Class 5 Maths Chapter 2 Summary Notes PDF Download
FAQs on Shapes and Angles Class 5 Maths Chapter 2 CBSE Notes - 2025-26
1. What are the key concepts to summarise for a quick revision of Class 5 Maths Chapter 2, Shapes and Angles?
For a quick revision of this chapter, focus on these core concepts:
- The difference between open and closed shapes.
- Identifying the number of sides and corners (vertices) in polygons like triangles and squares.
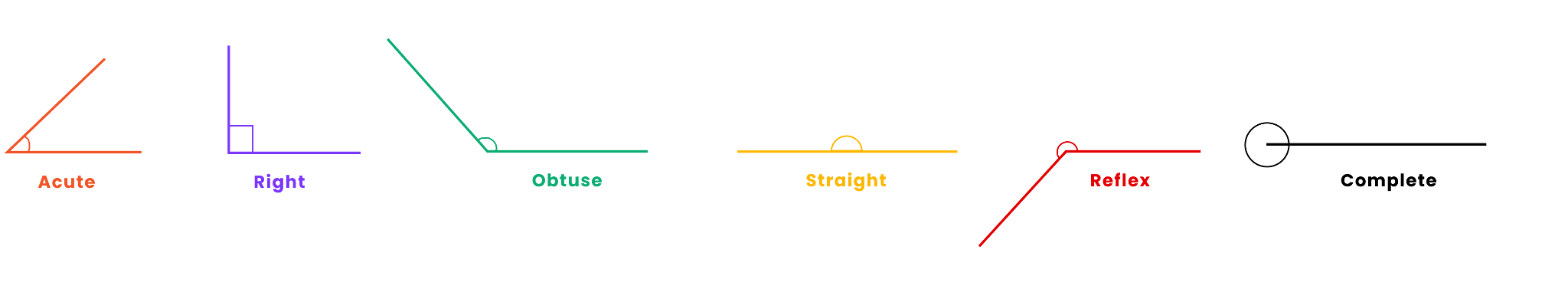
- Understanding the three main types of angles: acute, right, and obtuse.
- Using a right angle as a benchmark to compare and classify other angles.
2. What is the basic difference between an open shape and a closed shape?
A closed shape is a figure whose starting and ending points are the same, forming a complete boundary with no gaps (e.g., a circle or a triangle). An open shape is a figure that does not have a complete boundary, meaning its starting and ending points are different (e.g., the letter 'U' or 'M').
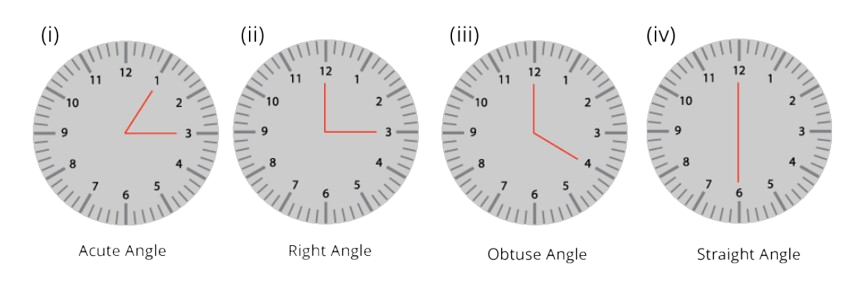
3. How are the three main types of angles defined for a quick recap?
The three main types of angles are defined by comparing them to a right angle:
- Right Angle: An angle that measures exactly 90 degrees, like the corner of a book.
- Acute Angle: An angle that is smaller than a right angle (less than 90 degrees).
- Obtuse Angle: An angle that is larger than a right angle (more than 90 degrees).
4. How can we identify shapes based on their sides and angles?
You can identify shapes by counting their sides and observing their angles. For example, a triangle always has three sides and three angles. A square has four equal sides and four right angles. A pentagon has five sides and five angles. This summary helps in quickly differentiating between various polygons.
5. Why is a right angle so important when learning about shapes and angles?
A right angle (90°) is important because it acts as a standard reference point. It's a common angle found in everyday objects like doors, windows, and books, making it easy to recognise. By comparing any given angle to a right angle, you can quickly determine if it is acute (smaller) or obtuse (larger) without needing a tool for every measurement.
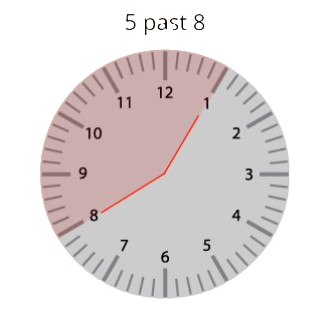
6. How can the hands of a clock be used to understand the concept of angles?
The hands of a clock are a perfect real-world example to revise angles. At 3:00, the hands form a right angle. At 2:00, they form an acute angle. At 4:00, they form an obtuse angle. Watching the hands move helps to visualise how the amount of turn between two lines creates different types of angles.
7. If you make the arms of an angle longer, does the measurement of the angle change?
No, the measurement of an angle does not change if you make its arms longer or shorter. The size of an angle depends only on the amount of opening or turn between the arms at the vertex. The length of the arms is irrelevant to the angle's measure, which is a crucial concept to avoid misconceptions during revision.
8. What is the key difference to remember between a square and a rectangle?
The key difference to summarise is related to their sides. While both shapes have four sides and four right angles, a square has all four sides of equal length. In a rectangle, only the opposite sides are equal in length.