
On the basis of Huygens wave theory, prove Snell's law of refraction of light.
Answer
585k+ views
Hint: The ray diagram needs to be drawn according to the need to prove the snell’s law of refraction from the Huygens wave theory, after drawing the diagram we have to figure out two triangles in the diagram that is by figuring one in both sides of the surface, remember that the triangles should be chosen in such a way that it should satisfy the snell’s law.
Complete step-by-step answer:
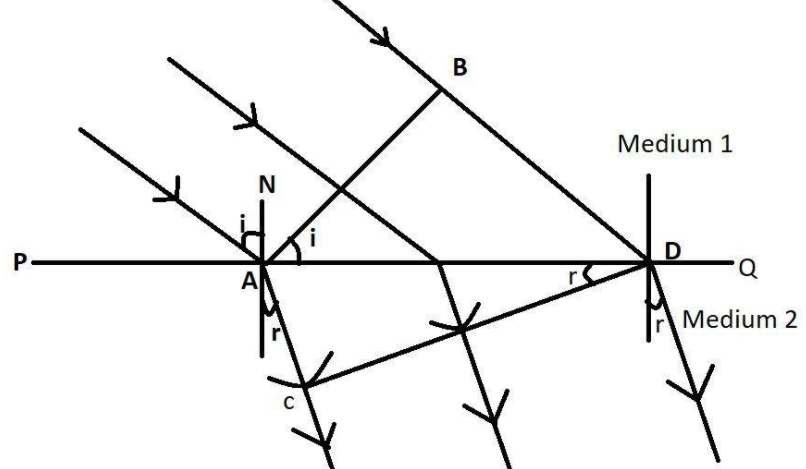
Laws of Refraction: Consider a plane wavefront AB incident on a surface PQ separating two mediums (1) and (2). The medium (1) is rarer, having refractive index $\mathrm{n}_{1}$, in which the light travels with a velocity $\mathrm{c}_{1}$. The medium (2) is denser, having refractive index $\mathrm{n}_{2}$, in which the light travels with a velocity $\mathrm{c}_{2}$.
At time $t=0,$ the incident wave front AB touches the boundary separating two mediums at A. The secondary wavelets from point B advance forward with a velocity $c_{1},$ and after time $t$ seconds
touches at D, thus covering a distance $B D=c_{1} t .$ In the same time interval of $t$ seconds, the secondary wavelets from $\mathrm{A},$ advance forward in the second and an envelope is drawn to obtain a new refracted wavefront as CD.
Consider triangle BAD and ACD,
$\sin i=\sin (a m g \leq B A D)=\dfrac{B D}{A D}=\dfrac{c_{1} t}{A D}$
$\sin r=\sin (\angle A D C)=\dfrac{A C}{A D}=\dfrac{c_{2} t}{A D}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}=\dfrac{c_{1} t}{c_{2} t}=\dfrac{c_{1}}{c_{2}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}=\dfrac{c_{1}}{c_{2}}=$ constant.
This constant is known as the refractive index of the second medium with respect to the first medium. And it is a fixed value.
$\dfrac{c_{1}}{c_{2}}=\dfrac{n_{2}}{n_{1}}$
$\therefore \dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}=\dfrac{c_{1}}{c_{2}}=\dfrac{n_{2}}{n_{1}}=1 n_{2}$
This is known as the Snell's law.
Note: The constant will always remain the same for a pair of two mediums that are unchanged, The value of the refractive index never changes. Snell’s law stated that for a pair of two mediums the refractive index always remains the same.
Complete step-by-step answer:

Laws of Refraction: Consider a plane wavefront AB incident on a surface PQ separating two mediums (1) and (2). The medium (1) is rarer, having refractive index $\mathrm{n}_{1}$, in which the light travels with a velocity $\mathrm{c}_{1}$. The medium (2) is denser, having refractive index $\mathrm{n}_{2}$, in which the light travels with a velocity $\mathrm{c}_{2}$.
At time $t=0,$ the incident wave front AB touches the boundary separating two mediums at A. The secondary wavelets from point B advance forward with a velocity $c_{1},$ and after time $t$ seconds
touches at D, thus covering a distance $B D=c_{1} t .$ In the same time interval of $t$ seconds, the secondary wavelets from $\mathrm{A},$ advance forward in the second and an envelope is drawn to obtain a new refracted wavefront as CD.
Consider triangle BAD and ACD,
$\sin i=\sin (a m g \leq B A D)=\dfrac{B D}{A D}=\dfrac{c_{1} t}{A D}$
$\sin r=\sin (\angle A D C)=\dfrac{A C}{A D}=\dfrac{c_{2} t}{A D}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}=\dfrac{c_{1} t}{c_{2} t}=\dfrac{c_{1}}{c_{2}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}=\dfrac{c_{1}}{c_{2}}=$ constant.
This constant is known as the refractive index of the second medium with respect to the first medium. And it is a fixed value.
$\dfrac{c_{1}}{c_{2}}=\dfrac{n_{2}}{n_{1}}$
$\therefore \dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}=\dfrac{c_{1}}{c_{2}}=\dfrac{n_{2}}{n_{1}}=1 n_{2}$
This is known as the Snell's law.
Note: The constant will always remain the same for a pair of two mediums that are unchanged, The value of the refractive index never changes. Snell’s law stated that for a pair of two mediums the refractive index always remains the same.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




