How to Solve Basic Division Sums for Kids
FAQs on Maths Division Worksheets: Practice Sums and Word Problems
1. How do you solve division sums for kids?
To solve division sums for kids, divide the total number equally among groups and find out how many are in each group.
Steps:
1. Identify the total number (dividend) and the number to divide by (divisor).
2. Use repeated subtraction, grouping objects, or draw pictures if needed.
3. Write the answer, called the quotient.
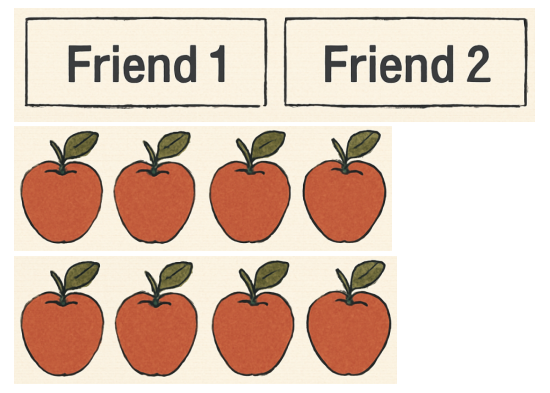
Example: For 12 ÷ 4, share 12 apples among 4 friends so each friend gets 3 apples.
2. What are basic division problems?
Basic division problems use small numbers and teach students how to share or group things equally.
Examples include:
- 12 ÷ 4 = 3
- 20 ÷ 5 = 4
- 16 ÷ 2 = 8
These build strong division concepts for Grade 2 to Grade 5 students.
3. How can students practice division easily?
Students practice division easily by using worksheets with sums, word problems, and pictures.
4. What is the best way to teach division to children?
The best way to teach division is by using real-life examples, visuals, and step-by-step practice.
5. What are division word problems for grade 3?
Division word problems for grade 3 use everyday situations to make learning interesting.
Example: If there are 18 pencils and 6 children, how many pencils will each child get?
Solution: 18 ÷ 6 = 3 pencils each.
Such activities help students apply maths in daily life.
6. How can I use this worksheet at home?
Use this division worksheet at home by printing it and solving sums with your child for quick revision.
Steps:
- Download and print the PDF
- Guide your child on instructions
- Let them solve independently
- Check answers using the answer key provided
7. Does this include an answer key?
Yes, each division worksheet includes a complete answer key.
8. Is this worksheet printable?
Yes, this maths division worksheet is fully printable as a PDF.
How it helps:
- Easy to use at home or in class
- Supports convenient practice without the need for screens
- Large fonts and visuals make it kid-friendly
9. What age group is it best for?
This maths division worksheet is best for Grade 2 to Grade 5 students (ages 7–11).
It covers basic and intermediate division concepts suitable for class 2, 3, 4, and 5 as per the current syllabus.
10. What skills are built by this activity?
This division worksheet builds skills such as numeracy, logical thinking, problem-solving, and mathematics fluency.
It also helps with:
- Understanding division by grouping and sharing
- Confidence in solving textbook sums
- Applying maths to real-life scenarios