
The locus of the centre of the circle, which touches externally the given two circles is:
A) Circle
B) Parabola
C) Hyperbola
D) Ellipse
Answer
589.5k+ views
Hint:
Consider three circles, out of which one touches the two other circles. Form the condition based on the fact that the circle touches the two other circles externally. Then, if after writing and solving the conditions, you get the distances from the centres to be a constant, then that means that the locus will be a hyperbola.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us consider two circles having the centres ${C_1}$ and ${C_2}$. Also, denote the radius of these two circles by ${r_1}$ and ${r_2}$ respectively.
Let us now consider another circle whose centre is P and whose radius is r. This circle is the circle touching the given two circles having the centres ${C_1}$ and ${C_2}$ externally.
Thus, we get the figure as:
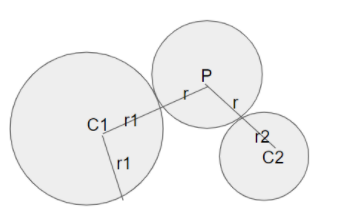
Thus, by the conditions of circles touching externally we get,
${C_1}P = r + {r_1}$
And, also, we get;
${C_2}P = r + {r_2}$
Where, P, ${C_1}$ and ${C_2}$ are the centers of the circles and r, ${r_1}$ and ${r_2}$ are the radii.
Thus, form both the equation obtained above we get;
$
{C_1}P - {C_2}P = {r_1} - {r_2} \\
= c \\
$
Where ‘c’ is constant.
Now, this means that as the point P or the centre of the circle moves in a way that the difference of its distances from the centres ${C_1}$ and ${C_2}$ is a constant.
Hence, we can clearly describe the locus of the centre of the circle, which touches externally the given two circles to be a hyperbola.
Thus, option (C) is the correct option.
Note:
In these types of questions, first, take any random figures that satisfy the given conditions. Apply the condition for the figure to be touching externally and solve them to find the locus of that figure touching the other figures.
Consider three circles, out of which one touches the two other circles. Form the condition based on the fact that the circle touches the two other circles externally. Then, if after writing and solving the conditions, you get the distances from the centres to be a constant, then that means that the locus will be a hyperbola.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us consider two circles having the centres ${C_1}$ and ${C_2}$. Also, denote the radius of these two circles by ${r_1}$ and ${r_2}$ respectively.
Let us now consider another circle whose centre is P and whose radius is r. This circle is the circle touching the given two circles having the centres ${C_1}$ and ${C_2}$ externally.
Thus, we get the figure as:

Thus, by the conditions of circles touching externally we get,
${C_1}P = r + {r_1}$
And, also, we get;
${C_2}P = r + {r_2}$
Where, P, ${C_1}$ and ${C_2}$ are the centers of the circles and r, ${r_1}$ and ${r_2}$ are the radii.
Thus, form both the equation obtained above we get;
$
{C_1}P - {C_2}P = {r_1} - {r_2} \\
= c \\
$
Where ‘c’ is constant.
Now, this means that as the point P or the centre of the circle moves in a way that the difference of its distances from the centres ${C_1}$ and ${C_2}$ is a constant.
Hence, we can clearly describe the locus of the centre of the circle, which touches externally the given two circles to be a hyperbola.
Thus, option (C) is the correct option.
Note:
In these types of questions, first, take any random figures that satisfy the given conditions. Apply the condition for the figure to be touching externally and solve them to find the locus of that figure touching the other figures.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




