Causes and Effects of Ozone Layer Depletion with Diagram and Examples
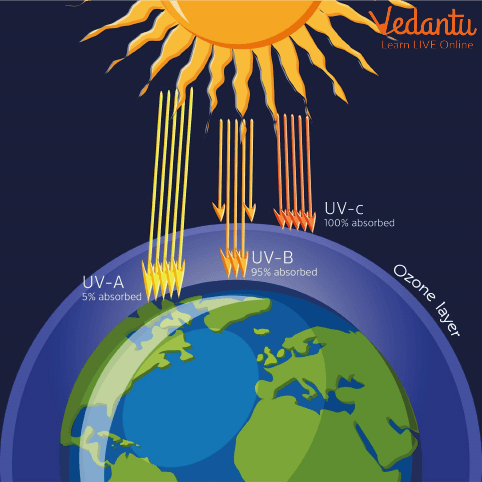
Ozone layer depletion describes the gradual thinning of Earth’s ozone layer, a naturally occurring region of the stratosphere that contains a high concentration of ozone (O3). The ozone layer absorbs much of the sun’s harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation, acting as a protective shield for living organisms on land and in water. Depletion of this layer leads to increased exposure to UV rays on Earth’s surface.
Ozone Layer: Structure and Function
The ozone layer is located within the stratosphere, about 15 to 35 kilometers above Earth. Ozone molecules in this region form when UV light splits an oxygen molecule (O2) into individual atoms, which then combine with other O2 molecules. This cycle both creates and destroys ozone naturally, maintaining a stable concentration under normal conditions.
The chief function of the ozone layer is to absorb most incoming UV-B and UV-C radiation from the sun. Without this layer, DNA damage in living organisms would increase, causing skin cancers, cataracts, and disruptions to food chains. Plants and aquatic organisms are also sensitive to increased UV, leading to ecological imbalance.
Causes of Ozone Layer Depletion
Human activity is the main cause of ozone depletion. Scientists in the 1970s discovered that certain man-made chemicals, especially chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), released chlorine and bromine when they rose to the stratosphere and were broken down by UV radiation. Free chlorine and bromine atoms can destroy thousands of ozone molecules, disrupting the natural ozone-oxygen cycle.
CFCs have been used in refrigerators, air conditioners, aerosol propellants, plastic foam manufacturing, firefighting agents, and solvents. Other contributors include halons and some industrial chemicals. Bromine-containing compounds, such as bromine monoxide (BrO), are even more efficient than chlorine at breaking down ozone.
| Source of Chemical | Key Substance | Ozone-Destroying Element |
|---|---|---|
| Refrigerants, coolants, foams | CFCs | Chlorine |
| Fire extinguishers | Halons | Bromine |
| Spray cans, solvents | Other halocarbons | Chlorine or Bromine |
Ozone Depletion Process
When chemicals such as CFCs are released into the atmosphere, they gradually migrate to the stratosphere. There, UV radiation breaks them down, releasing chlorine or bromine atoms. These atoms react with ozone (O3), splitting it into ordinary oxygen (O2) and a molecule of chlorine monoxide (ClO) or bromine monoxide (BrO). The destructive cycle continues, as each atom is released to repeat the process.
Bromine-based reactions are especially damaging, as bromine atoms remain active even longer than chlorine atoms.
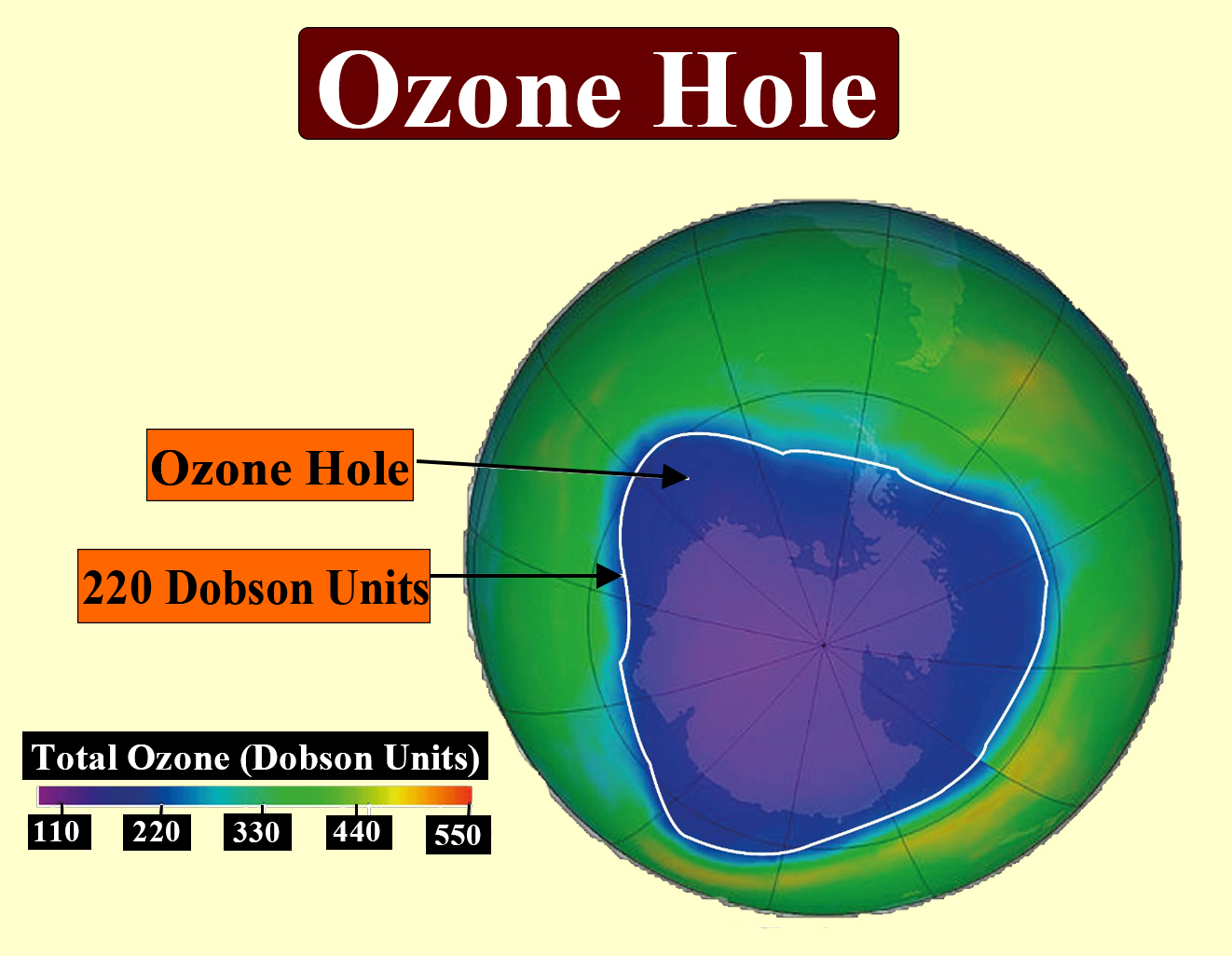
Antarctic Ozone Hole
The most severe ozone depletion has been observed over Antarctica, referred to as the Antarctic ozone hole. Since the late 1970s, studies found a dramatic springtime decrease, sometimes over 60 percent, in total ozone above Antarctica. This is due to unique weather patterns: extreme cold leads to the formation of polar stratospheric clouds during the polar night, isolating the region and concentrating reactive chlorine and bromine. When sunlight returns in the spring, a rapid release of these elements triggers massive ozone loss.
A similar but less severe process occurs over the Arctic. Ozone thinning there can reach up to 40 percent, typically in years with unusually cold stratospheric temperatures.
Effects of Ozone Layer Depletion
Damage to the ozone layer leads to increased levels of UV radiation at the surface, affecting human health, ecosystems, and materials. Key consequences include:
- Higher incidence of skin cancer and cataracts in humans
- Weakened immune systems
- Damage to plant tissues, reduced crop yields
- Harm to aquatic organisms, especially phytoplankton
- Increased degradation of plastics and materials
| Effect | Scientific Significance |
|---|---|
| Skin Cancer | More UV-B exposure increases DNA mutations in skin cells. |
| Phytoplankton Damage | Reduces food chain base and disrupts marine ecosystems. |
| Material Degradation | Faster wear of plastics, paints, and other exposed materials. |
Scientific Milestones and Discovery
Dutch chemist Paul Crutzen first described the role of nitrogen oxides in ozone breakdown in 1969. Later, Mario Molina and F. Sherwood Rowland recognized chlorofluorocarbons’ role in ozone destruction, showing how chlorine atoms could deplete vast amounts of ozone. Their discoveries were proven by satellite, balloon, and laboratory measurements. For this, Crutzen, Molina, and Rowland received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
Example Questions and Next Steps
- Explain in simple terms how CFCs cause ozone layer depletion.
- List two differences between ozone depletion and the greenhouse effect.
- Describe how the Antarctic ozone hole forms.
For further practice and to deepen your understanding of ozone-related concepts, refer to:
Greenhouse Effect |
Global Warming |
Environmental Issues
Summary
Ozone layer depletion is a global environmental challenge caused mainly by industrial chemicals like CFCs and halons. The most dramatic effects are seen over Antarctica during spring, forming the “ozone hole.” This leads to increased UV radiation reaching Earth, with harmful effects on life and materials. Understanding these scientific facts helps us make informed decisions about protecting the ozone layer for future generations.
Continue exploring topics in ecology, biodiversity, and climate change for a deeper knowledge of environmental interactions.


FAQs on Ozone Layer and Its Depletion: Key Concepts for Students
1. What is ozone depletion?
Ozone depletion refers to the gradual thinning and reduction of the ozone layer in Earth’s stratosphere due to chemical reactions involving pollutants like chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), halons, and other ozone-depleting substances. This causes a decrease in the layer’s ability to protect living organisms from harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
2. What causes ozone layer depletion?
Ozone layer depletion is mainly caused by the release of certain human-made chemicals into the atmosphere. The primary contributors are:
- Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs): Used in coolants, air conditioners, and aerosols
- Halons: Found in fire extinguishers
- Nitrous oxides (NOx): Emitted from jet planes and fossil fuel combustion
- Methyl bromide: Used as a pesticide
3. What is the importance of the ozone layer?
The ozone layer is vital because it:
- Absorbs and blocks over 97% of the sun’s harmful UV-B radiation
- Protects living organisms from genetic damage and diseases such as skin cancer, cataracts, and immune system suppression
- Maintains ecological balance by protecting plants and aquatic life
4. What are the effects of ozone layer depletion?
Ozone layer depletion results in:
- Increased UV radiation reaching Earth’s surface
- Higher risks of skin cancer, cataracts, and sunburn
- Suppression of immune systems in humans and animals
- Damage to phytoplankton, affecting aquatic food chains
- Reduced agricultural productivity
5. How are CFCs responsible for ozone depletion?
CFCs (Chlorofluorocarbons) are stable chemicals that, when released, reach the stratosphere and are broken down by UV light. This releases chlorine atoms which:
- React with ozone (O3) molecules
- Convert them into oxygen (O2), thus destroying ozone
- One chlorine atom can destroy thousands of ozone molecules
6. What is the ozone hole?
The ozone hole refers to the region of severe ozone layer thinning, mainly observed over Antarctica during the springtime. It is caused by specific chemical reactions on polar stratospheric clouds and the presence of CFCs and halons.
7. Is the ozone layer recovering?
Yes, the ozone layer is showing signs of recovery due to global measures like the Montreal Protocol which phased out the use of ozone-depleting substances. However, full recovery is expected to take several more decades, and continuous monitoring is needed.
8. What is the Montreal Protocol?
The Montreal Protocol (1987) is an international agreement signed by 197 countries to phase out the production and use of major ozone-depleting substances such as CFCs and halons. It has played a crucial role in slowing and reversing ozone depletion.
9. What are some solutions to ozone layer depletion?
Solutions to prevent ozone depletion include:
- Banning or reducing the use of CFCs, halons, and related chemicals
- Switching to eco-friendly alternatives for refrigerants and aerosols
- International cooperation through protocols and agreements
- Increasing public awareness and implementing regulations
10. Differentiate between ozone depletion, the greenhouse effect, and global warming.
Ozone depletion: Thinning of the ozone layer due to chemicals like CFCs, increasing UV exposure.
Greenhouse effect: Trapping of heat in Earth’s atmosphere by greenhouse gases such as CO2, methane, causing warming.
Global warming: The rise in average global temperatures mainly due to the enhanced greenhouse effect. Each process affects Earth’s climate and living conditions differently.
11. What are the health impacts of ozone layer depletion?
Health impacts include:
- Increased risk of skin cancers and sunburns
- Higher occurrence of cataracts and other eye disorders
- Suppressed immune response making people more susceptible to diseases
12. What layers of the atmosphere contain ozone, and where is maximum concentration found?
Ozone is present throughout the atmosphere, but the maximum concentration – forming the ozone layer – is found in the stratosphere, approximately between 15 and 35 km above Earth’s surface.










