
The length of the optical path of two media in contact of lengths $ {d_1} $ and $ {d_2} $ of refractive indices $ {\mu _1} $ and $ {\mu _2} $ respectively is
$ \left( A \right){\mu _1}{d_1} + {\mu _2}{d_2} \\
\left( B \right)\dfrac{{{\mu _1}{d_2} + {\mu _2}{d_1}}}{{{\mu _1}{\mu _2}}} \\
\left( C \right)\dfrac{{{d_1}{d_2}}}{{{\mu _1}{\mu _2}}} \\
\left( D \right)\dfrac{{{d_1} + {d_2}}}{{{\mu _1}{\mu _2}}} \\ $
Answer
539.4k+ views
Hint: In order to solve this question, we are going to first see what an optical path actually is and then find the optical paths for the two mediums $ 1 $ and $ 2 $ respectively. Then, on adding the two refractive indices, we get the total optical path length of the two media in contact.
The optical path of a medium of refractive index $ \mu $ and thickness $ t $ is given by
$ Optical{\text{ }}path = \mu t $
Complete step by step solution:
First of all let us see what an optical path means
The optical path can be defined as the product of the geometrical length of the original path followed by light through a given system and the refractive index of the medium through which it propagates.
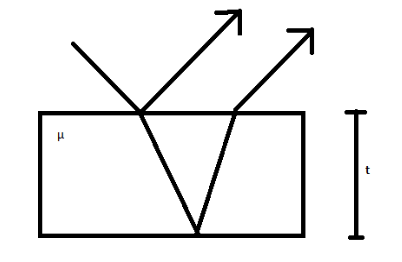
$ Optical{\text{ }}path = \mu t $
Where, $ \mu $ is the refractive index
$ t $ is the thickness of the medium.
Thus, in medium 1, the thickness is $ {d_1} $ , so the optical path is
$ Optical{\text{ }}path = {\mu _1}{d_1} $
In medium 2, the thickness is $ {d_2} $ , so the optical path is
$ Optical{\text{ }}path = {\mu _2}{d_2} $
Now, to find the optical path of the two media, we will have to add the two optical paths as obtained above, thus, the optical path becomes
$ {\left( {Optical{\text{ }}path} \right)_{medium1}} + {\left( {Optical{\text{ }}path} \right)_{medium2}} $
Therefore, the total length becomes
$ {\mu _1}{d_1} + {\mu _2}{d_2} $
Hence, option $ \left( A \right){\mu _1}{d_1} + {\mu _2}{d_2} $ is the correct answer.
Note:
This is the optical path length and not to be confused with the optical path difference at any cost. The expression for the optical path difference is $ {\mu _1}{d_1} - {\mu _2}{d_2} $ . This gives the difference for the two optical paths while for the total optical path, the two optical lengths are added for the final answer.
The optical path of a medium of refractive index $ \mu $ and thickness $ t $ is given by
$ Optical{\text{ }}path = \mu t $
Complete step by step solution:
First of all let us see what an optical path means
The optical path can be defined as the product of the geometrical length of the original path followed by light through a given system and the refractive index of the medium through which it propagates.

$ Optical{\text{ }}path = \mu t $
Where, $ \mu $ is the refractive index
$ t $ is the thickness of the medium.
Thus, in medium 1, the thickness is $ {d_1} $ , so the optical path is
$ Optical{\text{ }}path = {\mu _1}{d_1} $
In medium 2, the thickness is $ {d_2} $ , so the optical path is
$ Optical{\text{ }}path = {\mu _2}{d_2} $
Now, to find the optical path of the two media, we will have to add the two optical paths as obtained above, thus, the optical path becomes
$ {\left( {Optical{\text{ }}path} \right)_{medium1}} + {\left( {Optical{\text{ }}path} \right)_{medium2}} $
Therefore, the total length becomes
$ {\mu _1}{d_1} + {\mu _2}{d_2} $
Hence, option $ \left( A \right){\mu _1}{d_1} + {\mu _2}{d_2} $ is the correct answer.
Note:
This is the optical path length and not to be confused with the optical path difference at any cost. The expression for the optical path difference is $ {\mu _1}{d_1} - {\mu _2}{d_2} $ . This gives the difference for the two optical paths while for the total optical path, the two optical lengths are added for the final answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




