
What is space wave propagation? State the factors which limit its range of propagation. Derive an expression for the maximum line of sight distance between two antennas for space wave propagation.
Answer
570.9k+ views
Hint: Electromagnetic waves use space (usually atmosphere) as the medium of propagation.
Modes of electromagnetic wave propagation are ground waves, sky waves and space waves.
Complete step by step answer:
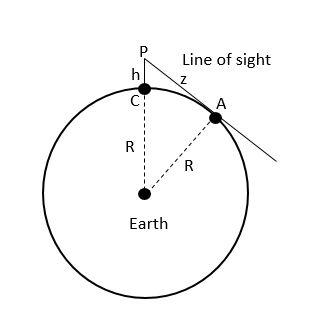
When a wave propagates in a straight line, from the transmitting antenna to the receiving antenna, its ‘mode of propagation’ is called space wave communication. Space waves are used for the line of sight (LOS) communication. Space wave communication involves the transmission from the transmitter, travelling along a straight line in space, reaching the receiving antenna. The range of their frequencies is 40 MHz and above. The range of space wave propagation is limited by line of sight distance between transmission to receiver/repeater antenna. From the figure, the range of antenna $PC$ is $PA$.
Using Pythagoras theorem
$
{\left( {R + h} \right)^2} = P{A^2} + {R^2} \\
\Rightarrow PA = \sqrt {{h^2} + 2Rh} \\
\approx \sqrt {2Rh\left( {h \ll R} \right)} \\
$
Note:
For efficient transmission, the size of the antenna should be comparable to the wavelength of the transmitted signal. For standard $AM$ broadcast, the size of the antenna is quite large and ground based vertical towers are used as antennas. Ground has a strong influence on the propagation of the wave and the wave bend round the curvature of the earth. Hence, it is also called surface wave propagation. Its range depends on the transmitted power and frequency. It is used for frequencies up to $1.5$ MHz. When the electromagnetic waves from the transmitting antenna reach the receiving antenna directly or after the reflection from earth’s surface then the wave propagation is called space then the wave communication. Hence, it is called line-of-sight communication. It is used for transmission of frequencies more than 30 MHz.
Modes of electromagnetic wave propagation are ground waves, sky waves and space waves.
Complete step by step answer:

When a wave propagates in a straight line, from the transmitting antenna to the receiving antenna, its ‘mode of propagation’ is called space wave communication. Space waves are used for the line of sight (LOS) communication. Space wave communication involves the transmission from the transmitter, travelling along a straight line in space, reaching the receiving antenna. The range of their frequencies is 40 MHz and above. The range of space wave propagation is limited by line of sight distance between transmission to receiver/repeater antenna. From the figure, the range of antenna $PC$ is $PA$.
Using Pythagoras theorem
$
{\left( {R + h} \right)^2} = P{A^2} + {R^2} \\
\Rightarrow PA = \sqrt {{h^2} + 2Rh} \\
\approx \sqrt {2Rh\left( {h \ll R} \right)} \\
$
Note:
For efficient transmission, the size of the antenna should be comparable to the wavelength of the transmitted signal. For standard $AM$ broadcast, the size of the antenna is quite large and ground based vertical towers are used as antennas. Ground has a strong influence on the propagation of the wave and the wave bend round the curvature of the earth. Hence, it is also called surface wave propagation. Its range depends on the transmitted power and frequency. It is used for frequencies up to $1.5$ MHz. When the electromagnetic waves from the transmitting antenna reach the receiving antenna directly or after the reflection from earth’s surface then the wave propagation is called space then the wave communication. Hence, it is called line-of-sight communication. It is used for transmission of frequencies more than 30 MHz.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




