
What happens if Mutations are not corrected?
Answer
479.1k+ views
Hint: Mutations are the changes in the DNA sequence. These changes can arise due to improper or faulty DNA replication, external factors like viruses, UV radiations etc. Mutations can disrupt normal activity of genes.
Complete answer:
• The DNA polymerase enzyme adds nucleotides during DNA replication. Sometimes mistakes can arise during adding nucleotides. It can be in the form of substitution, insertion, deletion or translocation of the sequence. This leads to mutation.
• Most of the time, the mutations are corrected by the process of proofreading by the exonuclease activity and mismatch corrections.
• If the mutations are not corrected, the cell does not recognise the errors and the incorrect sequence gets replicated. It leads to permanent change in the sequence of the DNA.
• The mutations lead to disruption of the normal activity of the DNA or the gene. This leads to faulty synthesis of protein and sometimes no expression of the genes. It can lead to various complications such as cancer, sickle cell anaemia, and many other genetic disorders.
• Certain types of mutations are shown in the figure below.
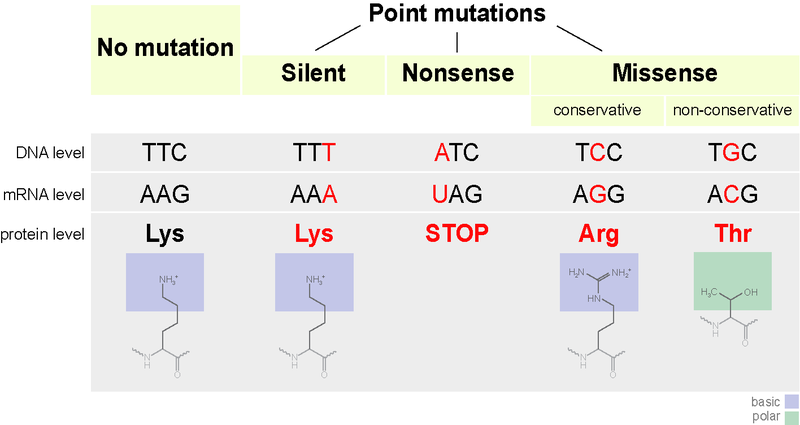
Additional Information:
The proofreading activity of the DNA polymerase helps in correcting faulty replication. This enzyme shows the spell check activity which helps in removing the error nucleotides from the 3’ end before the primer extension.
Note:
The errors are also corrected by the process of mismatch pairing. It occurs after the replication. Some mutations are good which lead to evolution whereas the others are harmful for the organism. The mutations lead to the genetic drift in an organism.
Complete answer:
• The DNA polymerase enzyme adds nucleotides during DNA replication. Sometimes mistakes can arise during adding nucleotides. It can be in the form of substitution, insertion, deletion or translocation of the sequence. This leads to mutation.
• Most of the time, the mutations are corrected by the process of proofreading by the exonuclease activity and mismatch corrections.
• If the mutations are not corrected, the cell does not recognise the errors and the incorrect sequence gets replicated. It leads to permanent change in the sequence of the DNA.
• The mutations lead to disruption of the normal activity of the DNA or the gene. This leads to faulty synthesis of protein and sometimes no expression of the genes. It can lead to various complications such as cancer, sickle cell anaemia, and many other genetic disorders.
• Certain types of mutations are shown in the figure below.

Additional Information:
The proofreading activity of the DNA polymerase helps in correcting faulty replication. This enzyme shows the spell check activity which helps in removing the error nucleotides from the 3’ end before the primer extension.
Note:
The errors are also corrected by the process of mismatch pairing. It occurs after the replication. Some mutations are good which lead to evolution whereas the others are harmful for the organism. The mutations lead to the genetic drift in an organism.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




