
How do you read gel electrophoresis results?
Answer
554.4k+ views
Hint: Agarose gel electrophoresis refers to a method used in molecular biology. It is used to isolate DNA fragments and to examine the separated fragments of DNA.
Complete answer:
Gel electrophoresis is a technique used to isolate DNA fragments based on their size to observe other macromolecules, such as RNA and proteins. Electrophoresis involves running a current through molecules of interest that contain a gel. Molecules can move through the gel in different directions or at varying speeds depending on their size and load, allowing them to be isolated from each other.
Following are the steps of electrophoresis:
Preparing the samples for running.
A gel solution of agarose TAE is prepared.
The gel casting.
Setting up the chamber for electrophoresis.
Gel loading.
Via electrophoresis.
Electrophoresis halting and DNA visualization.
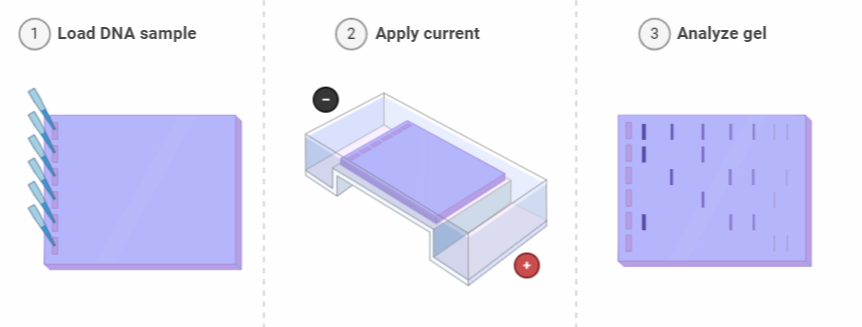
Agarose gel has a mesh-like structure that makes it easier to separate DNA fragments. Smaller DNA fragments show rapid movement through these pores, while larger fragments are trapped in these pores, indicating delayed movement. With hollow pockets (called wells) on one end of the gel surface, the gel is allowed to settle.
Therefore, the DNA in these wells is loaded. DNA has a negative charge due to the presence of the phosphate ions. This helps DNA molecules move towards a positively charged anode. The distance travelled by DNA molecules in the agarose gel is proportionate to its molecular logarithmic weight.
It is more difficult for them to move through the pores of the gel than the supercoiled forms. Thus, open circular monomers are discovered in the gel.
Note:
The main advantage of the agarose gel method is that at the end of the process, it can be quickly processed and the DNA molecule used as a sample can also be retrieved without any damage to it. The DNA samples are not denatured by Agarose gel and they remain in their own form. The downside of gel electrophoresis is also that when the electrical current is passed through it, it will melt. For this purpose, genetic material is likely to follow shapes that are not necessary.
Complete answer:
Gel electrophoresis is a technique used to isolate DNA fragments based on their size to observe other macromolecules, such as RNA and proteins. Electrophoresis involves running a current through molecules of interest that contain a gel. Molecules can move through the gel in different directions or at varying speeds depending on their size and load, allowing them to be isolated from each other.
Following are the steps of electrophoresis:
Preparing the samples for running.
A gel solution of agarose TAE is prepared.
The gel casting.
Setting up the chamber for electrophoresis.
Gel loading.
Via electrophoresis.
Electrophoresis halting and DNA visualization.

Agarose gel has a mesh-like structure that makes it easier to separate DNA fragments. Smaller DNA fragments show rapid movement through these pores, while larger fragments are trapped in these pores, indicating delayed movement. With hollow pockets (called wells) on one end of the gel surface, the gel is allowed to settle.
Therefore, the DNA in these wells is loaded. DNA has a negative charge due to the presence of the phosphate ions. This helps DNA molecules move towards a positively charged anode. The distance travelled by DNA molecules in the agarose gel is proportionate to its molecular logarithmic weight.
It is more difficult for them to move through the pores of the gel than the supercoiled forms. Thus, open circular monomers are discovered in the gel.
Note:
The main advantage of the agarose gel method is that at the end of the process, it can be quickly processed and the DNA molecule used as a sample can also be retrieved without any damage to it. The DNA samples are not denatured by Agarose gel and they remain in their own form. The downside of gel electrophoresis is also that when the electrical current is passed through it, it will melt. For this purpose, genetic material is likely to follow shapes that are not necessary.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




