Maths Notes for Chapter 10 Tenths and Hundredths Class 5 - FREE PDF Download
FAQs on Tenths and Hundredths Class 5 Maths Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26
1. What are tenths and hundredths in Class 5 Maths Chapter 10?
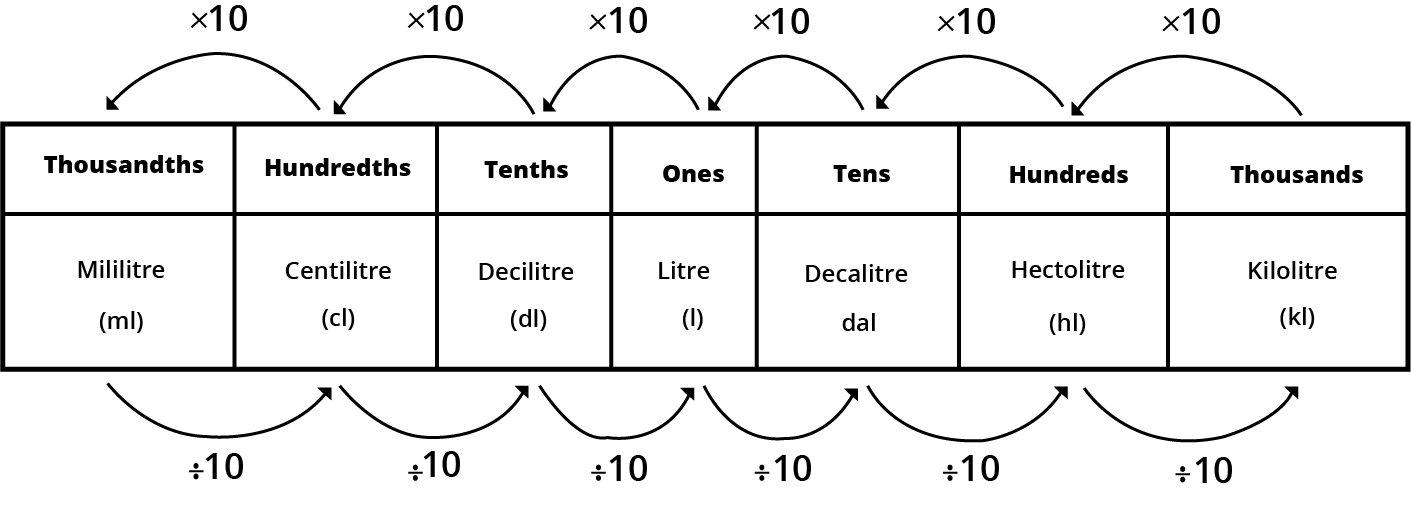
Tenths and hundredths are parts of a whole divided into 10 and 100 equal parts, respectively. They are types of decimal numbers used to represent fractions of a whole.
2. How do I understand the place value of tenths and hundredths?
Tenths are represented as 0.1 and are the first digit after the decimal point. Hundredths are represented as 0.01 and are the second digit after the decimal point. The place value determines the size of each decimal digit.
3. Where can I download the Class 5th Maths Chapter 10 Tenths and Hundredths notes PDF?
You can download the notes PDF from educational websites that offer free resources for Class 5 Maths. Look for your school's learning portal or trusted educational sites for access.
4. What is the importance of learning tenths and hundredths in Class 5 Maths?
Understanding tenths and hundredths is important for grasping decimal numbers, which are used in various real-life situations such as money and measurements. It also provides a foundation for more advanced math topics.
5. How can I convert fractions to decimals for Class 5 Maths Chapter 10?
To convert fractions to decimals, divide the numerator by the denominator. For example, 1/10 becomes 0.1, and 1/100 becomes 0.01.
6. What types of problems are included in the Chapter 10 notes PDF?
The notes PDF typically includes problems on identifying and writing decimals, converting fractions to decimals, comparing and ordering decimals, and performing addition and subtraction with decimals.
7. How can visual aids help with understanding tenths and hundredths?
Visual aids such as grids, pie charts, or number lines can help you see how tenths and hundredths fit into a whole, making the concept of decimals more tangible and easier to understand.
8. What are some effective study tips for Class 5 Maths Chapter 10?
Review the concepts regularly, practice problems consistently, use visual aids, and ensure you understand how to perform operations with decimals. Regular revision will reinforce your learning.
9. Can I use the Chapter 10 notes PDF for exam preparation?
Yes, the notes PDF is a valuable resource for exam preparation. It covers all essential concepts and provides practice problems to help you prepare effectively for your exams.
10. How can I ensure I am using the Class 5th Maths Chapter 10 notes effectively?
To use the notes effectively, read through the explanations carefully, complete all practice exercises, review your work, and use additional resources if needed. Regular practice and revision will help solidify your understanding.