




How Boiling and Condensation Shape Everyday Life
Today, we will learn about boiling and condensation. Boiling is the method in which a liquid state turns into a gaseous state. Heating water into steam is the best example of understanding the boiling process. When liquid is heated, then it turns into vapour. When the liquid turns into a gas state, then more heat is required.
Boiling and Condensation
In Science, condensation is the process where water vapour turns into liquid. In this process, cooling takes place. Condensation methods are advantageous for cleaning low-flow, highly concentrated exhaust gas streams. In this article, we will learn about boiling and condensation in detail.
What is Boiling?
In Chemistry, when a liquid is heated to its boiling point, this phase change is known as boiling. It takes place by changing the liquid state into the gas state. When a liquid reaches its boiling point, then the pressure exerted on its surface by the atmosphere is equal to the liquid's vapour pressure.
Boiling is a physical transformation in which the molecules are not chemically changed. Boiling occurs when atoms or molecules in a liquid are able to fully separate from transitioning from a liquid to a gaseous state.
The temperature at which a particular liquid starts to boil is known as the boiling point. For example, water has a boiling point of 100ºC at 1 atm of pressure. A liquid's boiling point is affected by temperature, air pressure, and the liquid's vapour pressure.
Boiling occurs when the liquid's vapour pressure and air pressure are equal. The more powerful molecules become gas, spread out, and create bubbles when boiling takes place. These come to the surface and soar into the sky.
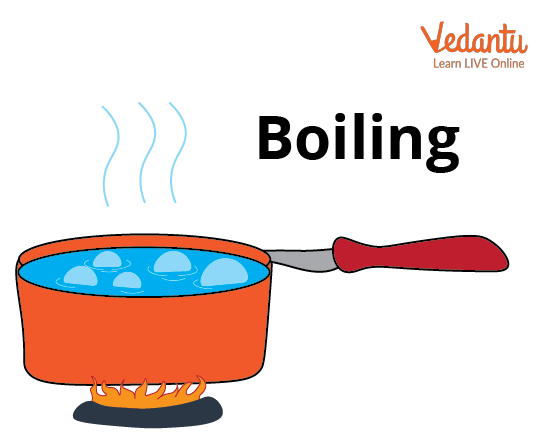
Boiling of Water
What is Condensation?
In Science, condensation is the process where water changes from its gaseous state to its liquid state.
The water cycle is a mechanism that shows how water transforms inside the Earth's atmosphere. The process of water changing from a gaseous state to a liquid state is known as condensation, which is the opposite phase of evaporation.
In the atmosphere, water exists in three states: solid, liquid, and gas. Since molecules are spread out across a large volume of space, they turn into a gas at a temperature of 100°C. Gas has a loose molecular structure. The molecular structure of the liquid, such as water, is more packed than that of gas because the molecules are packed closer together over a smaller surface area. At 20°C, the water turns liquid. Solids such as ice have extraordinarily tight molecular structures and at 0°C, water turns to ice.
Example
As the water vapour cools in the sky, clouds are created. Tiny water droplets form when the temperature of the water vapour reaches the dew point or lower. These droplets condense onto small dust particles to form clouds.
Summary
In this article, we learned that Evaporation and Condensation are two crucial steps of the water cycle. Evaporation is defined as the conversion of liquid to gas and escaping into the air whereas condensation refers to the conversion from gaseous to a liquid state. Both of the processes discussed above carry out opposite conversions of matter.
FAQs on Boiling and Condensation Made Easy
1. What is the basic definition of boiling?
Boiling is a specific type of vaporization where a liquid turns into a gas when it is heated to a specific temperature, known as the boiling point. It is a 'bulk phenomenon', meaning bubbles of gas form throughout the entire volume of the liquid, not just at the surface. This process occurs when the liquid's vapour pressure becomes equal to the pressure of the surrounding atmosphere.
2. What is condensation and how does it happen?
Condensation is the process where a substance in a gaseous state, like water vapour, changes to its liquid state. It is the reverse of vaporization. This change typically occurs when the gas is cooled to its dew point, causing the gas particles to lose energy, slow down, and come close enough to form a liquid.
3. What is the main difference between boiling and condensation?
The main difference lies in the change of state and energy transfer. Boiling is the change from a liquid to a gas, which requires the absorption of heat energy (an endothermic process). In contrast, condensation is the change from a gas to a liquid, which involves the release of heat energy (an exothermic process).
4. How is boiling fundamentally different from evaporation?
While both processes change a liquid to a gas, they are different in key ways.
- Temperature: Evaporation can happen at any temperature below the boiling point, whereas boiling only occurs at the specific boiling point.
- Location: Evaporation is a surface phenomenon, happening only at the liquid's surface. Boiling is a bulk phenomenon, occurring throughout the entire liquid.
- Speed: Evaporation is generally a slow and silent process, while boiling is a fast and often violent process that forms bubbles.
5. Why do boiling and condensation occur at the same temperature for a substance?
Boiling and condensation occur at the same temperature because they represent two sides of the same phase transition. This temperature, like 100°C for water at standard pressure, is the equilibrium point where the liquid and gas phases can coexist. To boil, the substance must absorb a specific amount of energy (latent heat of vaporization) to turn into gas. To condense, it must release that exact same amount of energy to turn back into a liquid.
6. What are some real-world examples that show condensation in action?
You can see examples of condensation all around you. Common examples include:
- Water droplets forming on the outside of a cold glass or bottle.
- The formation of dew on grass and leaves in the morning.
- Your bathroom mirror 'fogging up' after a hot shower.
- The formation of clouds in the sky as water vapour cools at high altitudes.
7. How does a pressure cooker use the principles of boiling to cook food faster?
A pressure cooker works by increasing the boiling point of water. The sealed lid traps steam, which builds up the pressure inside the pot. As external pressure increases, the water needs to reach a higher temperature to boil (well above 100°C). This higher cooking temperature significantly speeds up the chemical reactions that cook the food, making the process much faster than boiling in an open pot.
8. Why does water in high-altitude clouds often remain liquid even if the temperature is below 0°C?
This phenomenon is known as supercooling. For water to freeze, its molecules need a nucleus, like a tiny dust or pollen particle, to arrange themselves into a crystal structure. In the very clean air of high altitudes, these nuclei can be scarce. As a result, water droplets can remain in a liquid state even at temperatures below their normal freezing point of 0°C, a state known as being supercooled.





















