What Is Microsporogenesis? Steps and Significance for Students
Microsporogenesis is a fundamental biological process that plays a vital role in the reproduction of flowering plants. Understanding microsporogenesis helps elucidate how pollen grains form within the anther. This topic is essential for students, as it connects plant reproduction, genetics, and agricultural practices, offering insight into plant breeding and crop improvement.
What is Microsporogenesis?
Microsporogenesis refers to the sequence of events resulting in the formation of microspores from microspore mother cells inside the anther of flowering plants. Microspores later develop into pollen grains, which are crucial for plant fertilization. To define microsporogenesis simply: it is the process that ensures genetic diversity and successful sexual reproduction in plants, paralleling the importance of megasporogenesis in ovule formation.
Structure of the Anther in Microsporogenesis
The anther, the pollen-producing part of the stamen, contains several layers and tissues essential for microsporogenesis. The walls comprise the epidermis, endothecium, middle layers, and the innermost tapetum. At the core, sporogenous tissue gives rise to microspore mother cells, which initiate pollen development. A clear understanding of anther anatomy is fundamental when exploring the structure of microsporogenesis.

Process of Microsporogenesis
To describe the process of microsporogenesis, let’s follow the orderly stages occurring in the anther. Each step is essential for the formation of viable and genetically diverse pollen grains.
- Development of Archesporial Cells: Specialized cells in the anther’s sporogenous tissue form the archesporial cells.
- Formation of Primary Sporogenous Cells: Archesporial cells divide mitotically to produce primary sporogenous cells.
- Generation of Microspore Mother Cells: Primary sporogenous cells differentiate into microspore mother cells (also called pollen mother cells).
- Meiotic Division: Each microspore mother cell undergoes meiosis, yielding a tetrad of four haploid microspores.
- Tetrad Separation: The four microspores detach from each other following special enzymes secreted by the tapetum.
- Pollen Grain Maturation: Each microspore transforms into a mature pollen grain, released from the anther for pollination.
This reductional cell division ensures genetic variation, vital for crop improvement and resilience to environmental changes, as further discussed in meiosis.
Microsporogenesis Diagram
A diagram of microsporogenesis illustrates the sequence, from the microspore mother cell through meiosis to the formation of pollen grains. Understanding the microsporogenesis diagram helps visualize cellular changes and the emergence of pollen critical for plant fertilization.
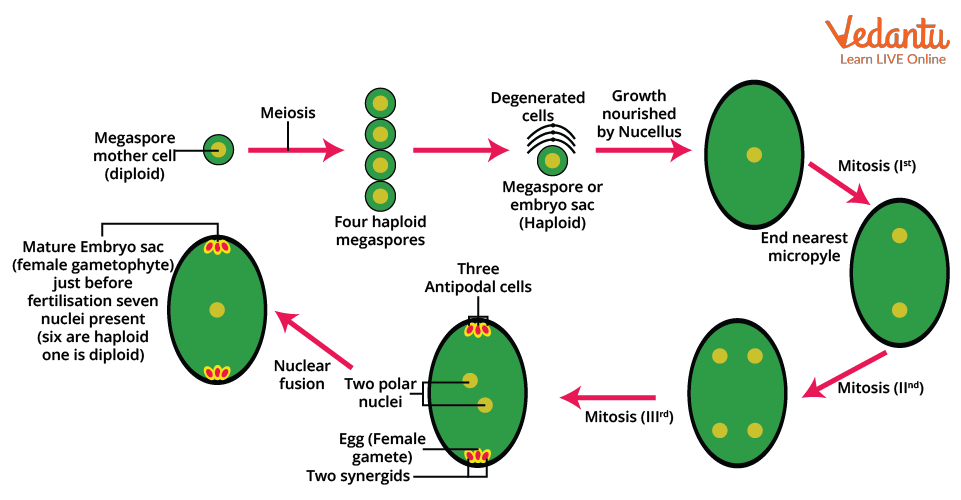
Observing these diagrams clarifies the intricate nature of plant reproductive biology and is commonly required in biology exams or projects, like those found in CBSE Class 7 Important Diagrams.
Comparison: Microsporogenesis and Megasporogenesis
| Aspect | Microsporogenesis | Megasporogenesis |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Anther (male part) | Ovule (female part) |
| Mother Cell | Microspore mother cell | Megaspore mother cell |
| Product | Microspores (pollen grains) | Megaspores (embryo sac formation) |
| Function | Leads to male gamete formation | Leads to female gamete formation |
While both processes involve meiosis and gametophyte development, microsporogenesis and megasporogenesis differ in their location and outcome, ensuring both male and female gametes are available for fertilization. This coordinated development supports the diversity and success of plant species.
Significance of Microsporogenesis
The process of microsporogenesis is critical for ensuring plant genetic diversity. It enables the formation of numerous pollen grains that contribute to cross-pollination, directly impacting food production and crop yields. Understanding microsporogenesis is essential in fields like food science and plant breeding, helping scientists develop resilient, high-yield crops crucial for global food security.
Applications and Real-World Relevance
Knowledge of microsporogenesis is used in modern agriculture, especially in hybrid seed production and plant breeding. By manipulating this process, researchers can enhance traits like disease resistance and yield. It also plays a role in understanding the effects of climate changes on reproductive success in plants, which is vital for adapting crops to changing environments.
Explore More Biology Topics
For deeper insight into plant development and related biological processes, explore topics like cell theory, biomolecules, and plant reproduction. Vedantu provides a comprehensive range of resources to support your learning at every stage.
In summary, microsporogenesis is a vital cellular process in plant reproduction. It not only produces the pollen required for fertilization but also ensures genetic variation and plant survival. Grasping its stages and significance empowers students and professionals to contribute meaningfully to fields like agriculture, botany, and environmental science.


FAQs on Microsporogenesis: Process and Diagram
1. What is microsporogenesis?
Microsporogenesis is the process by which microspore mother cells undergo meiosis to form microspores inside the anthers of flowering plants. This process leads to the development of pollen grains.
Key steps include:
- Formation of pollen mother cells (microspore mother cells) in the anther
- Meiotic division of these cells to produce four haploid microspores
- Arrangement of microspores in a tetrad
2. Describe the steps of microsporogenesis.
Microsporogenesis involves a series of well-defined steps that lead to the formation of haploid microspores.
Steps include:
- Development of archesporial cells in the anther
- Division of archesporial cells to produce parietal and sporogenous tissues
- Formation of microspore mother cells (MMCs)
- Each MMC undergoes meiosis to produce a tetrad of haploid microspores
- Separation and maturation of microspores into pollen grains
3. Where does microsporogenesis occur in plants?
Microsporogenesis occurs inside the anthers of flowering plants.
Details include:
- The anther contains pollen sacs (microsporangia)
- Within these sacs, microspore mother cells undergo meiosis
- The result is the formation of haploid microspores leading to pollen grains
4. What is the significance of microsporogenesis in plants?
Microsporogenesis is vital because it ensures genetic diversity and the formation of functional male gametophytes in plants.
Significance includes:
- Production of viable pollen grains for fertilization
- Facilitates cross-pollination and genetic variation
- Essential for the plant’s sexual reproduction and crop improvement
5. How is a microspore mother cell different from a microspore?
Microspore mother cell (MMC) is a diploid cell that undergoes meiosis to produce haploid microspores.
Differences:
- MMC is diploid (2n); microspore is haploid (n)
- MMC undergoes meiosis; microspore is the product
- MMC is larger and less specialized; microspore develops into pollen grain
6. What are the main products of microsporogenesis?
The main products of microsporogenesis are haploid microspores, which later develop into pollen grains.
Summary:
- Each microspore mother cell forms a tetrad of four microspores
- Microspores eventually mature into pollen grains
7. What are the differences between microsporogenesis and megasporogenesis?
While both processes involve the formation of reproductive cells via meiosis, they differ in location and function.
Key differences:
- Microsporogenesis occurs in anthers; results in pollen grains (male gametes)
- Megasporogenesis takes place in ovules; produces embryo sac (female gametes)
- Microspores are produced in large numbers; megaspores are fewer and usually only one survives
8. What changes occur in the anther during microsporogenesis?
During microsporogenesis, the anther undergoes various structural and cellular changes.
Major changes:
- Development of archesporial tissue
- Formation of microspore mother cells
- Meiosis leading to microspore tetrads
- Degeneration of tapetum (nutrition to developing microspores)
- Release of mature pollen grains from pollen sacs
9. What is the role of the tapetum during microsporogenesis?
The tapetum is the innermost layer of the anther wall and plays a critical role in nourishing the developing microspores.
Key functions:
- Supplies nutrients and enzymes required for microspore development
- Helps in the formation of pollen wall (exine)
- Degenerates at maturity, releasing the contents to aid pollen development
10. Why is meiosis important in microsporogenesis?
Meiosis is essential in microsporogenesis as it reduces the chromosome number from diploid to haploid and introduces genetic variation.
Importance:
- Ensures production of haploid microspores
- Enables genetic recombination and variation among offspring
- Necessary for maintaining chromosome number across generations










