
What is the relation between Wavelength and Refractive index.
Answer
524.7k+ views
Hint: In order to answer the above question, we will first define the term wavelength and refractive index. We will also write the equation for the following. We will understand the terms and try to find the relation or an equation connecting these two terms.
Complete step by step solution:
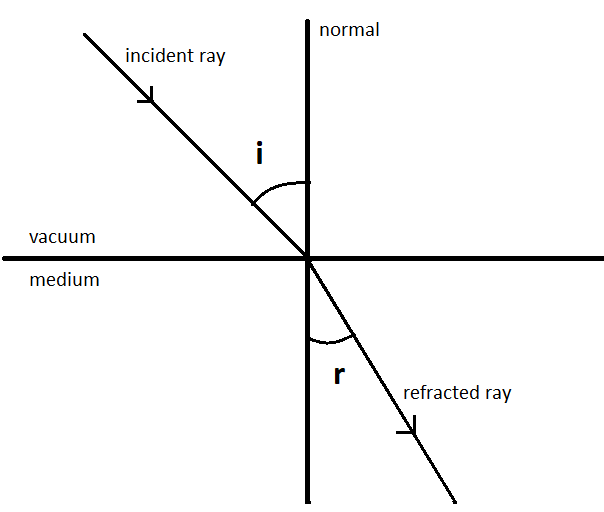
As we all know, the bending of a ray of light as it passes through one medium and through another is measured by the refractive index, also known as the index of refraction. If $i$ is the angle of incidence of a ray in vacuum (the angle between the incoming ray and the natural, which is perpendicular to the surface of a medium), and $r$ is the angle of refraction (angle between the ray in the medium and the normal), The refractive index $n$ is equal to the ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction; in other words,
$n=\dfrac{\sin \left( i \right)}{\sin \left( r \right)}$
The refractive index can also be stated as the velocity of light $c$ of a given wavelength in empty space divided by the velocity of light $v$ in a material,
$n=\dfrac{c}{v}$
Now, the wavelength of a wave is the distance between consecutive crests, especially the points of an electromagnetic wave. Wavelength and frequency are inextricably linked. The shorter the wavelength, the higher the frequency. Since all light waves travel at the same speed through a vacuum, the number of wave crests moving by a given point per second is determined by the wavelength.
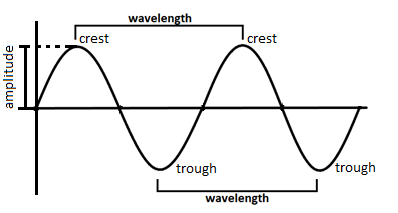
The Wavelength is represented by the symbol $\lambda $. Any wave's Wavelength Formula is given by
$\lambda =\dfrac{v}{f}$
The wavelength is measured in metres, the velocity is measured in metres per second, and the frequency is measured in hertz.
Now, if we look at both the formulas, i.e., the formula of the refractive index of a material and the formula of the wavelength, we can write
$\lambda =\dfrac{c}{nf}$ because $\left[ n=\dfrac{c}{v} \right]$
Therefore, we can conclude that the wavelength is inversely proportional to the refractive index of the material in which the wave is travelling.
Note:
It is very important to note here that the frequency of the wave will also change inversely to the wavelength. If the wavelength of the wave is shortened, it implies that the frequency will be increased as the number of cycles completed in a unit interval of time will be increased.
Complete step by step solution:
As we all know, the bending of a ray of light as it passes through one medium and through another is measured by the refractive index, also known as the index of refraction. If $i$ is the angle of incidence of a ray in vacuum (the angle between the incoming ray and the natural, which is perpendicular to the surface of a medium), and $r$ is the angle of refraction (angle between the ray in the medium and the normal), The refractive index $n$ is equal to the ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction; in other words,
$n=\dfrac{\sin \left( i \right)}{\sin \left( r \right)}$

The refractive index can also be stated as the velocity of light $c$ of a given wavelength in empty space divided by the velocity of light $v$ in a material,
$n=\dfrac{c}{v}$
Now, the wavelength of a wave is the distance between consecutive crests, especially the points of an electromagnetic wave. Wavelength and frequency are inextricably linked. The shorter the wavelength, the higher the frequency. Since all light waves travel at the same speed through a vacuum, the number of wave crests moving by a given point per second is determined by the wavelength.

The Wavelength is represented by the symbol $\lambda $. Any wave's Wavelength Formula is given by
$\lambda =\dfrac{v}{f}$
The wavelength is measured in metres, the velocity is measured in metres per second, and the frequency is measured in hertz.
Now, if we look at both the formulas, i.e., the formula of the refractive index of a material and the formula of the wavelength, we can write
$\lambda =\dfrac{c}{nf}$ because $\left[ n=\dfrac{c}{v} \right]$
Therefore, we can conclude that the wavelength is inversely proportional to the refractive index of the material in which the wave is travelling.
Note:
It is very important to note here that the frequency of the wave will also change inversely to the wavelength. If the wavelength of the wave is shortened, it implies that the frequency will be increased as the number of cycles completed in a unit interval of time will be increased.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




