




Core Grammar Topics for Class 5 Students Explained
Grammar is called the system and structure of a language. The rules of grammar let us decide the order we put words in and which form of a word to use.
In this article, we will discuss the basics of English Grammar, like how a sentence forms, the rules for writing a grammatically correct sentence, transitive verb and intransitive verb, active voice and passive voice with their sentence structure, and noun and its types. Parents should refer to the English Grammar for Class 5 PDF for details on every topic.
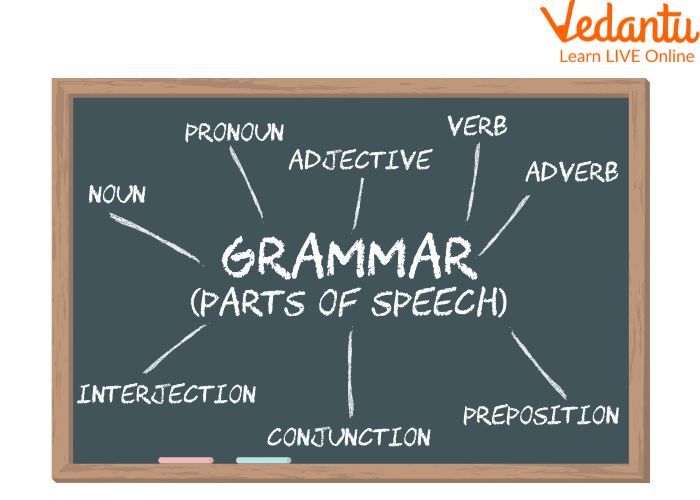
All Parts of Speech
Class 5 English Grammar - The Sentence
When we write or speak, we try to group sensible words to convey a clear, meaningful message. In fact, grouping is not sufficient; these words need to be in proper order and sequence for clear understanding. Words arranged in order should express a complete sense of meaning.
Read the following sentences:
Useful is a spoon utensil.
A spoon is a useful utensil.
Are they different?
Rules to Make a Sentence
A sentence is a group of words forming a meaningful message.
A sentence always makes clear sense.
A sentence always starts with a capital letter and ends with a full stop, question mark, or exclamation mark.
A sentence must consist of a word i.e. verb.
Now read these Group of Words:
In the glass.
A glass of milk.
The above words make sense but not completely. These groups of words are called phrases.
Kind of Sentences
Sentences are of four types:
Assertive Sentences
Imperative Sentences
Interrogative Sentences
Exclamatory Sentences
1. Assertive Sentences - These are also called declarative sentences, which declare a fact. They end with a full stop.
Examples:
I'm going to play.
2. Imperative Sentences - These sentences give a command, make requests or express a wish.
Examples:
Go to your office. (Order)
Please lend me your book. (Request)
Have a safe ride. (wish)
3. Interrogative Sentences - These sentences are used to ask questions. They end with a question mark.
Examples:
Who has broken my pencil?
4. Exclamatory Sentences - These sentences express sudden or strong feelings such as wonder, surprise, wonder, happiness, etc. They often end with an exclamatory mark.
Examples:
That was ridiculous!
Active and Passive Voice
Sentences can be of two types: active and passive voice.
Ram is eating a mango.
A mango is being eaten by Ram.
What’s the difference between them?
In sentence 1, the subject (Ram) is the doer of the action i.e. the subject of the verb acts or is active. The verb, eating is, therefore, said to be in the Active voice.
Structure: Subject + verb + object.
In sentence 2, the subject (mango) is the receiver of the action. Here, the subject of the verb does not perform the action or is passive.
Structure: Object + verb + subject.
Girl Depicting Parts of Grammar
Verb - Transitive or Intransitive
The verb is a part of speech that depicts action. It tells what is happening or what is done at the moment.
Transitive Verb
The lion was killed.
This sentence doesn’t make complete sense.
The lion killed a deer.
So, here it makes sense, the verb which requires an object after it is called the transitive verb.
Intransitive Verb
The tree grows.
It makes complete sense. Here the verb “grows” doesn’t require any object after it to make a meaningful sentence.
Noun
The noun is a reference to a place, person, or thing. When this is one, they are called singular nouns, and when they are multiple, they are called plural nouns.
For example- boy, pen, a copy is singular nouns, and boys, pens, and copies are plural nouns.
Class 5 English Grammar Worksheets with Answers
He _____ never forgotten his bottle. (Ans. has)
I ______ played cricket. (Ans. have)
Convert into passive voice: Rahul is playing cricket. (Ans. Cricket is being played by Rahul)
Write five plural nouns. (Ans. Books, Pencils, Bottles, Boxes, Cups)
Write one interrogative sentence. (Ans. How was your day?)
Summary
In this article containing English Grammar for Class 5 PDF, we discussed the sentences, verbs, voice, and nouns, which are basics of English Grammar. The given worksheet will help you to identify the types of questions related to grammar with their answers provided. A sentence is a complete sense, made up of words arranged in an order to convey a meaning, or thought.
The basic rules of making a sentence are:
The sentence should begin with a capital letter and end with a full stop.
A sentence must consist of a doing word i.e. verbs.
The words should be arranged in order to convey a clear meaning i.e. sentence structure.
FAQs on Class 5 English Grammar: Learn and Master Essential Concepts
1. What is English Grammar and why is it important for a Class 5 student to learn?
English Grammar is a set of rules that helps us to arrange words correctly to form meaningful sentences. For a Class 5 student, learning grammar is very important because it teaches you how to read, write, and speak English clearly. It is the foundation for building strong communication skills for the future.
2. What are the main grammar topics covered in the CBSE Class 5 English syllabus for 2025-26?
According to the CBSE syllabus for 2025-26, the key grammar concepts for Class 5 students include:
- Parts of Speech: Nouns, Pronouns, Verbs, Adjectives, Adverbs, Prepositions, and Conjunctions.
- Sentences: Understanding the types of sentences (Declarative, Interrogative, Imperative, Exclamatory).
- Tenses: Introduction to Simple Present, Simple Past, and Simple Future tenses.
- Punctuation: Correct usage of full stops, commas, and question marks.
- Vocabulary: Building knowledge of Synonyms, Antonyms, and Homophones.
3. What is the difference between a common noun and a proper noun?
A common noun is a general name for a person, place, animal, or thing (e.g., 'boy', 'city', 'dog'). A proper noun is the special or specific name for a particular person, place, animal, or thing, and it always begins with a capital letter (e.g., 'Ravi', 'Delhi', 'Tommy').
4. How do pronouns like 'he', 'she', and 'they' help improve our writing?
Pronouns are very useful because they help us avoid repeating the same nouns over and over again. For example, instead of saying, "Ria is a good girl. Ria loves to dance," we can use a pronoun to make it sound better: "Ria is a good girl. She loves to dance." This makes the sentences flow more smoothly.
5. What are verbs and how do they show tenses in a sentence?
A verb is an action word (like 'run', 'eat') or a state of being word (like 'is', 'are'). Verbs are special because they can change their form to show tenses, which tell us when the action happened. For example:
- Present Tense: I play cricket. (Happening now)
- Past Tense: I played cricket. (Happened before)
- Future Tense: I will play cricket. (Will happen later)
6. What is the main job of an adjective in a sentence?
The main job of an adjective is to describe or give more information about a noun or a pronoun. It answers questions like 'what kind?', 'how many?', or 'which one?'. For example, in the phrase "the red car," the word 'red' is an adjective because it describes the car.
7. What are conjunctions and what is their role in connecting ideas?
Conjunctions are words used to join words, phrases, or sentences together. They act like a bridge to connect different ideas. The most common conjunctions are 'and', 'but', and 'or'. For example, 'I want to play, but it is raining outside.' Here, 'but' connects two different thoughts.
8. Why is using the correct punctuation, like a full stop or a question mark, so important?
Using correct punctuation is extremely important because it tells the reader how to understand a sentence. A full stop (.) shows that a thought has ended. A question mark (?) changes the same sentence into a question. Without correct punctuation, the meaning of our writing can become confusing. For example, 'You are going' is a statement, while 'You are going?' is a question.
9. How can we tell the difference between an adjective and an adverb?
The easiest way to tell the difference is to see what word they are describing. An adjective describes a noun (a person, place, or thing). An adverb describes a verb (an action), telling us how the action is done. For example:
- Adjective: He is a slow runner. ('slow' describes the noun 'runner')
- Adverb: He runs slowly. ('slowly' describes the verb 'runs')
10. What are the four main types of sentences taught in Class 5?
In Class 5 English grammar, students learn about four main types of sentences:
- Declarative Sentence: Makes a statement and ends with a full stop. (e.g., The sun rises in the east.)
- Interrogative Sentence: Asks a question and ends with a question mark. (e.g., Where are you going?)
- Imperative Sentence: Gives a command or makes a request. (e.g., Please close the door.)
- Exclamatory Sentence: Shows strong feeling or excitement and ends with an exclamation mark. (e.g., What a beautiful day!)















