
What are conservative forces?
Answer
584.7k+ views
HintConservative force has a property that work done in moving a particle between two points is independent of the path taken.
Complete step-by-step solution:The work done by such forces
Does not depend upon path.
Depends only and only initial and final position.
For example:- If A and B are the two points and a conservative force acts on point A and B. Then we assume the three ways to go at point B . 1,2 and 3 are the three ways.
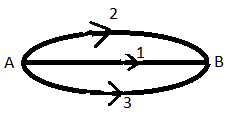
If the force is conservative, then work done by this force by first path, by second path and third path are equal.
Let \[{{W}_{1}}\] be the work done along path 1, ${{W}_{2}}$ be the work done along path 2 and ${{W}_{3}}$ be the work done along path 3
Then,
${{W}_{1}}={{W}_{2}}={{W}_{3}}$
Examples of conservative forces are gravitational force , spring force, and electrostatic force.
First we talk about gravitational force, let us assume $\left( m \right)$ .Which is placed on an inclined plane.
For path 1:-
Angle between force $\left( mg \right)$ and displacement $\left( l \right)$ is$\left({{90}^{\circ }}+\theta \right)$
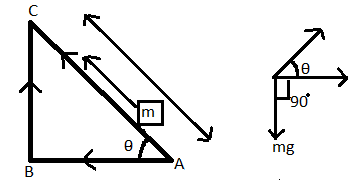
Than $\begin{align}
& {{W}_{1}}=FS\cos \phi \\
& {{W}_{1}}=mgl\left( \cos \left( {{90}^{\circ }}+\theta \right) \right) \\
& \\
\end{align}$ $\left[ \cos \left( {{90}^{\circ }}+\theta \right)=-\sin \theta \right]$
${{W}_{1}}=-mgl\sin \theta $ …………………..(i)
For path 2
First we go from point A to point B and then from point B to point C.
$W={{W}_{AB}}+{{W}_{BC}}$
When we go from A to B then the angle between force and displacement is ${{90}^{\circ }}$ $\left( \cos {{90}^{\circ }}=0 \right)$ .
Than $\begin{align}
& {{W}_{AB}}=FS\cos {{90}^{\circ }} \\
& {{W}_{AB}}=0 \\
\end{align}$
When we go from point B to C then the angle between force and displacement is ${{180}^{{}^\circ }}$.
${{W}_{BC}}=-mgl\sin \theta $
${{W}_{2}}={{W}_{AB}}+{{W}_{BC}}$
${{W}_{2}}=-mgl\sin \theta $ ……………….. (ii)
${{W}_{1}}={{W}_{2}}$
So the work done in the first path is equal to work done in the second path. So it is independent of path.
Note:
Students think that whose path has long distance then work done is maximum for that path, but for conservative force work done does not depend on path distance.
Complete step-by-step solution:The work done by such forces
Does not depend upon path.
Depends only and only initial and final position.
For example:- If A and B are the two points and a conservative force acts on point A and B. Then we assume the three ways to go at point B . 1,2 and 3 are the three ways.

If the force is conservative, then work done by this force by first path, by second path and third path are equal.
Let \[{{W}_{1}}\] be the work done along path 1, ${{W}_{2}}$ be the work done along path 2 and ${{W}_{3}}$ be the work done along path 3
Then,
${{W}_{1}}={{W}_{2}}={{W}_{3}}$
Examples of conservative forces are gravitational force , spring force, and electrostatic force.
First we talk about gravitational force, let us assume $\left( m \right)$ .Which is placed on an inclined plane.
For path 1:-
Angle between force $\left( mg \right)$ and displacement $\left( l \right)$ is$\left({{90}^{\circ }}+\theta \right)$

Than $\begin{align}
& {{W}_{1}}=FS\cos \phi \\
& {{W}_{1}}=mgl\left( \cos \left( {{90}^{\circ }}+\theta \right) \right) \\
& \\
\end{align}$ $\left[ \cos \left( {{90}^{\circ }}+\theta \right)=-\sin \theta \right]$
${{W}_{1}}=-mgl\sin \theta $ …………………..(i)
For path 2
First we go from point A to point B and then from point B to point C.
$W={{W}_{AB}}+{{W}_{BC}}$
When we go from A to B then the angle between force and displacement is ${{90}^{\circ }}$ $\left( \cos {{90}^{\circ }}=0 \right)$ .
Than $\begin{align}
& {{W}_{AB}}=FS\cos {{90}^{\circ }} \\
& {{W}_{AB}}=0 \\
\end{align}$
When we go from point B to C then the angle between force and displacement is ${{180}^{{}^\circ }}$.
${{W}_{BC}}=-mgl\sin \theta $
${{W}_{2}}={{W}_{AB}}+{{W}_{BC}}$
${{W}_{2}}=-mgl\sin \theta $ ……………….. (ii)
${{W}_{1}}={{W}_{2}}$
So the work done in the first path is equal to work done in the second path. So it is independent of path.
Note:
Students think that whose path has long distance then work done is maximum for that path, but for conservative force work done does not depend on path distance.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




