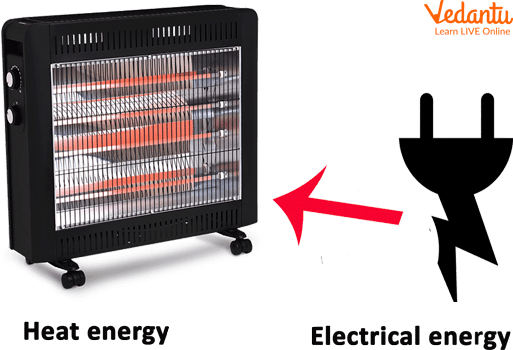
Electricity Energy Transformation into Heat Energy
In a TV, it turns into light and sound energy.

Electricity Energy Transformation into Light and Sound Energy
Various Instances of Transformation of Energy Around us
Following are the list of various instances of transformation of energy around us:
Electrical energy is converted into thermal energy by a toaster.
An electric blender converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
Nuclear energy is converted by the Sun into ultraviolet, infrared, and gamma energy, which are all kinds of electromagnetic energy.
To move, our bodies transform chemical energy from food into mechanical and electrical energy.
A natural gas stove turns the chemical energy released after combustion into thermal energy that is utilised to cook food.
So, these are the energy transformation examples in daily life, which we see at our home and neighbour places.
Energy Transformation Worksheet
For the following energy transformation worksheet questions, write an explanation for each energy transformation:
1. Flashlight
Ans: When you switch on the torch flashlight, the circuit closes. Chemical energy is turned into electrical energy in cells. The electrical energy that travels through the torch bulb is subsequently converted into light energy, and the torch bulb shines.
2. Speaking into a Telephone.
Ans: The sound waves are transported to a diaphragm, a thin metal disc inside the phone, and converted into electrical energy. The electrical energy goes via cables to another phone and is changed back to electrical energy, which can be heard by the person on the other end of the phone!
3. Solar Panel
Ans: Solar technologies use photovoltaic (PV) panels or mirrors to concentrate solar radiation to convert sunlight into electrical energy. This energy can be converted into electricity or stored in batteries or thermal storage.
Summary
As solar panels allow for light energy to convert into heat and electrical energy. Imagine you can power a useful machine using energy that's formerly being expended. For example, a cyclist is riding a bike at home for exercise, but the cyclist is also powering a toaster oven. In this illustration, the cyclist is expending energy on the bike, but the moving pedals can also transfer energy to a battery, or by using a pulley system. Use this study trial to imagine how energy can be transferred to produce stir or power a machine. Also, consider how energy can be used to perform useful tasks, with the help of a machine.
FAQs on Energy Transformation: Meaning, Types & Examples
1. What is meant by the term energy transformation?
Energy transformation, also known as energy conversion, is the process of changing energy from one form to another. This fundamental principle explains how energy is utilised in the universe. For example, a ceiling fan is designed to convert electrical energy into the mechanical energy of its rotating blades, which in turn moves the air.
2. What is the Law of Conservation of Energy?
The Law of Conservation of Energy states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed; it can only be transformed from one form to another. This means that in any closed system, the total amount of energy before and after a transformation remains exactly the same. Even when energy seems to be 'lost,' it has simply been converted into another form, such as heat or sound.
3. Can you provide some common examples of energy transformation in our daily lives?
Certainly. Energy transformations are happening all around us. Here are a few common examples:
Lighting a Bulb: Electrical energy is transformed into light energy and heat energy.
Running: The chemical energy stored in our body from food is converted into kinetic (movement) energy.
Using a Microwave: Electrical energy is transformed into microwave radiation (a form of electromagnetic energy) to heat food.
Photosynthesis: Plants convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy stored in glucose.
4. What are the main types of energy involved in these transformations?
Energy exists in many forms, but the main types commonly involved in transformations include:
Mechanical Energy: The energy of motion (kinetic) or position (potential).
Chemical Energy: Energy stored in the bonds of atoms and molecules.
Electrical Energy: Energy from the flow of electric charge.
Thermal Energy (Heat): The internal energy of a system due to the temperature.
Radiant Energy: Energy that travels in waves, such as light or sound.
Nuclear Energy: Energy stored in the nucleus of an atom.
5. How is energy transformation different from energy transfer?
This is a key distinction. Energy transfer is the movement of energy from one object or system to another, where the form of energy often stays the same (e.g., heat transferring from a hot pan to your hand). In contrast, energy transformation is the conversion of energy from one form into a different form (e.g., a battery converting chemical energy into electrical energy). A process can involve both; for example, a power plant transforms chemical energy into electrical energy, which is then transferred through wires to your home.
6. How does a hydroelectric power plant illustrate energy transformation?
A hydroelectric power plant is an excellent large-scale example of sequential energy transformations:
First, water stored behind a dam possesses gravitational potential energy due to its height.
When the water is released, this potential energy is converted into kinetic energy as the water flows downwards.
The moving water strikes the blades of a turbine, converting its kinetic energy into the mechanical energy of the spinning turbine.
Finally, the turbine is connected to a generator, which transforms this mechanical energy into electrical energy that can be distributed to homes and businesses.
7. Why is understanding energy transformation important for studying science?
Understanding energy transformation is crucial because it is a unifying concept that connects different branches of science. In Physics, it explains how machines work and how heat and motion are related. In Chemistry, it explains the energy changes during chemical reactions. In Biology, it is fundamental to understanding processes like photosynthesis and cellular respiration, which are the basis of life on Earth. It helps us see the world as an interconnected system governed by the flow and conversion of energy.
8. If energy cannot be destroyed, why are we always told to 'conserve energy'?
This is an excellent question. While the total amount of energy is always conserved, its usefulness can decrease. During every transformation, some energy is inevitably converted into a less useful, dissipated form, usually as waste heat lost to the surroundings. For example, a car engine converts only a fraction of the chemical energy in fuel into kinetic energy; the rest is lost as heat. 'Conserving energy' really means reducing the consumption of primary energy resources (like coal and oil) and improving the efficiency of our devices to minimise the amount of energy converted into these non-useful forms.









