




An Introduction to The Colour Palette
A colour palette, in the digital world, refers to the full range of colours that can be displayed on a device screen or other interface, or in some cases, a collection of colours and tools for use in paint and illustration programs. In the traditional RYB colour wheel, the primary colours are red, yellow, and blue. You can create secondary colours—orange, green, and purple—by mixing primary colours. Red and yellow create orange. Yellow and blue create green. The colour palette explains a lot about the design of the device or technology. It can also tell the visual capabilities for human users.
The palette's in earlier days used hexadecimal values to represent and select the variety of colours present in the system. Modern colour palettes are likely to show a colour wheel or a sophisticated tab, with a variety of colours for users to choose from.
Uses of Colour Palette
Colour Palettes help you find new colours by mixing two or more colours together. The palette allows us to decide the saturation of the colour, other colour schemes, value of colour, which colour to pick, and many more.
It helps UI designers to make their interfaces bright and colourful. Colour palette plays an important role in your brand's identity and it is what makes your brand stand out. It helps the brand to make the UI pleasing and attractive when used properly.
Main Types of Colour Palette
There are several kinds of Colour Palette that you can use to create your own Colour Scheme, there are four main types that are widely used. These are:
Monochromatic Colour Palette: For keeping things straight and simple, you should go for a monochromatic palette as it provides the same hue in different shades and tones. It is best to choose this palette when working with a corporate colour that doesn't need a lot of mix-ups.
They are impossible to mess up because they're literally the same colour with different shades, so the chances of messing up are minimal.
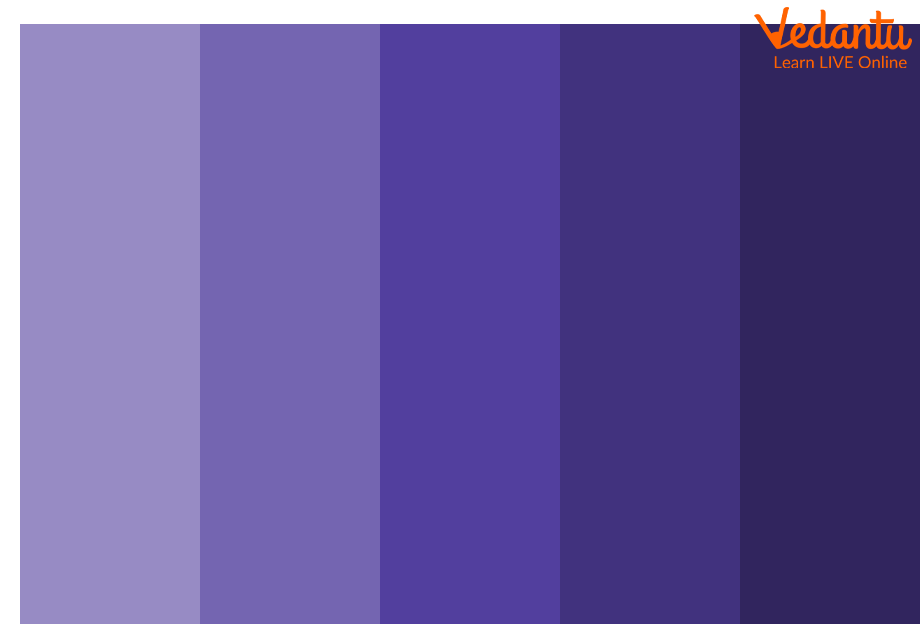
Monochromatic Colour Palette
Complementary Colour Palette: It consists of the opposite colours in the colour wheel, so they are best to use if you want to maintain balance and order. These are very bright and help to grab the eyes of the viewers. Companies use this palette mainly for logo or packaging purposes as it's very catchy.
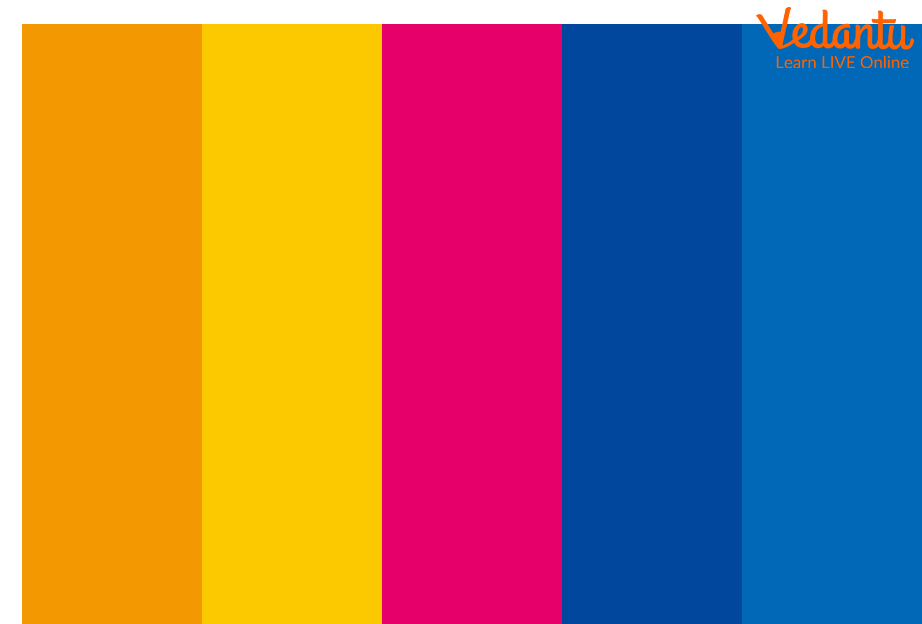

Complementary Colour Palette
Analogous Colour Palette: These palettes are straightforward to create as you have to just pick a primary colour, for example red and pick some of the shades around it. These palettes help to gain the focus of the reader as they are of the same shade. Analogous colour palette should be used where we have to strike an image in the mind of the reader.
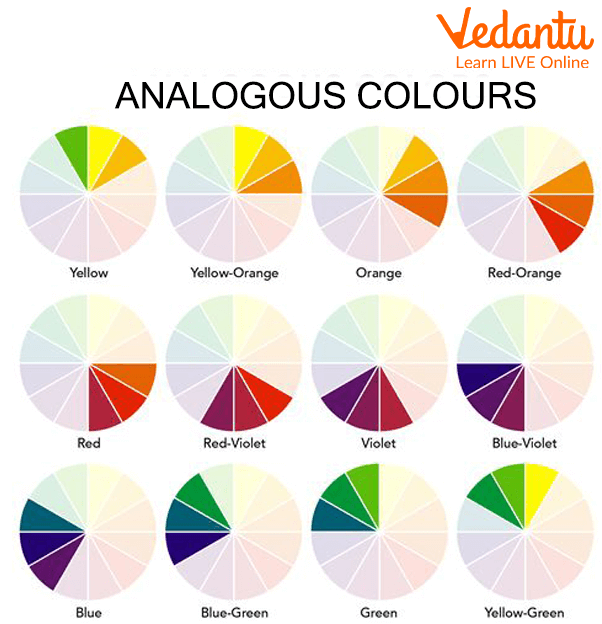
Analogous Colour Palette
Triadic Colour Palette: A Triadic Colour Palette consists of three colours placed evenly on the colour wheel. For example Red, Yellow and Blue, Purple, Green and Orange, etc. This is one of the most complex colour palettes, but if done correctly can give you tremendous results. You'd have to do a lot of experimentation to get the right colours together.
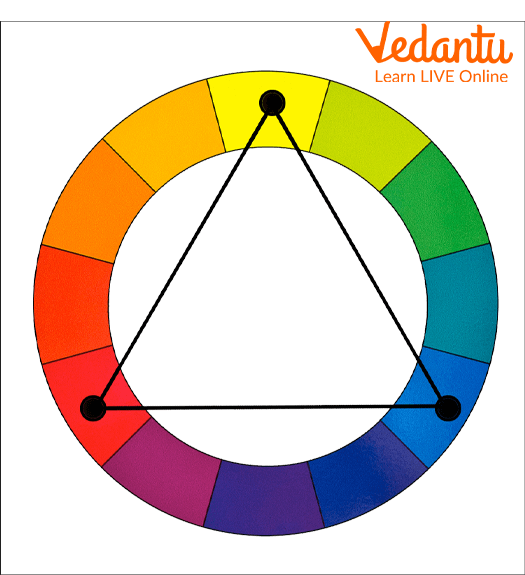
Triadic Colour Palette
Ten Widely Used Colours in Colour Palettes and their Meanings
Many designers and marketers use colour psychology to strategize and create better product lines that increase sales. They have to use the right colours to send the right meaning to the target audience so that they can get the desired result.
Here's a list of the most common colours and what are their meanings:-
Red:- Red symbolises energy and power.
Blue:- Blue symbolises confidence and calm.
Yellow:- Yellow symbolises positivity and zest.
Green:- Green symbolises Natural and security.
Black:- Black symbolises power, mystery, and maturity.
White:- White symbolises purity and perfection.
Purple:- Purple symbolises luxury and royalty.
Pink:- Pink symbolises feminine and safe.
Grey:- Grey symbolises elegance and uncertainty.
Orange:- Orange symbolises enthusiasm and creativity.
Summary
Colour palette refers to the full range of colours that can be displayed on a device's screen or on some other programs like Paint.
Colour Palettes help you find new colours by mixing two or more colours together.
It helps the brand to make the UI pleasing and attractive when used properly.
There are four main types of colour palette. These are monochromatic, triadic, analogous, and complementary Colour Palette.
Colours play a significant role in the mind of the readers, so it's important for us to choose a colour scheme properly.
Learning by Doing
1. Which are the types of colour palettes?
Triadic colour palette
Analogous colour palette
Complement colour palette
All of the above
2. What does green colour in a colour palette symbolise?
Elegance and uncertainty
Enthusiasm and creativity
Luxury and royalty
Natural and security
Sample Solved Questions
1. What is a colour palette?
Ans: Colour palette refers to the full range of colours that can be displayed on a device's screen or on some other programs like Paint.
2. How many colours are there in the colour palette?
Ans: There are eleven standard colours in every colour palette. These are black, white, red, green, yellow, blue, pink, grey, brown, orange, and purple.
3. What are the main types of colour palettes?
Ans: The main types of colour palettes are listed below:
Monochromatic: It is straight and simple. You should go for a monochromatic palette as it provides the same hue in different shades and tones.
Analogous: These palettes help to gain the focus of the reader as they are of the same shade. These make an impact in the mind of readers and last for longer durations as they're catchy.
Complementary: It consists of the opposite colours in the colour wheel, so they are best to use if you want to maintain balance and order.
Triadic: A Triadic Colour Palette consists of three colours placed evenly on the colour wheel. This is the most complex one out of all the other palettes as it requires experimentation to get the desired result.
FAQs on The Colour Palette
1. What is a colour palette in the context of computer science and design?
A colour palette is a specific set of colours chosen to represent a brand, application, or website. In computer science, it's used to ensure visual consistency, create a specific mood, guide user attention, and make the user interface (UI) aesthetically pleasing and easy to navigate.
2. What is the difference between primary, secondary, and tertiary colours on a colour wheel?
These terms describe how colours are mixed and form the basis of a colour palette.
- Primary Colours: Red, yellow, and blue. They are the base colours and cannot be created by mixing others.
- Secondary Colours: Green, orange, and purple. They are made by mixing two primary colours together.
- Tertiary Colours: These are made by mixing a primary colour with an adjacent secondary colour, resulting in shades like red-orange or blue-green.
3. What are some common types of colour schemes used to build a palette?
Common colour schemes are based on the relationships between colours on the colour wheel. Key types include:
- Complementary: Colours opposite each other on the wheel (e.g., red and green), creating high contrast.
- Analogous: Colours that are next to each other on the wheel (e.g., yellow, yellow-green, and green), creating a harmonious look.
- Triadic: Three colours that are evenly spaced on the colour wheel, offering a balanced yet vibrant palette.
4. How do warm and cool colours affect the mood of a website or app?
Warm colours (like reds, oranges, and yellows) are associated with energy, happiness, and urgency. They are often used for call-to-action buttons. Cool colours (like blues, greens, and purples) are associated with calmness, trust, and professionalism, making them suitable for backgrounds or informational sections.
5. What do the terms 'hue,' 'saturation,' and 'brightness' mean when defining a colour?
These three properties are the building blocks for any colour in a digital palette:
- Hue: This is the pure colour itself (e.g., 'red' or 'blue').
- Saturation: This refers to the intensity or purity of the hue. High saturation means a vibrant colour, while low saturation appears dull or greyish.
- Brightness: This describes how light or dark the colour is, ranging from black to white.
6. Why is the 60-30-10 rule useful for applying a colour palette in a design?
The 60-30-10 rule is a classic design guideline for creating a balanced colour scheme. It suggests that 60% of your design should be a dominant colour, 30% should be a secondary colour, and 10% should be an accent colour. This helps ensure that the interface doesn't feel overwhelming and guides the user's eye effectively.
7. What role do neutral colours like black, white, and grey play in a colour palette?
Neutral colours are essential for balance and usability. They often serve as the background of a design, allowing the main colours to stand out. White creates a sense of space and cleanliness, black can convey power and sophistication, and grey is a versatile option that helps reduce visual noise.























