
Phenol on treatment with conc. $HN{{O}_{3}}$ gives:
(A) Picric acid
(B) Ortho and meta-nitrophenols
(C) Ortho and para-nitrophenols
(D) None of the above
Answer
520.6k+ views
Hint: Find out which reaction takes place when conc. $HN{{O}_{3}}$ reacts with phenol. Phenol is an aromatic alcohol so think which type of reaction phenol will undergo easily. Take a look at the question carefully and think what will happen if dilute reagent is used instead of concentrated one and then select the correct answer.
Complete step by step solution:
- Phenol is an aromatic alcohol. We know aromatic compounds easily give electrophilic substitution reactions.
- Electrophilic substitution reactions are the reactions in which an electrophile replaces a functional group generally a proton from the reactant.
- conc. $HN{{O}_{3}}$ is concentrated nitric acid. It is a nitrating reagent.
- Phenol will undergo nitration reaction in the presence of conc. nitric acid, $HN{{O}_{3}}$ to give 2, 4, 6-trinitrophenol which is also known as picric acid.
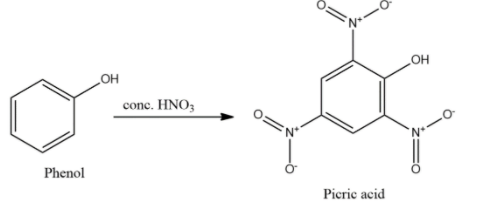
- Phenol will undergo nitration in presence of nitric acid also but will form either mono- or di-substituted ortho- or para-nitrophenols.
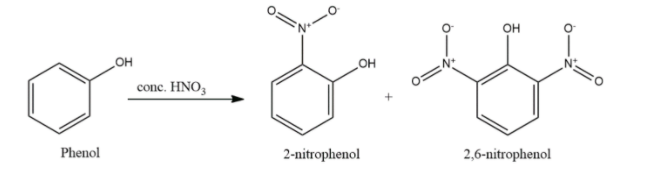
- Phenols are nucleophilic in nature and hence undergo electrophilic substitution reactions like nitration, sulphonation, alkylation, acetylation and halogenation.
- Therefore, phenol on treatment with conc. $HN{{O}_{3}}$ gives picric acid.
- Therefore, the answer is option (A).
Note: Remember phenols are nucleophilic in nature and easily give electrophilic substitution reactions. If phenol is treated with concentrated nitric acid then picric acid is formed. If phenol is treated with dilute nitric acid, mono or disubstituted nitrophenols are formed. o-nitrophenols are more stable than p-nitrophenols due to intramolecular hydrogen bonding.
Complete step by step solution:
- Phenol is an aromatic alcohol. We know aromatic compounds easily give electrophilic substitution reactions.
- Electrophilic substitution reactions are the reactions in which an electrophile replaces a functional group generally a proton from the reactant.
- conc. $HN{{O}_{3}}$ is concentrated nitric acid. It is a nitrating reagent.
- Phenol will undergo nitration reaction in the presence of conc. nitric acid, $HN{{O}_{3}}$ to give 2, 4, 6-trinitrophenol which is also known as picric acid.

- Phenol will undergo nitration in presence of nitric acid also but will form either mono- or di-substituted ortho- or para-nitrophenols.

- Phenols are nucleophilic in nature and hence undergo electrophilic substitution reactions like nitration, sulphonation, alkylation, acetylation and halogenation.
- Therefore, phenol on treatment with conc. $HN{{O}_{3}}$ gives picric acid.
- Therefore, the answer is option (A).
Note: Remember phenols are nucleophilic in nature and easily give electrophilic substitution reactions. If phenol is treated with concentrated nitric acid then picric acid is formed. If phenol is treated with dilute nitric acid, mono or disubstituted nitrophenols are formed. o-nitrophenols are more stable than p-nitrophenols due to intramolecular hydrogen bonding.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




