What Is the Difference Between Natural and Artificial Environment?
The types of environment describe the different surroundings—both natural and human-made—that shape life on Earth. Understanding these helps students connect biology, geography, and social studies. This page explains the main types of environment, highlights their features and differences, and provides relevant examples. Let’s explore how our world is organized and influenced by its environments.
What is Environment? Key Components
Environment refers to everything that surrounds living organisms, including air, water, land, and all living and non-living things. It provides essential resources and conditions for organisms to thrive, adapt, and interact. Environmental types are broadly classified based on their origin, composition, and influence on life.
Main Types of Environment
Types of environment are mainly divided into two categories: natural and artificial. This fundamental distinction helps us better understand how ecosystems function and how humans impact the world.
1. Natural Environment
Natural environment refers to the areas and features that exist without human alteration. It includes the earth’s land, water, air, and living organisms. Natural environments create the habitats essential for biodiversity and ecosystem balance.
- Forests, grasslands, mountains
- Rivers, lakes, oceans
- Atmosphere, climate, weather
- Wildlife, plants, microorganisms
2. Artificial (Man-Made) Environment
Artificial environment, or man-made environment, comprises spaces, objects, and systems created or heavily modified by humans to support their lifestyles. These environments often meet social, business, or technological needs.
- Cities and towns
- Buildings, roads, bridges
- Farms, parks, industry
- Infrastructure, laws, and technology
Difference Between Natural and Artificial Environment
| Type of Environment | Description | Key Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Natural Environment | Exists independently of human activity. Includes all natural features and living organisms. | Soil, rivers, forests, mountains, climate, animals |
| Artificial Environment | Created, altered, or maintained by humans to satisfy specific needs. | Houses, offices, transportation, dams, schools |
This table highlights how natural environments form the basis for life, while artificial environments result from human innovation.
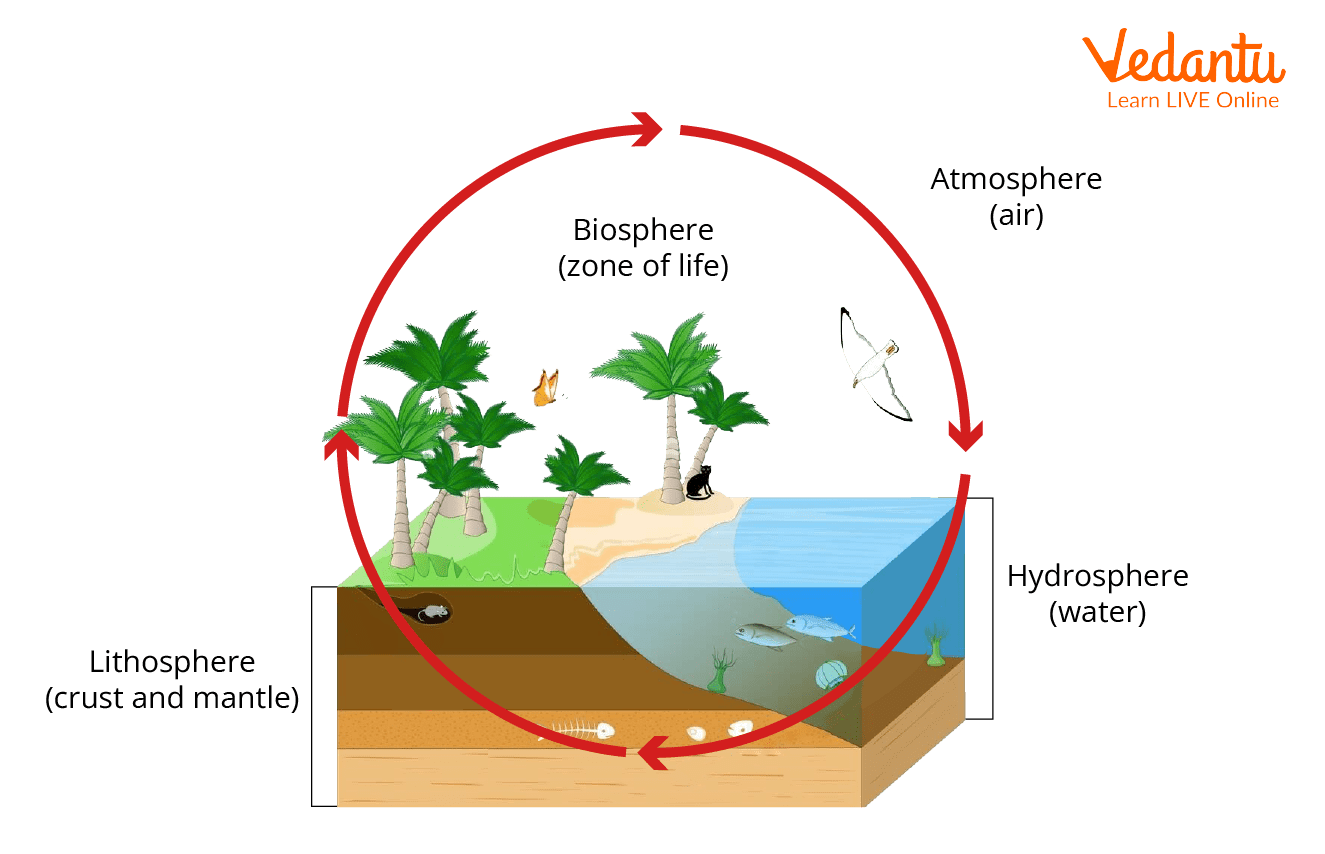
Classification of the Natural Environment (Spheres of the Earth)
Scientists often classify the types of environment into “spheres” for more detailed study. Each sphere represents different components of the planet:
- Lithosphere: The solid land part, including rocks and soil.
- Hydrosphere: All water bodies—oceans, rivers, lakes, glaciers.
- Atmosphere: The layer of gases surrounding Earth, responsible for weather and climate.
- Biosphere: The living world—plants, animals, and microorganisms.
- Anthroposphere: Human-designed or modified regions (e.g., cities, farmlands).
These spheres interact constantly, impacting weather systems, habitats, and the availability of natural resources. You can learn more about natural phenomena and environmental effects in our detailed notes on effects of climate changes.
Biotic and Abiotic Factors in the Environment
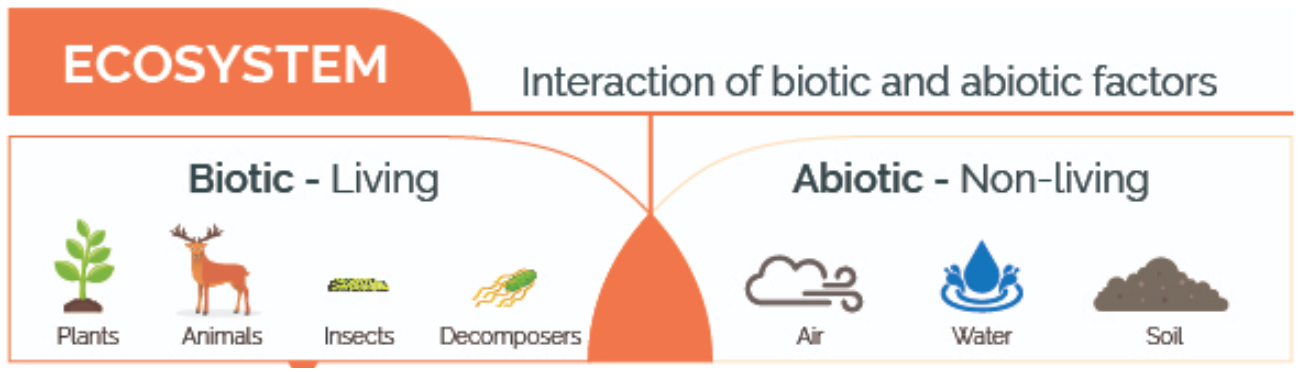
Every type of environment consists of both biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) factors. These influence all living processes, habitats, and ecological relationships.
- Biotic Factors: Plants, animals, bacteria, fungi
- Abiotic Factors: Water, sunlight, air, minerals, temperature
Together, these factors create the unique features of each environment—from deserts and rainforests to lakes and cities. Knowing the distinction is crucial for understanding biology, pollution types, and ecosystem dynamics. You can find dedicated content on biotic and abiotic on Vedantu.
Other Ways to Classify Types of Environment
Environments can be classified in more ways depending on the context. For example, in business, technology, and social sciences, you might encounter classifications such as:
- Terrestrial Environment: Land-based habitats (e.g., forests, deserts, grasslands)
- Aquatic Environment: Freshwater or marine settings (e.g., rivers, ponds, oceans)
- Atmospheric Environment: All air layers that influence weather and climate
- Social/Cultural Environment: The surroundings created by societies, customs, and organizations
- Business Environment: Internal and external factors that affect businesses; for details, see types of business environment
In technology, types of environment also mean computing and artificial intelligence settings. For example, the physical, virtual, and testing environments in AI research. To understand environment from an AI perspective, visit types of environment in AI with examples.
Human Impact and Environmental Pollution
Humans have drastically changed many natural environments through construction, agriculture, and technology. This has led to artificial environments dominating urban and industrial regions.
- Pollution (air, water, soil)
- Deforestation and habitat loss
- Urbanization, climate change, waste management
Understanding types of environment and pollution is key to solving ecological issues. For more on pollution types and solutions, read pollution and calamities on Vedantu.
Importance of Understanding Types of Environment
Learning about different types of environment helps students:
- Connect biology to real-world environmental and ecological issues
- Recognize how life depends on the interplay of biotic and abiotic factors
- Solve practical problems in agriculture, conservation, and health
- Succeed in exams by mastering foundational topics in biological science and ecology
Environmental literacy is critical for responsible citizenship, sustainable living, and scientific careers.
Types of Environment: Key Terms and Examples
| Term | Definition | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Biotic | All living or once-living organisms | Plants, animals, bacteria, fungi |
| Abiotic | Non-living physical and chemical factors | Sunlight, air, water, minerals |
| Biosphere | Zone where life exists on Earth | Forests, oceans, grasslands |
| Anthroposphere | Areas influenced or created by humans | Cities, roads, farms |
The table above summarizes core categories often encountered in environment studies and modern biology textbooks.
Application and Relevance of Types of Environment
Types of environment concepts apply in medicine (public health, disease spread), agriculture (crop choice, soil care), and technology (AI environments, business analysis). They support learning in topics such as food science and animal adaptations. Vedantu connects these lessons with real-world challenges, helping students become problem-solvers.
The study of types of environment provides a strong base for understanding our planet’s structure, living systems, and the effects of human actions. Recognizing natural and artificial environments makes it easier to solve problems in ecology, business, and technology, and prepares learners for success in school and beyond.


FAQs on Types Of Environment Explained for Students
1. What are the main types of environment?
The environment is commonly divided into two main types: natural environment and human-made (or artificial) environment. These classifications help us understand the surroundings that support life.
Natural Environment Includes:
- Biotic environment: Living things such as plants, animals, and microorganisms
- Abiotic environment: Non-living things like air, water, soil, sunlight, and minerals
- Social environment: Communities, cultures, traditions, and institutions created by humans
- Built environment: Cities, infrastructure, roads, buildings, and other constructions
2. What is a natural environment?
A natural environment refers to everything in our surroundings that is not created by humans. It includes biotic and abiotic components.
- Biotic factors: Plants, animals, and other living things
- Abiotic factors: Air, water, sunlight, soil, and climate
3. What is the difference between natural and human-made environment?
The natural environment consists of elements not made by humans, while the human-made environment includes all things created by people.
- Natural Environment: Air, water, forests, mountains, rivers, plants, animals
- Human-made Environment: Buildings, roads, vehicles, cities, monuments, institutions
4. What are biotic and abiotic components of the environment?
Biotic components are living elements and abiotic components are non-living physical and chemical parts of the environment.
- Biotic: Humans, animals, plants, fungi, bacteria
- Abiotic: Air, water, soil, sunlight, minerals, temperature
5. Why is the environment important for human life?
The environment provides essential resources and supports all forms of life.
- Supplies air, water, food, and shelter
- Maintains ecological balance
- Influences climate and weather
- Ensures survival of living organisms
6. What are the different components of the environment?
The environment is made up of several interconnected components:
- Natural components: Land, water, air, plants, animals
- Human-made components: Buildings, roads, industries
- Social components: Communities, institutions, traditions
7. How do humans interact with their environment?
Humans interact with the environment by using its resources and modifying it for their needs.
- Building homes and cities
- Agriculture and farming
- Industrial development
- Pollution and conservation efforts
8. What is a human-made environment? Give examples.
Human-made environment refers to surroundings created or modified by people.
- Examples: Cities, buildings, roads, bridges, parks, factories, dams
9. What are the major threats to the environment?
Major threats to the environment include both natural and human activities.
- Pollution: Air, water, and soil contamination
- Deforestation: Cutting down forests
- Global warming and climate change
- Loss of biodiversity
- Overpopulation
10. How can we protect our environment?
We can protect the environment through several practical steps:
- Reduce, reuse, and recycle materials
- Plant more trees and conserve forests
- Save water and energy
- Use public transport and eco-friendly technology
- Spread awareness about environmental issues










