
In NPN transistors, ${{10}^{10}}$ electrons enter the emitter region in ${{10}^{-6}}s$. If 2% electrons are lost in base region then collector current and current amplification factor (β) respectively are
$\begin{align}
& A.1.57mA,49 \\
& B.1.92mA,70 \\
& C.2mA,25 \\
& D.2.25mA,100 \\
\end{align}$
Answer
593.1k+ views
Hint: First of all find out the emitter current. After that find out the collector current using the formula
${{I}_{c}}=\alpha {{I}_{e}}$
$\alpha $ is given by how much current from the emitter reaches the collector. So using this $\alpha $ amplification factor can be found out.
Complete step by step answer:
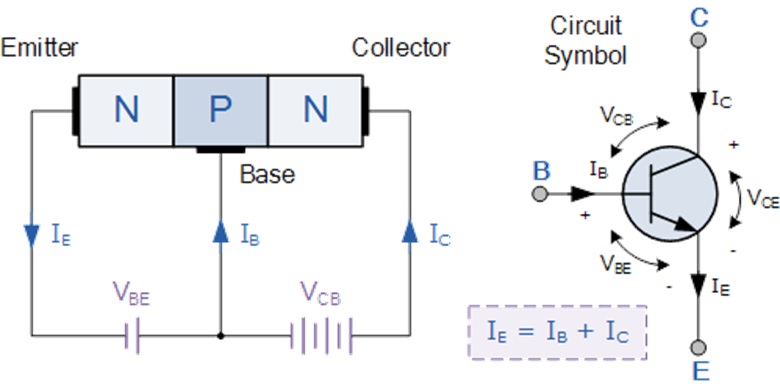
Current amplification factor in a bi junction transistor is described as the ratio of output current to its input current. In the common base configuration, current amplification factor is given as the ratio of collector current to the emitter current. The low current travels from the voltage source into the transistor base. The current at the base will turn on the transistor. Then the current is amplified and travels from the emitter of the transistor to the collector. This is how current amplification takes place in a bi junction transistor. The amplifier is a very complex circuit which is using properties of a transistor.
Here let us first write what all are given in the question.
Number of electrons entering emitter,
${{n}_{e}}={{10}^{10}}$
Time taken=${{10}^{-6}}s$
Therefore the current in the emitter is
${{I}_{e}}=\dfrac{{{q}_{e}}\times {{n}_{e}}}{t}$
${{I}_{e}}=\dfrac{{{10}^{10}}\times 1.6\times {{10}^{-19}}}{{{10}^{-6}}}$
$=1.6mA$
Since only 2% current is lost, therefore 98% will reach the collector
So
\[\alpha =0.98\]
And also we know that
${{I}_{c}}=\alpha {{I}_{e}}$
Therefore the collector current will be,
\[\begin{align}
& =\alpha \times {{I}_{e}} \\
& =0.98\times 1.6 \\
& {{I}_{c}}\approx 1.57mA \\
\end{align}\]
Also the current amplification factor will be,
\[\beta =\dfrac{\alpha }{1-\alpha }=49\]
Hence the correct answer is given by the option A.
Note:
MOSFETs are controlled by voltage not on their own. It is used to amplify current using a MOSFET by passing the input current through a resistor there by converting the current signal to a voltage. This signal voltage is controlling the MOSFET, which gives an output signal current.
${{I}_{c}}=\alpha {{I}_{e}}$
$\alpha $ is given by how much current from the emitter reaches the collector. So using this $\alpha $ amplification factor can be found out.
Complete step by step answer:
Current amplification factor in a bi junction transistor is described as the ratio of output current to its input current. In the common base configuration, current amplification factor is given as the ratio of collector current to the emitter current. The low current travels from the voltage source into the transistor base. The current at the base will turn on the transistor. Then the current is amplified and travels from the emitter of the transistor to the collector. This is how current amplification takes place in a bi junction transistor. The amplifier is a very complex circuit which is using properties of a transistor.
Here let us first write what all are given in the question.
Number of electrons entering emitter,
${{n}_{e}}={{10}^{10}}$
Time taken=${{10}^{-6}}s$
Therefore the current in the emitter is
${{I}_{e}}=\dfrac{{{q}_{e}}\times {{n}_{e}}}{t}$
${{I}_{e}}=\dfrac{{{10}^{10}}\times 1.6\times {{10}^{-19}}}{{{10}^{-6}}}$
$=1.6mA$
Since only 2% current is lost, therefore 98% will reach the collector
So
\[\alpha =0.98\]
And also we know that
${{I}_{c}}=\alpha {{I}_{e}}$
Therefore the collector current will be,
\[\begin{align}
& =\alpha \times {{I}_{e}} \\
& =0.98\times 1.6 \\
& {{I}_{c}}\approx 1.57mA \\
\end{align}\]
Also the current amplification factor will be,
\[\beta =\dfrac{\alpha }{1-\alpha }=49\]
Hence the correct answer is given by the option A.

Note:
MOSFETs are controlled by voltage not on their own. It is used to amplify current using a MOSFET by passing the input current through a resistor there by converting the current signal to a voltage. This signal voltage is controlling the MOSFET, which gives an output signal current.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




