
The correct order of reactivity toward electrophilic addition-
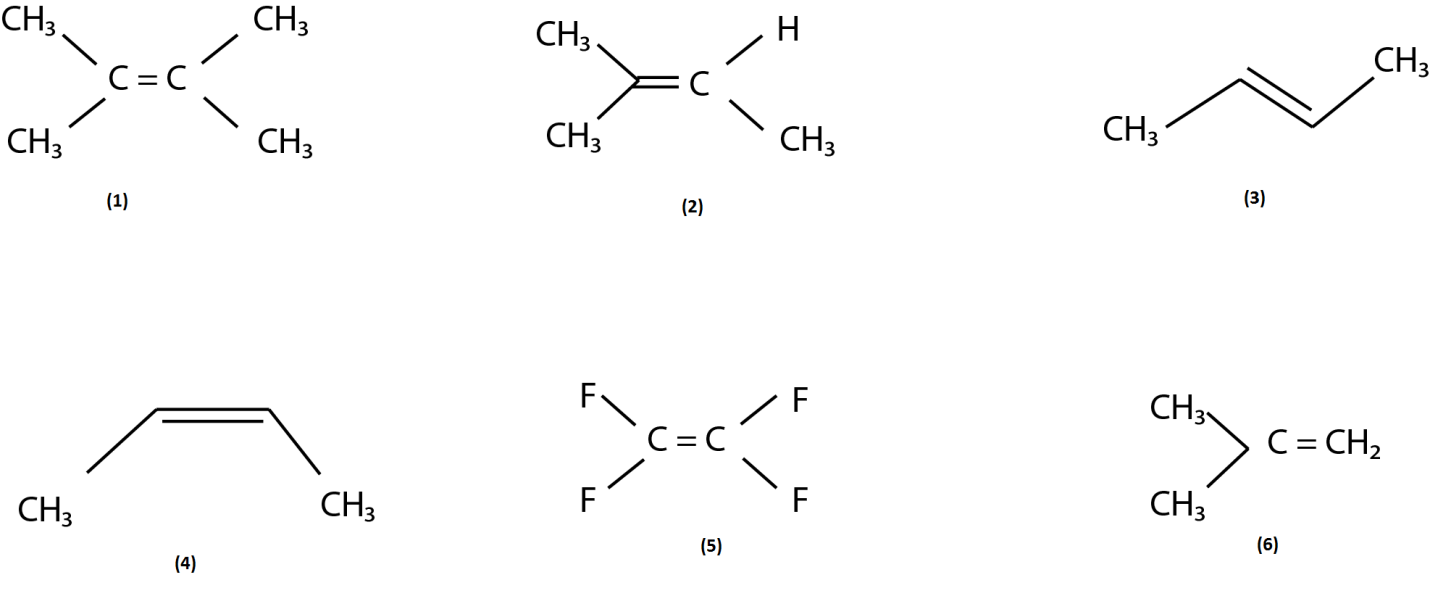
(A) $ 1 > 2 > 3 > 4 > 6 > 5 $
(B) $ 1 > 2 > 6 > 3 > 4 > 5 $
(C) $ 5 > 1 > 2 > 3 > 4 > 6 $
(D) $ 5 > 1 > 2 > 6 > 3 > 4 $

Answer
546.6k+ views
Hint: The reaction in which a pie bond breaks down to form two new sigma bonds is known as electrophilic addition reaction. The deriving force for this reaction is electrophile formation and its reactivity depends upon the stability of its conjugate carbocation.
Complete step by step answer:
In organic chemistry, the reaction in which a pie bond breaks and two new sigma bonds evolve is called an electrophilic addition reaction. Compounds or substrates having double bond or triple bond shows electrophilic addition reaction.
We can predict by the name of the reaction that electrophile formation takes place in this reaction and also the formation of electrophile is the deriving force of this reaction.
Electrophilic addition reaction takes place in two steps. In step 1 the formation of carbocation takes place and in the second step this carbocation attacks electron rich atoms present near the double bond. The stability of carbocation decides the rate of electrophilic addition reaction. More the stability of carbocation more is its reactivity.
So the reactivity depends on the stability of carbocation and the stability of carbocation depends upon the number of electron donation groups present in the organic compound.
Therefore the cation of diagram (1) is the most stable and the cation of diagram (5) is the least stable because it has electron withdrawing group fluorine which is the cause of instability of cation. And we all know that trans molecule is always more stable than cis molecule therefore (3) is more stable than (4).
So from the above discussion we can conclude that the order of reactivity towards the electrophilic addition is as follows: $ 1 > 2 > 3 > 4 > 6 > 5 $
Hence option (A) is the correct answer.
Note:
As we all know that an intermediate (compound present between the start and the end of a reaction) is formed in the electrophilic addition reaction and this intermediate is carbocation (deriving force of this reaction).
Complete step by step answer:
In organic chemistry, the reaction in which a pie bond breaks and two new sigma bonds evolve is called an electrophilic addition reaction. Compounds or substrates having double bond or triple bond shows electrophilic addition reaction.
We can predict by the name of the reaction that electrophile formation takes place in this reaction and also the formation of electrophile is the deriving force of this reaction.
Electrophilic addition reaction takes place in two steps. In step 1 the formation of carbocation takes place and in the second step this carbocation attacks electron rich atoms present near the double bond. The stability of carbocation decides the rate of electrophilic addition reaction. More the stability of carbocation more is its reactivity.
So the reactivity depends on the stability of carbocation and the stability of carbocation depends upon the number of electron donation groups present in the organic compound.
Therefore the cation of diagram (1) is the most stable and the cation of diagram (5) is the least stable because it has electron withdrawing group fluorine which is the cause of instability of cation. And we all know that trans molecule is always more stable than cis molecule therefore (3) is more stable than (4).
So from the above discussion we can conclude that the order of reactivity towards the electrophilic addition is as follows: $ 1 > 2 > 3 > 4 > 6 > 5 $
Hence option (A) is the correct answer.
Note:
As we all know that an intermediate (compound present between the start and the end of a reaction) is formed in the electrophilic addition reaction and this intermediate is carbocation (deriving force of this reaction).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




