Accountancy Notes for Chapter 2 Theory Base of Accounting Class 11 - FREE PDF Download
FAQs on Theory Base of Accounting Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 2 CBSE Notes - 2025-26
1. What is a quick summary of the key concepts in Class 11 Accountancy, Chapter 2, "Theory Base of Accounting"?
This chapter provides the foundational rules for accounting. For a quick recap, focus on: Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP), which are the common set of rules; the core Accounting Concepts like Business Entity and Going Concern; and the formal Accounting Standards (including IFRS) that ensure uniformity and comparability in financial statements.
2. For revision, what are the three fundamental accounting assumptions I must know from this chapter?
The three fundamental accounting assumptions you should remember are:
- Going Concern: The assumption that a business will continue its operations for the foreseeable future.
- Consistency: The principle that a company must use the same accounting methods from one period to the next to allow for fair comparison.
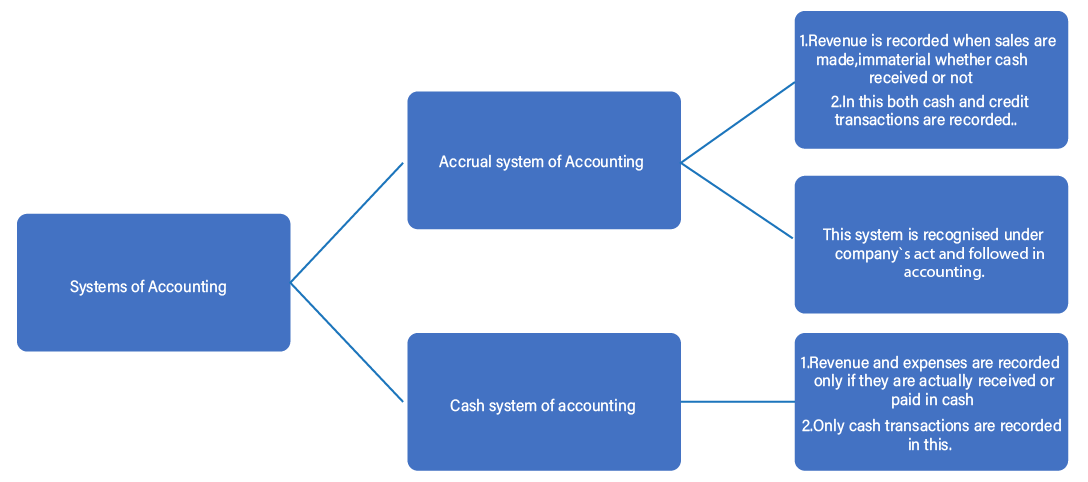
- Accrual: The concept of recording revenues and expenses when they are earned or incurred, not necessarily when cash is exchanged.
3. What is the main difference to remember between the 'Business Entity Concept' and the 'Money Measurement Concept'?
The key distinction for revision is:
- The Business Entity Concept states that the business is separate from its owner. All transactions are recorded from the business's viewpoint, not the owner's personal one.
- The Money Measurement Concept states that only transactions that can be expressed in monetary terms are recorded in the accounts. It provides a common unit for measurement.
4. How does the 'Matching Concept' ensure the accurate calculation of profit for a period?
The Matching Concept is crucial for accurate profit calculation because it dictates that all expenses incurred to earn revenue in a specific accounting period must be recorded in that same period. This prevents expenses from one period being incorrectly set against revenues of another, providing a true and fair view of profitability for that period.
5. Why is it necessary to follow a standard 'Theory Base of Accounting' like GAAP?
Following a standard theory base like GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles) is essential to ensure financial statements are reliable, consistent, and comparable. Without these common rules, every business could report its finances differently, making it impossible for investors, lenders, and management to compare performance or make informed decisions. It brings uniformity and credibility to financial reporting.
6. During revision, what is the best way to distinguish between Accounting Principles and Accounting Standards?
Think of it this way: Accounting Principles are the fundamental, general guidelines (like the 'Accrual Concept') that form the basis of accounting theory. Accounting Standards (like those issued by IASB or ICAI) are the specific, authoritative written rules that mandate how transactions should be treated and presented in financial statements. In short, Principles are the 'why,' and Standards are the 'how'.
7. How does the 'Conservatism' or 'Prudence' concept help in creating a reliable financial statement?
The Conservatism Concept, also known as Prudence, enhances reliability by ensuring that a business does not overstate its profits or assets. The guideline is to anticipate and record potential losses or liabilities as soon as they are foreseen, but only recognise revenues or gains when they are certain. This cautious approach provides a more realistic view of the company's financial health.
8. How do modern regulations like GST and IFRS connect to the core ideas in this chapter?
GST and IFRS are practical applications of the core concepts in the Theory Base of Accounting. IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standards) promotes the principles of comparability and transparency on a global scale. Similarly, GST ('One Nation, One Tax') implements the principle of uniformity in indirect taxation, simplifying the tax structure and ensuring consistency across the country.