
The angle between the particle velocity and wave velocity in a transverse waves is
$\begin{align}
& A.Zero \\
& B.\dfrac{\pi }{4} \\
& C.\dfrac{\pi }{2} \\
& D.\pi \\
\end{align}$
Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: Transverse wave is a kind of wave which is in vibration with the energy in a specific medium in the perpendicular direction of vibration. The particle in the medium vibrates in a normal direction with the direction of propagation of the wave. This is the basic concept in order to solve this question.
Complete step by step answer:
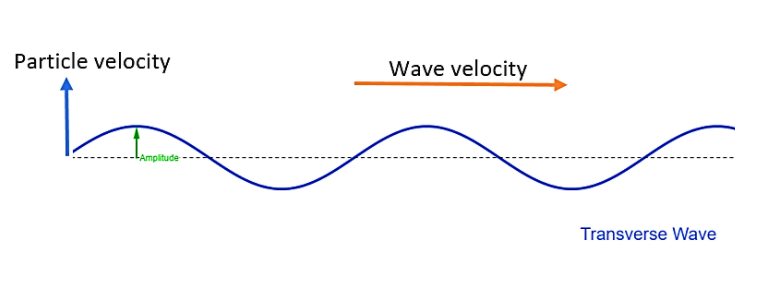
A transverse wave is referred to as a moving wave whose oscillations are given as the perpendicular to the direction of the wave or way of propagation. A common example is given by the waves that can be produced on a horizontal length of the string by keeping one end fixed and moving the other end up and down. Mechanical transverse waves need a material medium in order to propagate by means of vibrations in that medium which is perpendicular to the direction of travel.
Here in this question, it is mentioned that the wave is a transverse wave. As already mentioned, in transverse waves the particles of the medium are vibrating at right angles to the direction in which the wave is propagating. This is known as direction of wave velocity. So the angle between the particle velocity and wave velocity in the given transverse wave will be $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Transverse waves are characterized by peaks and valleys, called crests and troughs. Opposite to this, in a longitudinal wave, the particles of the medium are moving parallel to the direction of wave of travel. Electromagnetic waves abbreviated as EM waves like light are also transverse waves but they do not require any material medium and thus can even pass through a vacuum.
Complete step by step answer:

A transverse wave is referred to as a moving wave whose oscillations are given as the perpendicular to the direction of the wave or way of propagation. A common example is given by the waves that can be produced on a horizontal length of the string by keeping one end fixed and moving the other end up and down. Mechanical transverse waves need a material medium in order to propagate by means of vibrations in that medium which is perpendicular to the direction of travel.
Here in this question, it is mentioned that the wave is a transverse wave. As already mentioned, in transverse waves the particles of the medium are vibrating at right angles to the direction in which the wave is propagating. This is known as direction of wave velocity. So the angle between the particle velocity and wave velocity in the given transverse wave will be $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Transverse waves are characterized by peaks and valleys, called crests and troughs. Opposite to this, in a longitudinal wave, the particles of the medium are moving parallel to the direction of wave of travel. Electromagnetic waves abbreviated as EM waves like light are also transverse waves but they do not require any material medium and thus can even pass through a vacuum.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




