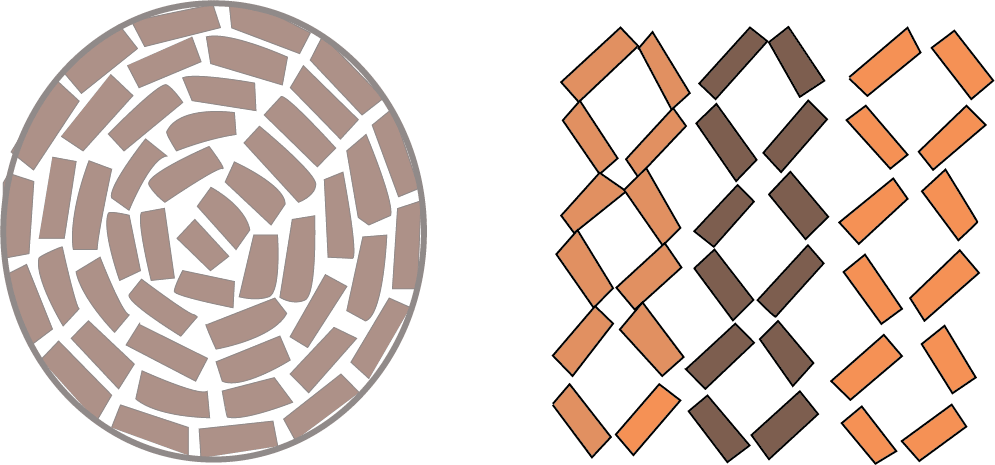Building with Bricks Class 4 Maths Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26
FAQs on Building with Bricks Class 4 Maths Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26
1. What is the main summary of the CBSE Class 4 Maths chapter, 'Building with Bricks'?
This chapter uses the common brick as a tool to introduce students to fundamental concepts of geometry and arithmetic. A quick revision of this chapter covers the properties of a 3D shape (cuboid), how to visualise objects from different views, the creation of various patterns, and calculations involving large numbers, such as the cost of bricks.
2. What are the key topics to focus on for a quick revision of 'Building with Bricks'?
For an effective revision, you should focus on the following key concepts from the chapter:
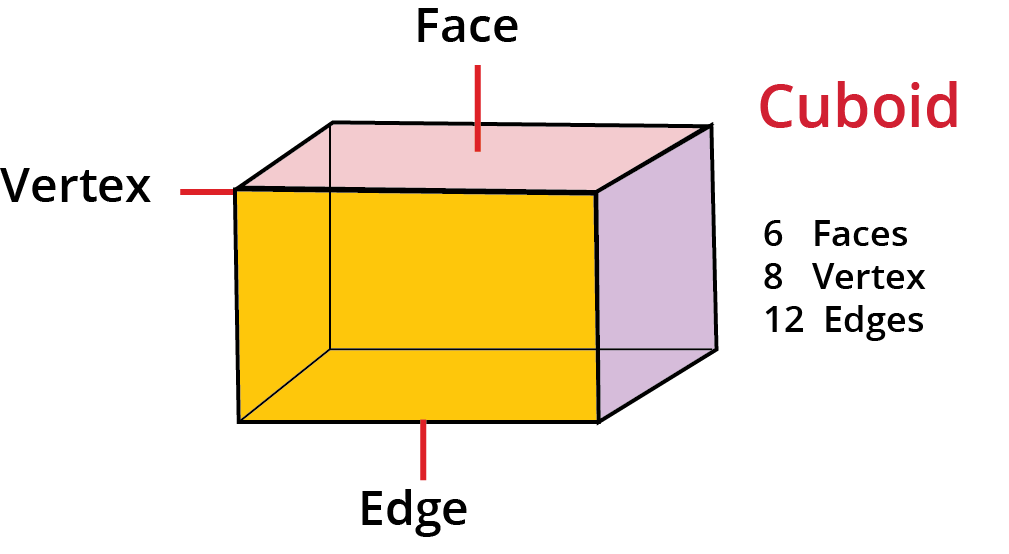
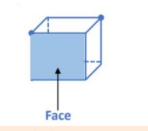
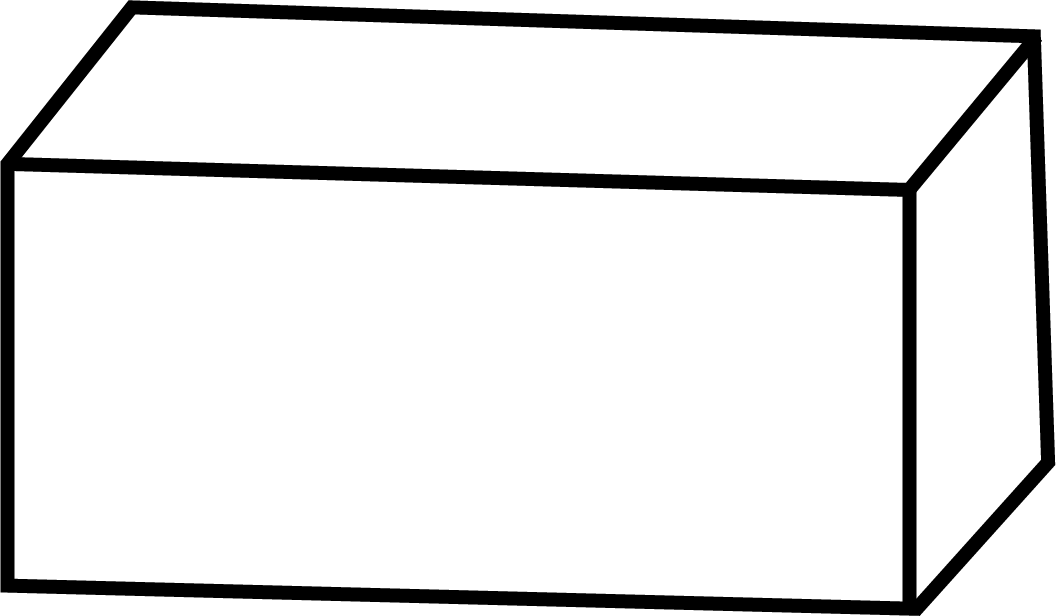
The properties of a brick: its faces (6), edges (12), and corners (8).
Identifying different views of a 3D object (top, front, side).
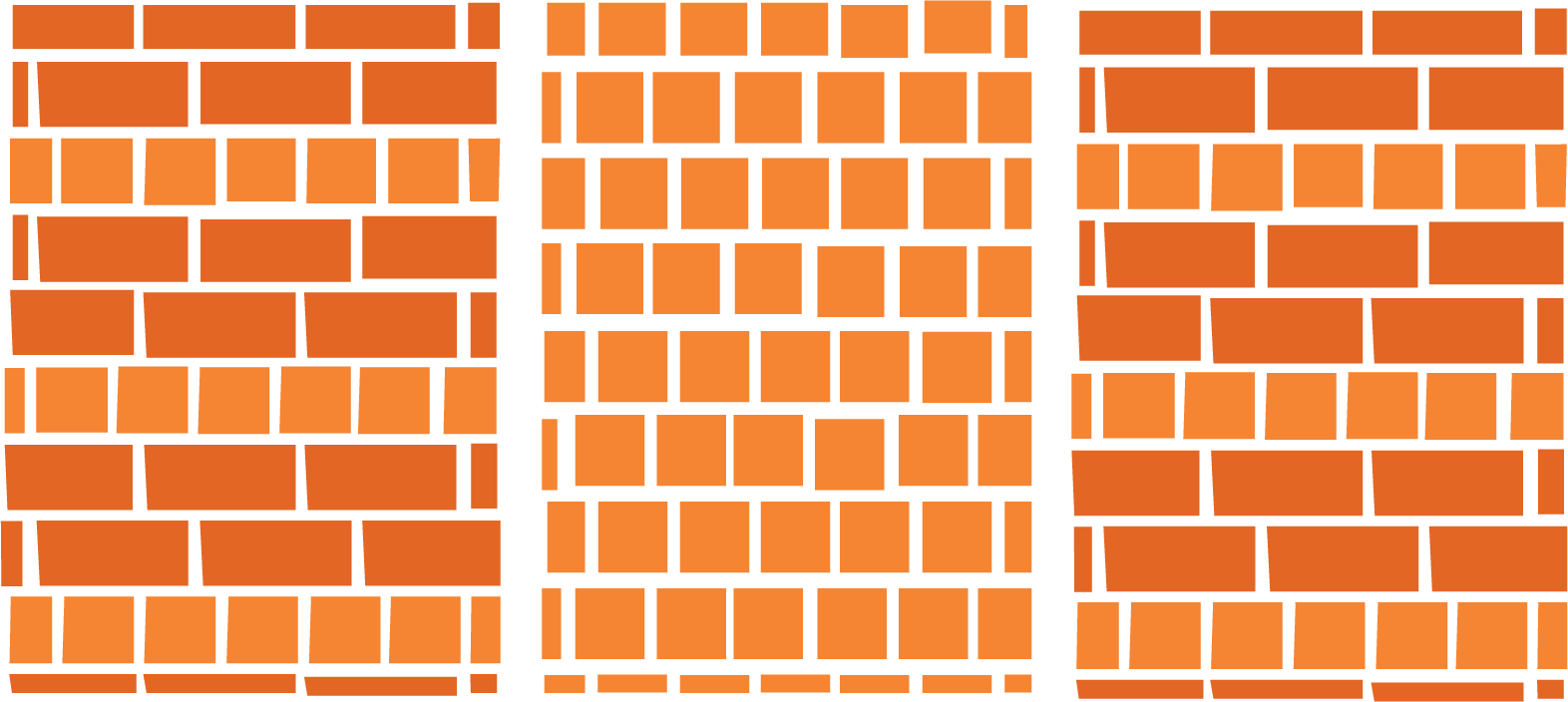
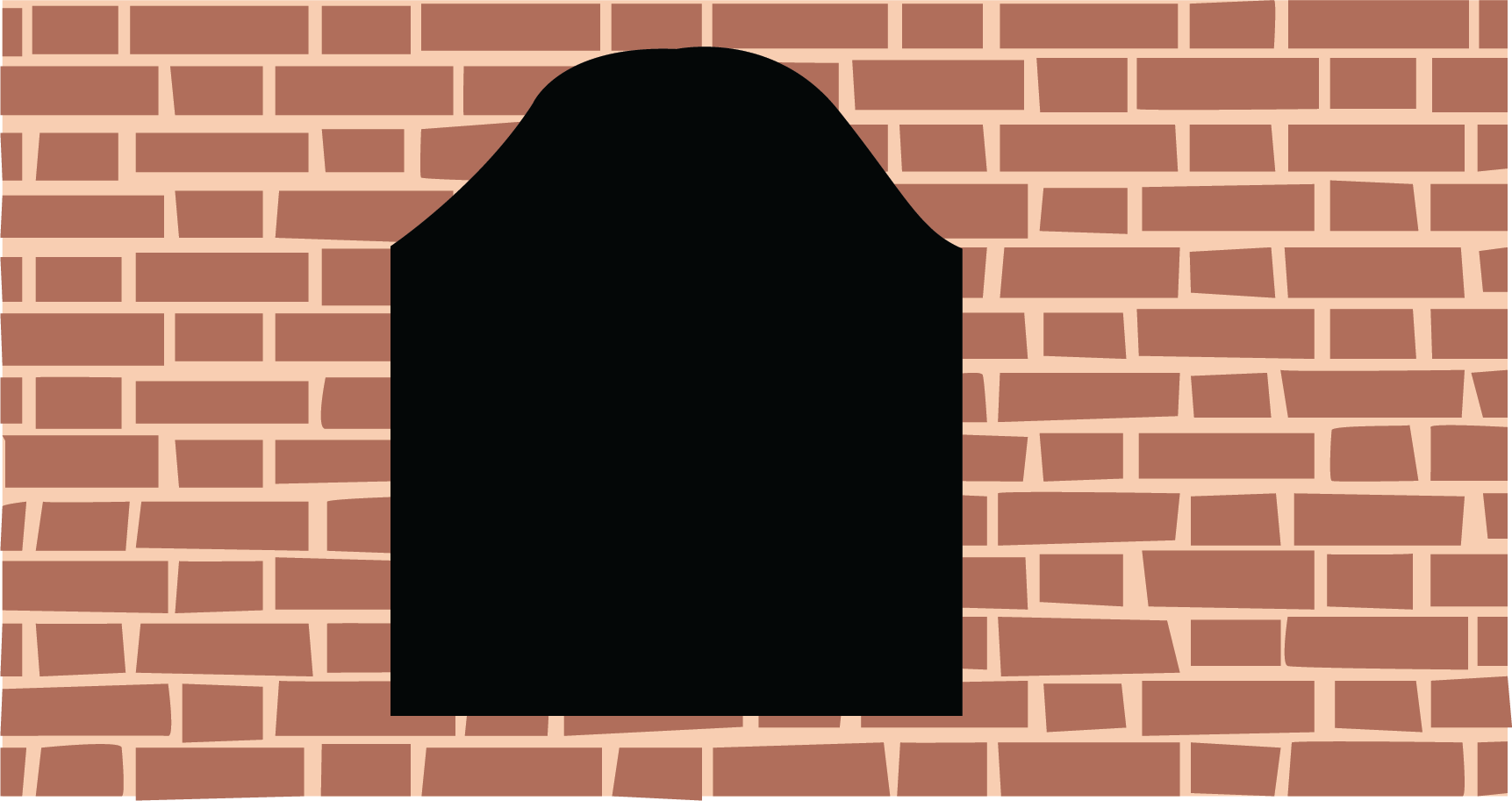
Recognising and creating different brick patterns, such as floor patterns, 'jaali' (latticework), and 'jharokha' (balcony) designs.
Solving word problems involving large numbers, especially related to the cost and quantity of bricks.
3. How can these revision notes for 'Building with Bricks' help in exam preparation?
These revision notes are designed to help you prepare for exams by summarising the entire chapter into easy-to-digest points. They highlight the most important definitions, formulas, and concepts, ensuring you can quickly recall what you've learned. The notes connect visual concepts like patterns with mathematical calculations, which is crucial for answering application-based questions.
4. What is the difference between a brick's face, edge, and corner?
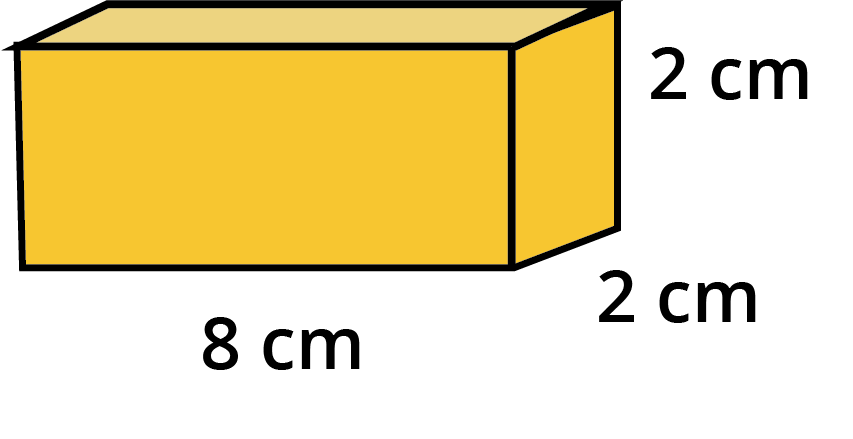
Understanding these terms is key to describing 3D shapes. A face is the flat surface of the brick. An edge is the straight line where two faces meet. A corner (or vertex) is the point where three edges meet. A standard brick has 6 faces, 12 edges, and 8 corners.
5. Why is a brick shaped like a cuboid and not a cube?
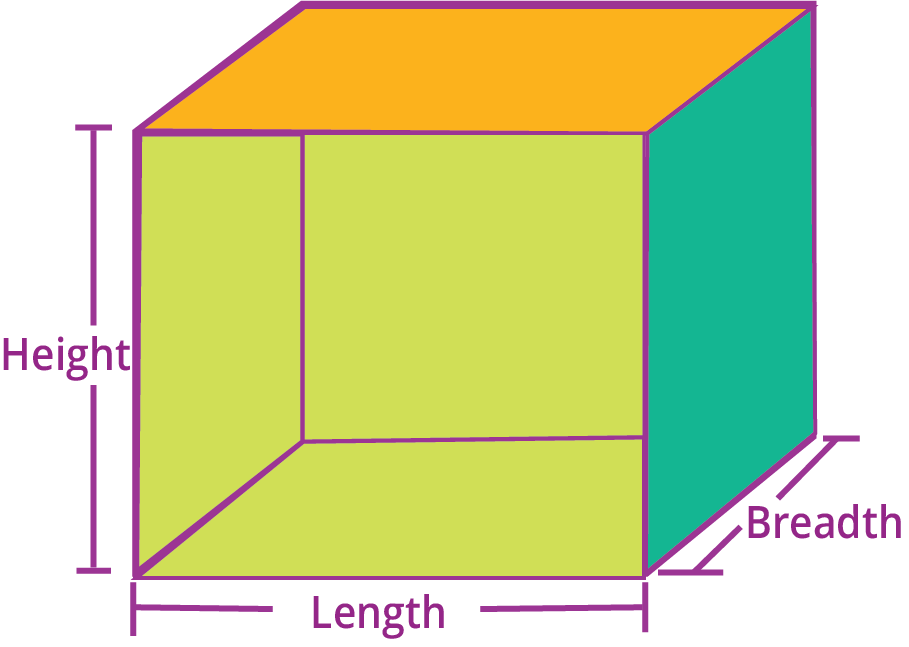
A brick is a cuboid because its length, width, and height are of different measurements. This shape is much more stable for construction than a cube. The different side lengths allow bricks to be laid in interlocking patterns (like a stretcher bond), which distributes weight evenly and creates a much stronger wall. A wall made of cubes would have continuous vertical joints, making it weak.
6. How does this chapter explain different wall patterns like the 'jaali' and 'jharokha'?
The chapter uses these traditional Indian architectural features to show the creative possibilities of brick arrangements. A 'jaali' is a perforated screen or latticework, created by leaving gaps between bricks in a wall. A 'jharokha' is a type of enclosed, overhanging balcony. The notes summarise how these beautiful and functional structures are simply a result of arranging bricks in specific, repeating patterns.
7. What is the difference between a drawing of a brick and a real brick?
A drawing of a brick is a 2D (two-dimensional) representation on a flat surface like paper. From a single drawing, you can typically see only up to three faces at once. A real brick is a 3D (three-dimensional) object that has length, width, and depth. You can hold it and turn it to see all six of its faces. This chapter helps build the skill of visualising a 3D object from its 2D drawing.
8. How does this chapter introduce calculations with large numbers?
The chapter seamlessly integrates arithmetic with geometry by using real-world scenarios. For example, it presents problems that require calculating the total cost of bricks needed for a wall. This involves multiplying the price of one brick by a large number (like 1000 or 5000), thereby giving practical context to calculations with numbers in the thousands.
9. How does understanding brick patterns help develop problem-solving skills?
Recognising and creating brick patterns is an exercise in spatial reasoning and logical thinking. It trains your brain to identify sequences, predict what comes next, and understand how smaller components fit together to form a larger system. These are foundational skills that are directly applicable to solving more complex mathematical problems in later classes.
10. Besides walls, where else can we apply the concept of patterns learned in this chapter?
The concept of creating complex structures from simple, repeating units is a fundamental idea in many fields. You can see similar patterns in:
The arrangement of floor tiles.
The design of fabrics and carpets (tessellations).
The structure of a honeycomb made by bees.
The pixels on a computer screen forming an image.
It is a core principle in art, design, and nature.