
Write Fleming's left hand rule.
Answer
594.3k+ views
Hint: If a conductor moved during a magnetic flux, an emf is induced across the conductor (according to Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction). Fleming’s left-hand rule is used to find the direction of the force vectors acting on the charged particle with respect to the direction of the magnetic field and current in the system.
Complete step by step answer:
Now let’s s see what's Fleming's left rule and the way it works:
Fleming's left rule is employed to work out the direction of the force exerted on a current-carrying wire placed during a magnetic flux. If the thumb, index (along magnetic field), and finger (along with current) are held mutually perpendicular then the thumb gives the direction of the force on the wire.
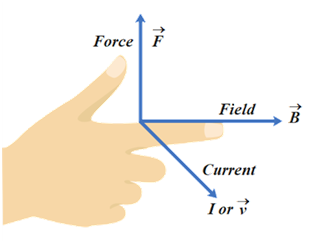
Fleming's left rule is employed to work out the direction of magnetic flux thanks to the current-carrying conductor, the direction of flux in solenoid wont to find magnetic poles also utilized in the motor.
Additional Information:
Fleming’s left and right rule application:
We know if a current-carrying conductor is placed during a magnetic flux, it experiences a force thanks to the magnetic flux.
On the opposite hand we all know that if a conductor moves during a magnetic flux , an emf is induced across the conductor (according to Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction).
There are two rules to work out the direction of motion (in electric motors) or the director of induced current (in electric generators). But these rules are mentioned as Fleming’s left rule (for motor) and Fleming’s right rule (for generator).
Fleming’s left rule:
Whenever a current-carrying conductor is placed during a magnetic flux, the conductor experiences a force. consistent with Flemings’ left rule if the thumb, forefinger, and finger of left are stretched perpendicular to each other as shown in the figure and if the forefinger represents the direction of magnetic flux, the middle finger represents the direction of the current.
Electric motor:
We know that motor is the application of Fleming's hand rule when an oblong coil carrying current is placed during a magnetic flux, a torque acts on the coil which rotates it continuously. When the coil rotates, the shaft attached thereto also rotates and thus it's ready to do mechanical work the thumb represents the direction of force..
Note:
Difference between Fleming's Left-Hand and Right-Hand Rule.
When a current-carrying conductor is placed under a magnetic flux, a force acts on the conductor. The direction of this force is often identified using Fleming’s left Rule.
We know that if a moving conductor is brought under a magnetic flux, the current is going to be induced in the conductor, and therefore the direction of the induced current is often found using Fleming’s right Rule.
Complete step by step answer:
Now let’s s see what's Fleming's left rule and the way it works:
Fleming's left rule is employed to work out the direction of the force exerted on a current-carrying wire placed during a magnetic flux. If the thumb, index (along magnetic field), and finger (along with current) are held mutually perpendicular then the thumb gives the direction of the force on the wire.

Fleming's left rule is employed to work out the direction of magnetic flux thanks to the current-carrying conductor, the direction of flux in solenoid wont to find magnetic poles also utilized in the motor.
Additional Information:
Fleming’s left and right rule application:
We know if a current-carrying conductor is placed during a magnetic flux, it experiences a force thanks to the magnetic flux.
On the opposite hand we all know that if a conductor moves during a magnetic flux , an emf is induced across the conductor (according to Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction).
There are two rules to work out the direction of motion (in electric motors) or the director of induced current (in electric generators). But these rules are mentioned as Fleming’s left rule (for motor) and Fleming’s right rule (for generator).
Fleming’s left rule:
Whenever a current-carrying conductor is placed during a magnetic flux, the conductor experiences a force. consistent with Flemings’ left rule if the thumb, forefinger, and finger of left are stretched perpendicular to each other as shown in the figure and if the forefinger represents the direction of magnetic flux, the middle finger represents the direction of the current.
Electric motor:
We know that motor is the application of Fleming's hand rule when an oblong coil carrying current is placed during a magnetic flux, a torque acts on the coil which rotates it continuously. When the coil rotates, the shaft attached thereto also rotates and thus it's ready to do mechanical work the thumb represents the direction of force..
Note:
Difference between Fleming's Left-Hand and Right-Hand Rule.
When a current-carrying conductor is placed under a magnetic flux, a force acts on the conductor. The direction of this force is often identified using Fleming’s left Rule.
We know that if a moving conductor is brought under a magnetic flux, the current is going to be induced in the conductor, and therefore the direction of the induced current is often found using Fleming’s right Rule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




