
In an n-type semiconductor, the Fermi level is present:
A. just below the valence band
B. just below the conduction band
C. just above the valence band
D. in the middle of valence and conduction bands
Answer
567.6k+ views
Hint: This is a theoretical question based on the concept of the extrinsic semiconductors. Firstly, we will discuss the n-type semiconductor. Then, we will continue with its properties, and finally with the study of the Fermi level.
Complete answer:
An n-type semiconductor is a category of an extrinsic semiconductor. In the case of n-type semiconductors, the electron donor atoms play an important role, as these types of semiconductors are doped with the electron donor atoms.
The donor atoms contribute the free electrons to the semiconductors, thus, the n-type semiconductors have free electrons in plenty when compared to the holes. Basically, the pentavalent atoms are introduced into the semiconductors. Here, the pentavalent atoms refer to the atoms having 5 valence electrons.
The energy level diagram of an n-type semiconductor :
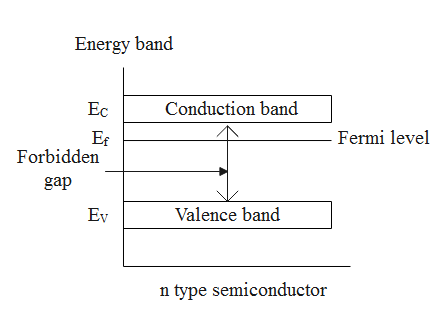
The terms used in the diagram are defined as follows.
Conduction band – an energy band filled with the free electrons.
Valence band – an energy band filled with the holes.
The forbidden gap – the gap between the conduction and the valence band.
Fermi level – the highest energy level that an electron can occupy at absolute 0 temperature.
From the energy level diagram of the n-type semiconductor, it’s clear that the Fermi level is present near the conduction band and far away from the valence band.
In the case of n-type semiconductor, the Fermi level is present just below the conduction band.
As the Fermi level is present just below the conduction band in the case of n-type semiconductor, thus, the option (B) is correct.
Note:
The pentavalent impurity atoms (atoms that provide extra electrons) introduced into the semiconductors are antimony, phosphorous, arsenic, etc. These impurity atoms are added to the pure germanium or silicon semiconductors to make them n-type semiconductors. Therefore, in n-type semiconductors, the electrons are called the majority charge carriers and the holes are called the minority charge carriers.
Complete answer:
An n-type semiconductor is a category of an extrinsic semiconductor. In the case of n-type semiconductors, the electron donor atoms play an important role, as these types of semiconductors are doped with the electron donor atoms.
The donor atoms contribute the free electrons to the semiconductors, thus, the n-type semiconductors have free electrons in plenty when compared to the holes. Basically, the pentavalent atoms are introduced into the semiconductors. Here, the pentavalent atoms refer to the atoms having 5 valence electrons.
The energy level diagram of an n-type semiconductor :

The terms used in the diagram are defined as follows.
Conduction band – an energy band filled with the free electrons.
Valence band – an energy band filled with the holes.
The forbidden gap – the gap between the conduction and the valence band.
Fermi level – the highest energy level that an electron can occupy at absolute 0 temperature.
From the energy level diagram of the n-type semiconductor, it’s clear that the Fermi level is present near the conduction band and far away from the valence band.
In the case of n-type semiconductor, the Fermi level is present just below the conduction band.
As the Fermi level is present just below the conduction band in the case of n-type semiconductor, thus, the option (B) is correct.
Note:
The pentavalent impurity atoms (atoms that provide extra electrons) introduced into the semiconductors are antimony, phosphorous, arsenic, etc. These impurity atoms are added to the pure germanium or silicon semiconductors to make them n-type semiconductors. Therefore, in n-type semiconductors, the electrons are called the majority charge carriers and the holes are called the minority charge carriers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




